REACT
约 24684 字大约 82 分钟
2025-01-20
1-1 开发环境搭建
create-react-app是一个快速创建React开发环境的工具,底层由Webpack构件,封装了配置细节,开箱即用 执行命令:
npx create-react-app react-basic- npx - Node.js工具命令,查找并执行后续的包命令
- create-react-app - 核心包(固定写法),用于创建React项目
- react-basic React项目的名称(可以自定义)
注意
创建React项目的更多方式 https://zh-hans.react.dev/learn/start-a-new-react-project
1-2 JSX基础
1-2-1 什么是JSX
概念:JSX是JavaScript和XMl(HTML)的缩写,表示在JS代码中编写HTML模版结构,它是React中构建UI的方式
const message = 'this is message'
function App(){
return (
<div>
<h1>this is title</h1>
{message}
</div>
)
}优势:
- HTML的声明式模版写法
- JavaScript的可编程能力
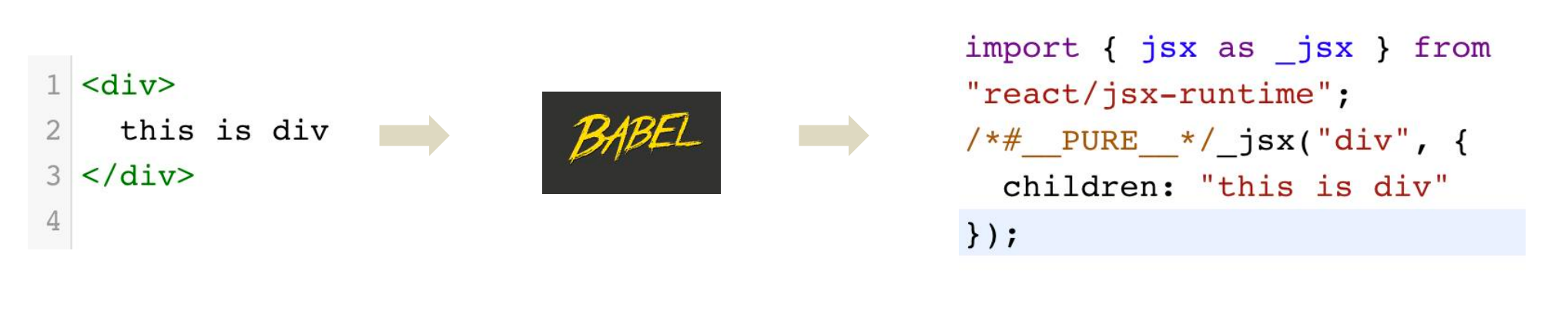
1-2-2 JSX的本质
JSX并不是标准的JS语法,它是 JS的语法扩展,浏览器本身不能识别,需要通过解析工具做解析之后才能在浏览器中使用
1-2-3 JSX高频场景-JS表达式
在JSX中可以通过
大括号语法{}识别JavaScript中的表达式,比如常见的变量、函数调用、方法调用等等
- 使用引号传递字符串
- 使用JS变量
- 函数调用和方法调用
- 使用JavaScript对象
注意
注意:if语句、switch语句、变量声明不属于表达式,不能出现在{}中
const message = 'this is message'
function getAge(){
return 18
}
function App(){
return (
<div>
<h1>this is title</h1>
{/* 字符串识别 */}
{'this is str'}
{/* 变量识别 */}
{message}
{/* 变量识别 */}
{message}
{/* 函数调用 渲染为函数的返回值 */}
{getAge()}
</div>
)
}1-2-4 JSX高频场景-列表渲染

在JSX中可以使用原生js种的
map方法实现列表渲染
const list = [
{id:1001, name:'Vue'},
{id:1002, name: 'React'},
{id:1003, name: 'Angular'}
]
function App(){
return (
<ul>
{list.map(item=><li key={item.id}>{item}</li>)}
</ul>
)
}1-2-5 JSX高频场景-条件渲染
在React中,可以通过逻辑与运算符&&、三元表达式(?😃 实现基础的条件渲染
const flag = true
const loading = false
function App(){
return (
<>
{flag && <span>this is span</span>}
{loading ? <span>loading...</span>:<span>this is span</span>}
</>
)
}1-2-6 JSX高频场景-复杂条件渲染
需求:列表中需要根据文章的状态适配 解决方案:自定义函数 + 判断语句
const type = 1 // 0|1|3
function getArticleJSX(){
if(type === 0){
return <div>无图模式模版</div>
}else if(type === 1){
return <div>单图模式模版</div>
}else(type === 3){
return <div>三图模式模版</div>
}
}
function App(){
return (
<>
{ getArticleJSX() }
</>
)
}1-3 React的事件绑定
1-3-1 基础实现
React中的事件绑定,通过语法
on + 事件名称 = { 事件处理程序 },整体上遵循驼峰命名法
function App(){
const clickHandler = ()=>{
console.log('button按钮点击了')
}
return (
<button onClick={clickHandler}>click me</button>
)
}1-3-2 使用事件参数
在事件回调函数中设置形参e即可
function App(){
const clickHandler = (e)=>{
console.log('button按钮点击了', e)
}
return (
<button onClick={clickHandler}>click me</button>
)
}1-3-3 传递自定义参数
语法:事件绑定的位置改造成箭头函数的写法,在执行clickHandler实际处理业务函数的时候传递实参
function App(){
const clickHandler = (name)=>{
console.log('button按钮点击了', name)
}
return (
<button onClick={()=>clickHandler('jack')}>click me</button>
)
}注意
注意:不能直接写函数调用,这里事件绑定需要一个函数引用
1-3-4 同时传递事件对象和自定义参数
语法:在事件绑定的位置传递事件实参e和自定义参数,clickHandler中声明形参,注意顺序对应
function App(){
const clickHandler = (name,e)=>{
console.log('button按钮点击了', name,e)
}
return (
<button onClick={(e)=>clickHandler('jack',e)}>click me</button>
)
}1-4 React组件基础使用
1-4-1 组件是什么
概念:一个组件就是一个用户界面的一部分,它可以有自己的逻辑和外观,组件之间可以互相嵌套,也可以服用多次 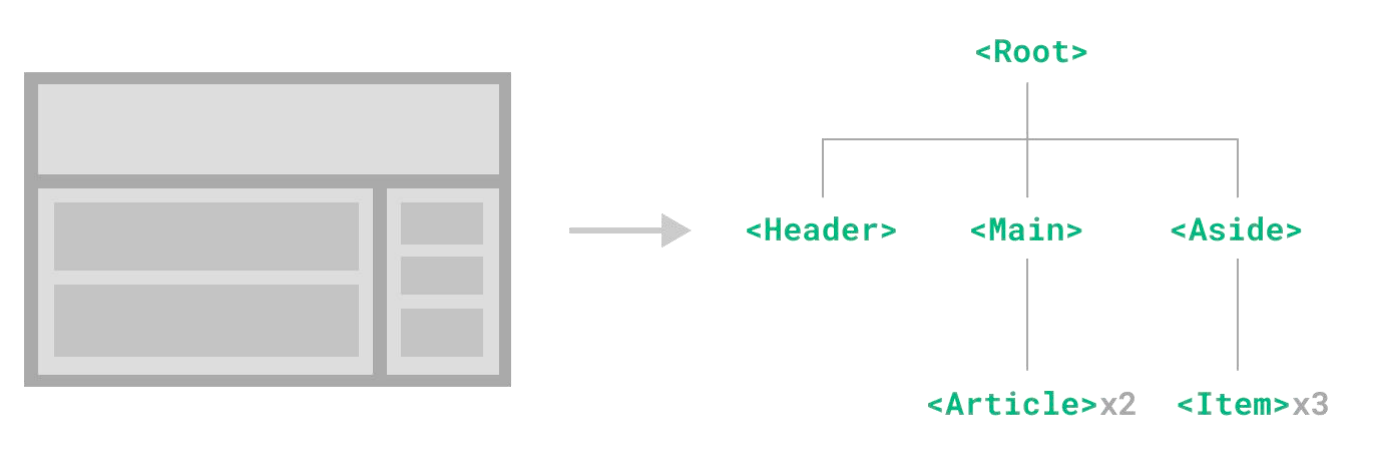
1-4-2 组件基础使用
在React中,一个组件就是首字母大写的函数,内部存放了组件的逻辑和视图UI, 渲染组件只需要把组件当成标签书写即可
// 1. 定义组件
function Button(){
return <button>click me</button>
}
// 2. 使用组件
function App(){
return (
<div>
{/* 自闭和 */}
<Button/>
{/* 成对标签 */}
<Button></Button>
</div>
)
}1-4-3 组件状态管理-useState
3-1 基础使用
useState 是一个 React Hook(函数),它允许我们向组件添加一个
状态变量, 从而控制影响组件的渲染结果 和普通JS变量不同的是,状态变量一旦发生变化组件的视图UI也会跟着变化(数据驱动视图)
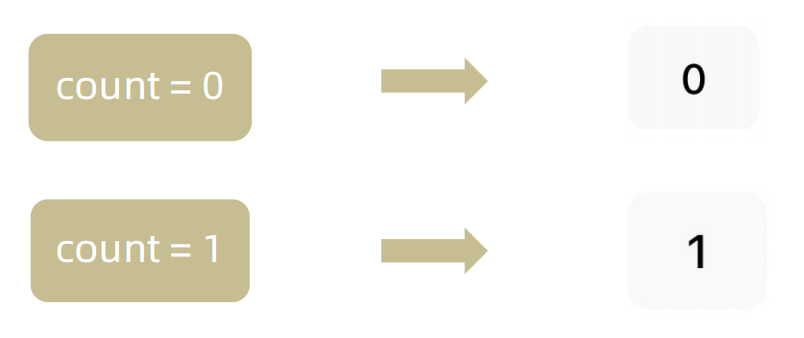
function App(){
const [ count, setCount ] = React.useState(0)
return (
<div>
<button onClick={()=>setCount(count+1)}>{ count }</button>
</div>
)
}3-2 状态的修改规则
在React中状态被认为是只读的,我们应该始终
替换它而不是修改它, 直接修改状态不能引发视图更新
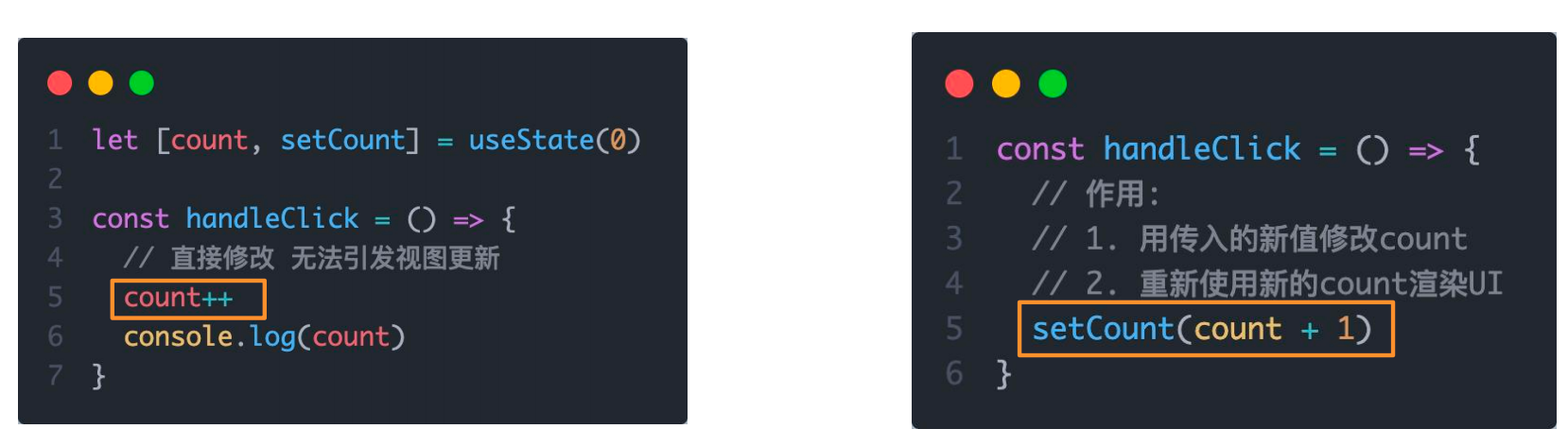
let [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const handleClick = () => {
// 直接修改 无法引发视图更新
count++;
console.log(count);
}
const handleClick = () => {
// 作用:
// 1. 用传入的新值修改count
// 2. 重新使用新的count渲染UI
setCount(count + 1);
}3-3 修改对象状态
对于对象类型的状态变量,应该始终给set方法一个
全新的对象来进行修改
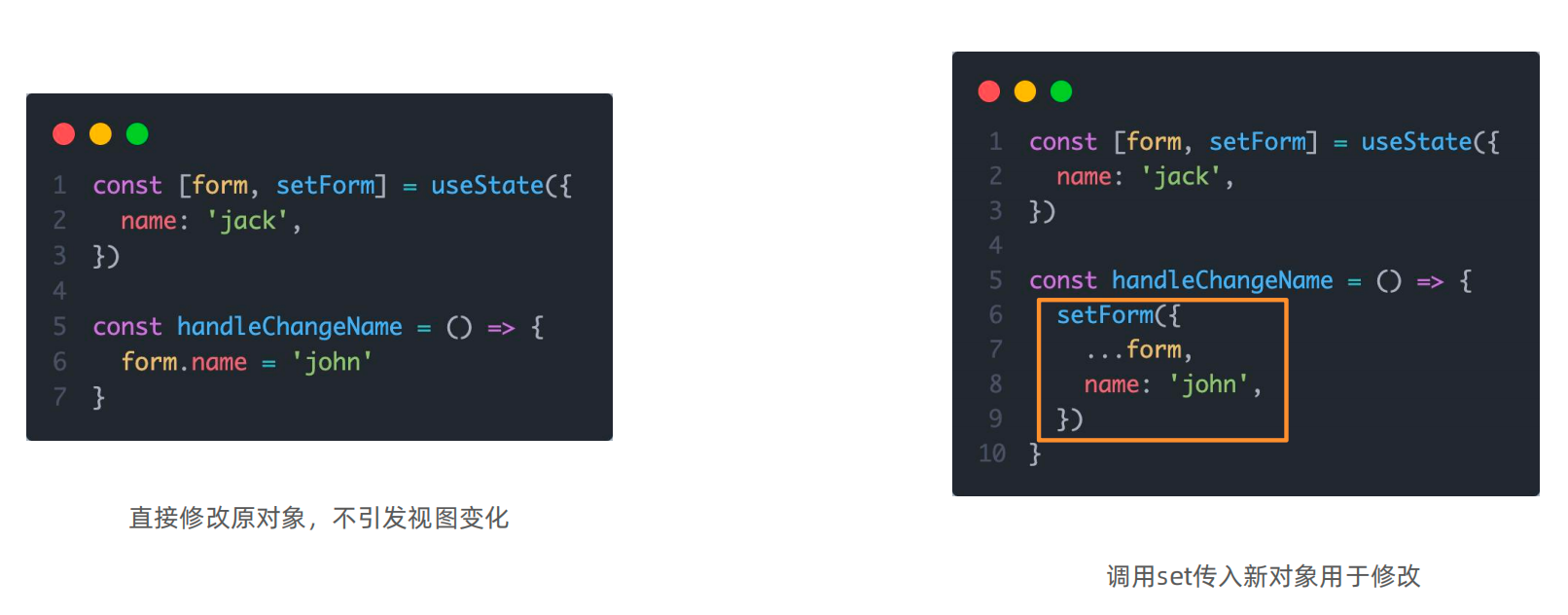
const [form, setForm] = useState({
name: 'jack',
});
const handleChangeName = () => {
form.name = 'john';
}
const [form, setForm] = useState({
name: 'jack',
});
const handleChangeName = () => {
setForm({
...form,
name: 'john',
});
}1-4-4-组件的基础样式处理
React组件基础的样式控制有俩种方式,行内样式和class类名控制
<div style={{ color:'red'}}>this is div</div>.foo{
color: red;
}import './index.css'
function App(){
return (
<div>
<span className="foo">this is span</span>
</div>
)
}1-5 B站评论案例
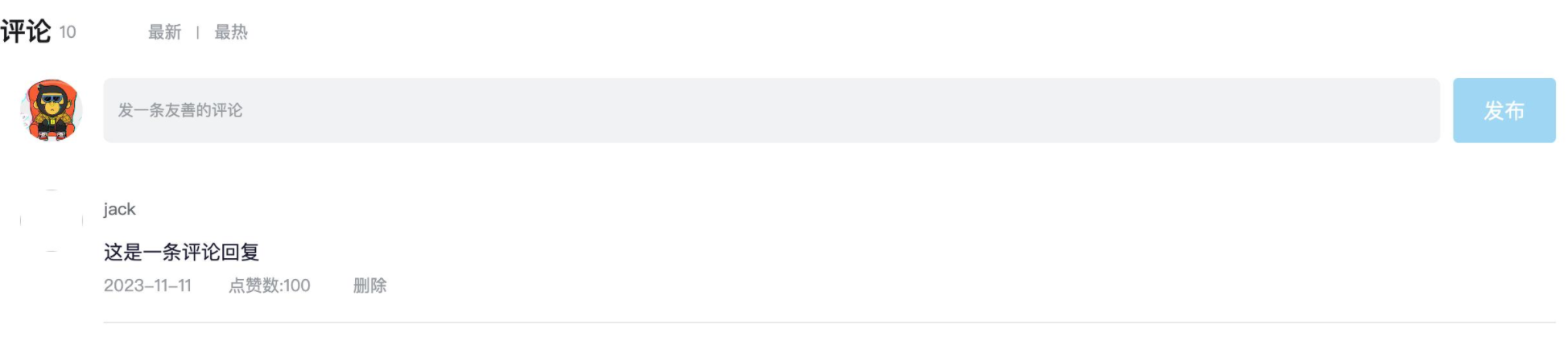
- 渲染评论列表
- 删除评论实现
- 渲染导航Tab和高亮实现
- 评论列表排序功能实现
1-5-1 基础模版
import { useState } from 'react'
import './App.scss'
import avatar from './images/bozai.png'
/**
* 评论列表的渲染和操作
*
* 1. 根据状态渲染评论列表
* 2. 删除评论
*/
// 评论列表数据
const defaultList = [
{
// 评论id
rpid: 3,
// 用户信息
user: {
uid: '13258165',
avatar: '',
uname: '周杰伦',
},
// 评论内容
content: '哎哟,不错哦',
// 评论时间
ctime: '10-18 08:15',
like: 88,
},
{
rpid: 2,
user: {
uid: '36080105',
avatar: '',
uname: '许嵩',
},
content: '我寻你千百度 日出到迟暮',
ctime: '11-13 11:29',
like: 88,
},
{
rpid: 1,
user: {
uid: '30009257',
avatar,
uname: '黑马前端',
},
content: '学前端就来黑马',
ctime: '10-19 09:00',
like: 66,
},
]
// 当前登录用户信息
const user = {
// 用户id
uid: '30009257',
// 用户头像
avatar,
// 用户昵称
uname: '黑马前端',
}
/**
* 导航 Tab 的渲染和操作
*
* 1. 渲染导航 Tab 和高亮
* 2. 评论列表排序
* 最热 => 喜欢数量降序
* 最新 => 创建时间降序
*/
// 导航 Tab 数组
const tabs = [
{ type: 'hot', text: '最热' },
{ type: 'time', text: '最新' },
]
const App = () => {
return (
<div className="app">
{/* 导航 Tab */}
<div className="reply-navigation">
<ul className="nav-bar">
<li className="nav-title">
<span className="nav-title-text">评论</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="total-reply">{10}</span>
</li>
<li className="nav-sort">
{/* 高亮类名: active */}
<span className='nav-item'>最新</span>
<span className='nav-item'>最热</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div className="reply-wrap">
{/* 发表评论 */}
<div className="box-normal">
{/* 当前用户头像 */}
<div className="reply-box-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img className="bili-avatar-img" src={avatar} alt="用户头像" />
</div>
</div>
<div className="reply-box-wrap">
{/* 评论框 */}
<textarea
className="reply-box-textarea"
placeholder="发一条友善的评论"
/>
{/* 发布按钮 */}
<div className="reply-box-send">
<div className="send-text">发布</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* 评论列表 */}
<div className="reply-list">
{/* 评论项 */}
<div className="reply-item">
{/* 头像 */}
<div className="root-reply-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img
className="bili-avatar-img"
alt=""
/>
</div>
</div>
<div className="content-wrap">
{/* 用户名 */}
<div className="user-info">
<div className="user-name">jack</div>
</div>
{/* 评论内容 */}
<div className="root-reply">
<span className="reply-content">这是一条评论回复</span>
<div className="reply-info">
{/* 评论时间 */}
<span className="reply-time">{'2023-11-11'}</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="reply-time">点赞数:{100}</span>
<span className="delete-btn">
删除
</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default App.app {
width: 80%;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.reply-navigation {
margin-bottom: 22px;
.nav-bar {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
.nav-title {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
width: 114px;
font-size: 20px;
.nav-title-text {
color: #18191c;
font-weight: 500;
}
.total-reply {
margin: 0 36px 0 6px;
color: #9499a0;
font-weight: normal;
font-size: 13px;
}
}
.nav-sort {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 13px;
.nav-item {
cursor: pointer;
&:hover {
color: #00aeec;
}
&:last-child::after {
display: none;
}
&::after {
content: ' ';
display: inline-block;
height: 10px;
width: 1px;
margin: -1px 12px;
background-color: #9499a0;
}
}
.nav-item.active {
color: #18191c;
}
}
}
}
.reply-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.box-normal {
display: flex;
transition: 0.2s;
.reply-box-avatar {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
width: 80px;
height: 50px;
}
.reply-box-wrap {
display: flex;
position: relative;
flex: 1;
.reply-box-textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
padding: 5px 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
color: #181931;
font-family: inherit;
line-height: 38px;
background-color: #f1f2f3;
border: 1px solid #f1f2f3;
border-radius: 6px;
outline: none;
resize: none;
transition: 0.2s;
&::placeholder {
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 12px;
}
&:focus {
height: 60px;
background-color: #fff;
border-color: #c9ccd0;
}
}
}
.reply-box-send {
position: relative;
display: flex;
flex-basis: 86px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin-left: 10px;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: 0.2s;
& .send-text {
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
color: #fff;
font-size: 16px;
}
&::after {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #00aeec;
border-radius: 4px;
opacity: 0.5;
content: '';
}
&:hover::after {
opacity: 1;
}
}
}
.bili-avatar {
position: relative;
display: block;
width: 48px;
height: 48px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.bili-avatar-img {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
display: block;
width: 48px;
height: 48px;
object-fit: cover;
border: none;
border-radius: 50%;
image-rendering: -webkit-optimize-contrast;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
// 评论列表
.reply-list {
margin-top: 14px;
}
.reply-item {
padding: 22px 0 0 80px;
.root-reply-avatar {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
width: 80px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.content-wrap {
position: relative;
flex: 1;
&::after {
content: ' ';
display: block;
height: 1px;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 14px;
background-color: #e3e5e7;
}
.user-info {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 4px;
.user-name {
height: 30px;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #61666d;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 30px;
cursor: pointer;
}
}
.root-reply {
position: relative;
padding: 2px 0;
color: #181931;
font-size: 15px;
line-height: 24px;
.reply-info {
position: relative;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 2px;
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 13px;
.reply-time {
width: 76px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.reply-like {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: 19px;
.like-icon {
width: 14px;
height: 14px;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #9499a0;
background-position: -153px -25px;
&:hover {
background-position: -218px -25px;
}
}
.like-icon.liked {
background-position: -154px -89px;
}
}
.reply-dislike {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: 19px;
.dislike-icon {
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
background-position: -153px -153px;
&:hover {
background-position: -217px -153px;
}
}
.dislike-icon.disliked {
background-position: -154px -217px;
}
}
.delete-btn {
cursor: pointer;
&:hover {
color: #00aeec;
}
}
}
}
}
}
.reply-none {
height: 64px;
margin-bottom: 80px;
color: #99a2aa;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 64px;
text-align: center;
}1-5-2 完成版本
import { useState } from 'react'
import './App.scss'
import avatar from './images/bozai.png'
import orderBy from 'lodash/orderBy'
/**
* 评论列表的渲染和操作
*
* 1. 根据状态渲染评论列表
* 2. 删除评论
*/
// 评论列表数据
const defaultList = [
{
// 评论id
rpid: 3,
// 用户信息
user: {
uid: '13258165',
avatar: '',
uname: '周杰伦',
},
// 评论内容
content: '哎哟,不错哦',
// 评论时间
ctime: '10-18 08:15',
like: 88,
},
{
rpid: 2,
user: {
uid: '36080105',
avatar: '',
uname: '许嵩',
},
content: '我寻你千百度 日出到迟暮',
ctime: '11-13 11:29',
like: 88,
},
{
rpid: 1,
user: {
uid: '30009257',
avatar,
uname: '黑马前端',
},
content: '学前端就来黑马',
ctime: '10-19 09:00',
like: 66,
},
]
// 当前登录用户信息
const user = {
// 用户id
uid: '30009257',
// 用户头像
avatar,
// 用户昵称
uname: '黑马前端',
}
/**
* 导航 Tab 的渲染和操作
*
* 1. 渲染导航 Tab 和高亮
* 2. 评论列表排序
* 最热 => 喜欢数量降序
* 最新 => 创建时间降序
*/
// 导航 Tab 数组
const tabs = [
{ type: 'hot', text: '最热' },
{ type: 'time', text: '最新' },
]
const App = () => {
// 导航 Tab 高亮的状态
const [activeTab, setActiveTab] = useState('hot')
const [list, setList] = useState(defaultList)
// 删除评论
const onDelete = rpid => {
// 如果要删除数组中的元素,需要调用 filter 方法,并且一定要调用 setList 才能更新状态
setList(list.filter(item => item.rpid !== rpid))
}
// tab 高亮切换
const onToggle = type => {
setActiveTab(type)
let newList
if (type === 'time') {
// 按照时间降序排序
// orderBy(对谁进行排序, 按照谁来排, 顺序)
newList = orderBy(list, 'ctime', 'desc')
} else {
// 按照喜欢数量降序排序
newList = orderBy(list, 'like', 'desc')
}
setList(newList)
}
return (
<div className="app">
{/* 导航 Tab */}
<div className="reply-navigation">
<ul className="nav-bar">
<li className="nav-title">
<span className="nav-title-text">评论</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="total-reply">{list.length}</span>
</li>
<li className="nav-sort">
{/* 高亮类名: active */}
{tabs.map(item => {
return (
<div
key={item.type}
className={
item.type === activeTab ? 'nav-item active' : 'nav-item'
}
onClick={() => onToggle(item.type)}
>
{item.text}
</div>
)
})}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div className="reply-wrap">
{/* 发表评论 */}
<div className="box-normal">
{/* 当前用户头像 */}
<div className="reply-box-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img className="bili-avatar-img" src={avatar} alt="用户头像" />
</div>
</div>
<div className="reply-box-wrap">
{/* 评论框 */}
<textarea
className="reply-box-textarea"
placeholder="发一条友善的评论"
/>
{/* 发布按钮 */}
<div className="reply-box-send">
<div className="send-text">发布</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* 评论列表 */}
<div className="reply-list">
{/* 评论项 */}
{list.map(item => {
return (
<div key={item.rpid} className="reply-item">
{/* 头像 */}
<div className="root-reply-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img
className="bili-avatar-img"
src={item.user.avatar}
alt=""
/>
</div>
</div>
<div className="content-wrap">
{/* 用户名 */}
<div className="user-info">
<div className="user-name">{item.user.uname}</div>
</div>
{/* 评论内容 */}
<div className="root-reply">
<span className="reply-content">{item.content}</span>
<div className="reply-info">
{/* 评论时间 */}
<span className="reply-time">{item.ctime}</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="reply-time">点赞数:{item.like}</span>
{user.uid === item.user.uid && (
<span
className="delete-btn"
onClick={() => onDelete(item.rpid)}
>
删除
</span>
)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-6 React表单控制
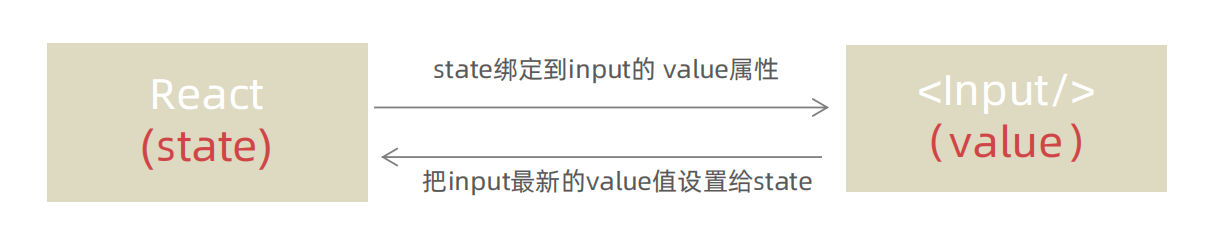
1-6-1 受控绑定
概念:使用React组件的状态(useState)控制表单的状态
function App(){
const [value, setValue] = useState('')
return (
<input
type="text"
value={value}
onChange={e => setValue(e.target.value)}
/>
)
}1-6-2 非受控绑定
概念:通过获取DOM的方式获取表单的输入数据
function App(){
const inputRef = useRef(null)
const onChange = ()=>{
console.log(inputRef.current.value)
}
return (
<input
type="text"
ref={inputRef}
onChange={onChange}
/>
)
}1-7 React组件通信
概念:组件通信就是
组件之间的数据传递, 根据组件嵌套关系的不同,有不同的通信手段和方法
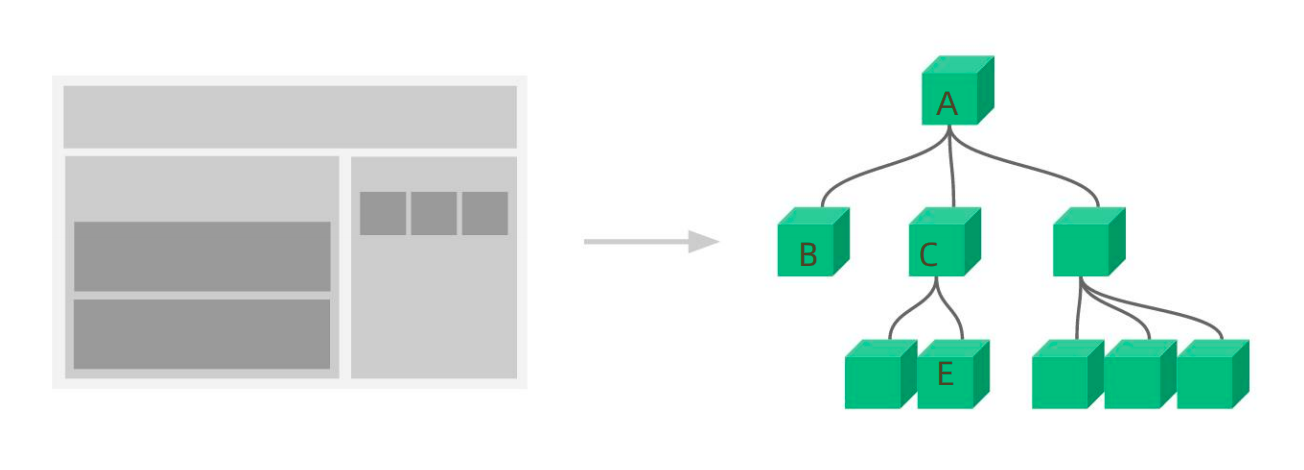
- A-B 父子通信
- B-C 兄弟通信
- A-E 跨层通信
1-7- 1父子通信-父传子
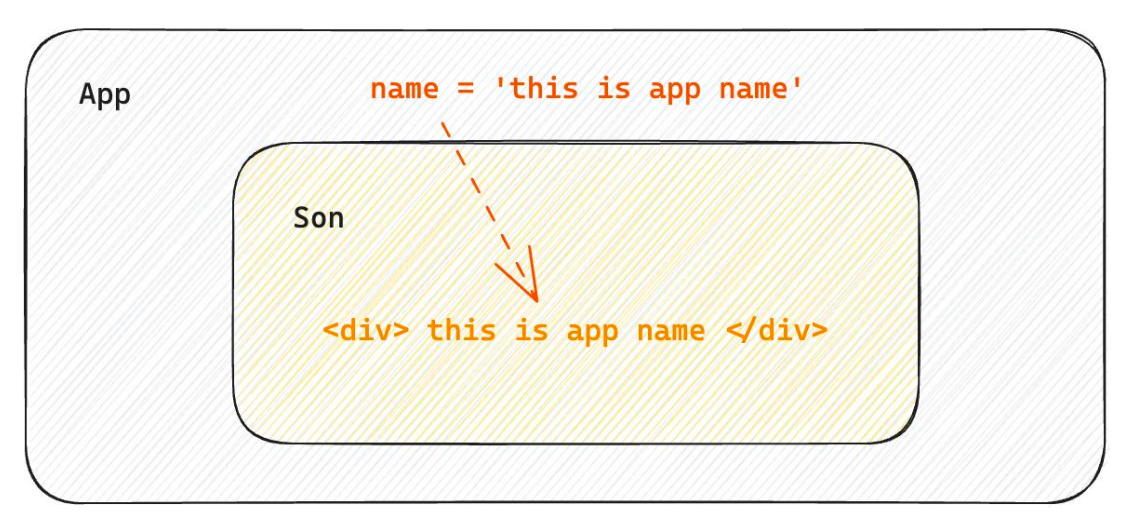
1-1 基础实现
- 父组件传递数据 - 在子组件标签上绑定属性
- 子组件接收数据 - 子组件通过props参数接收数据
function Son(props){
return <div>{ props.name }</div>
}
function App(){
const name = 'this is app name'
return (
<div>
<Son name={name}/>
</div>
)
}1-2 props说明
props可以传递任意的合法数据,比如数字、字符串、布尔值、数组、对象、函数、JSX  props是只读对象 子组件只能读取props中的数据,不能直接进行修改, 父组件的数据只能由父组件修改
props是只读对象 子组件只能读取props中的数据,不能直接进行修改, 父组件的数据只能由父组件修改
1-3 特殊的prop-chilren
场景:当我们把内容嵌套在组件的标签内部时,组件会自动在名为children的prop属性中接收该内容

1-7-2 父子通信-子传父
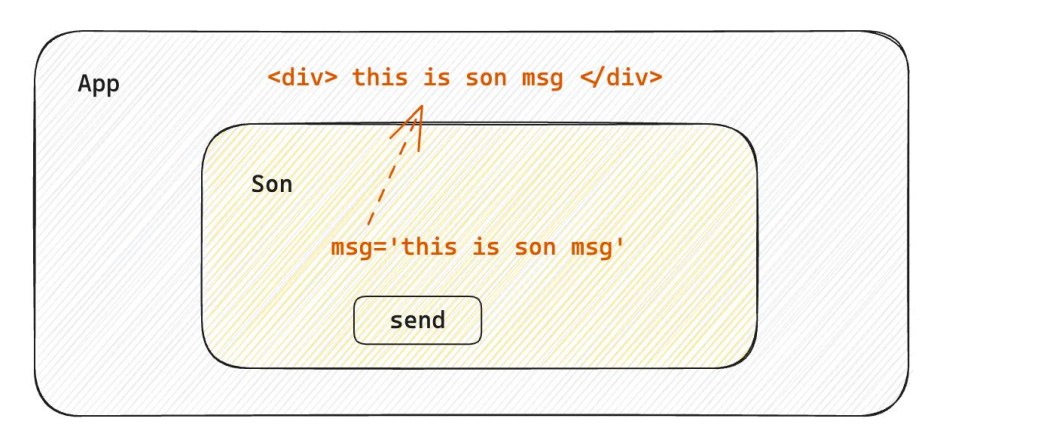
核心思路:在子组件中调用父组件中的函数并传递参数
function Son({ onGetMsg }){
const sonMsg = 'this is son msg'
return (
<div>
{/* 在子组件中执行父组件传递过来的函数 */}
<button onClick={()=>onGetMsg(sonMsg)}>send</button>
</div>
)
}
function App(){
const getMsg = (msg)=>console.log(msg)
return (
<div>
{/* 传递父组件中的函数到子组件 */}
<Son onGetMsg={ getMsg }/>
</div>
)
}1-7-3 兄弟组件通信
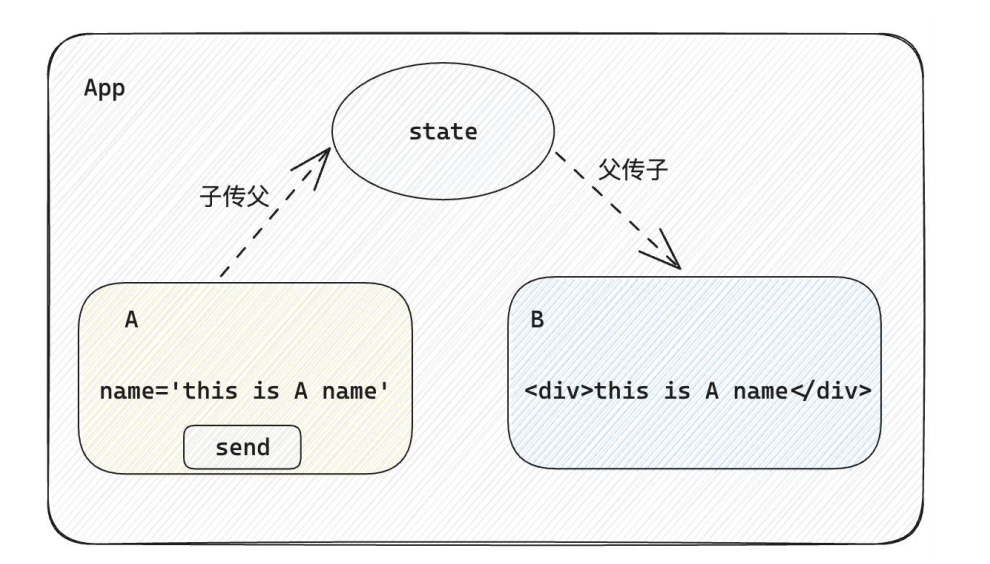
实现思路: 借助
状态提升机制,通过共同的父组件进行兄弟之间的数据传递
- A组件先通过子传父的方式把数据传递给父组件App
- App拿到数据之后通过父传子的方式再传递给B组件
// 1. 通过子传父 A -> App
// 2. 通过父传子 App -> B
import { useState } from "react"
function A ({ onGetAName }) {
// Son组件中的数据
const name = 'this is A name'
return (
<div>
this is A compnent,
<button onClick={() => onGetAName(name)}>send</button>
</div>
)
}
function B ({ name }) {
return (
<div>
this is B compnent,
{name}
</div>
)
}
function App () {
const [name, setName] = useState('')
const getAName = (name) => {
setName(name)
}
return (
<div>
this is App
<A onGetAName={getAName} />
<B name={name} />
</div>
)
}
export default App1-7-4跨层组件通信
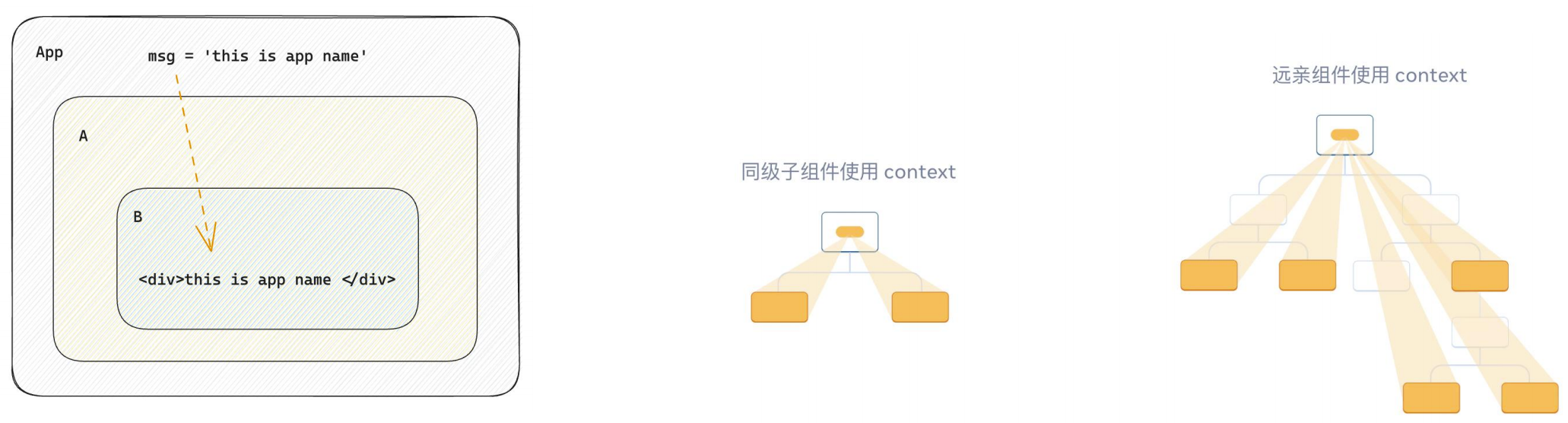 实现步骤:
实现步骤:
- 使用
createContext方法创建一个上下文对象Ctx - 在顶层组件(App)中通过
Ctx.Provider组件提供数据 - 在底层组件(B)中通过
useContext钩子函数获取消费数据
// App -> A -> B
import { createContext, useContext } from "react"
// 1. createContext方法创建一个上下文对象
const MsgContext = createContext()
function A () {
return (
<div>
this is A component
<B />
</div>
)
}
function B () {
// 3. 在底层组件 通过useContext钩子函数使用数据
const msg = useContext(MsgContext)
return (
<div>
this is B compnent,{msg}
</div>
)
}
function App () {
const msg = 'this is app msg'
return (
<div>
{/* 2. 在顶层组件 通过Provider组件提供数据 */}
<MsgContext.Provider value={msg}>
this is App
<A />
</MsgContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-8 React副作用管理-useEffect
1-8-1 概念理解
useEffect是一个React Hook函数,用于在React组件中创建不是由事件引起而是由渲染本身引起的操作(副作用), 比 如发送AJAX请求,更改DOM等等 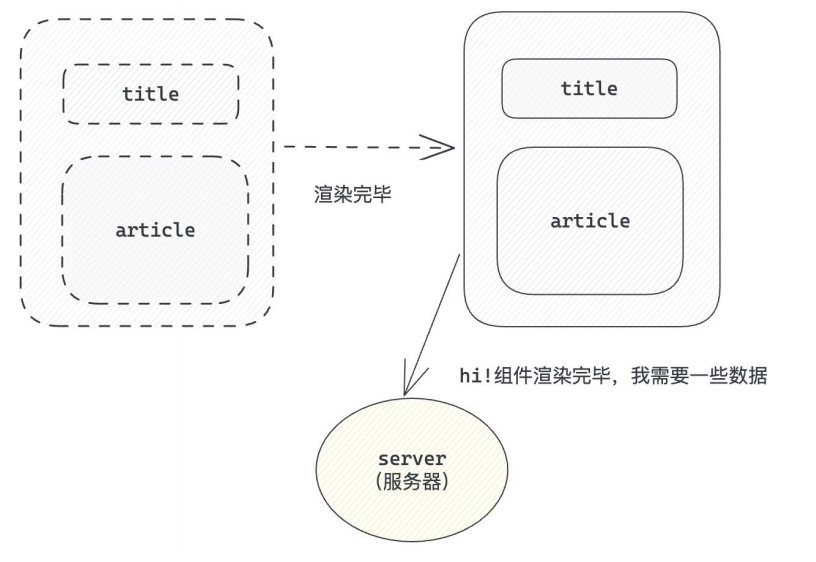
注意
说明:上面的组件中没有发生任何的用户事件,组件渲染完毕之后就需要和服务器要数据,整个过程属于“只由渲染引起的操作”
1-1 基础使用
需求:在组件渲染完毕之后,立刻从服务端获取平道列表数据并显示到页面中
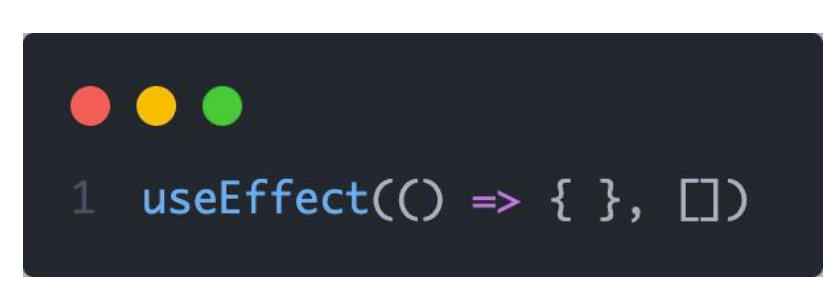 说明:
说明:
- 参数1是一个函数,可以把它叫做副作用函数,在函数内部可以放置要执行的操作
- 参数2是一个数组(可选参),在数组里放置依赖项,不同依赖项会影响第一个参数函数的执行,当是一个空数组的时候,副作用函数只会在组件渲染完毕之后执行一次
注意
接口地址:http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels
1-8-2 useEffect依赖说明
useEffect副作用函数的执行时机存在多种情况,根据传入依赖项的不同,会有不同的执行表现
| 依赖项 | 副作用功函数的执行时机 |
|---|---|
| 没有依赖项 | 组件初始渲染 + 组件更新时执行 |
| 空数组依赖 | 只在初始渲染时执行一次 |
| 添加特定依赖项 | 组件初始渲染 + 依赖项变化时执行 |
1-8-3 清除副作用
概念:在useEffect中编写的由渲染本身引起的对接组件外部的操作,社区也经常把它叫做副作用操作,比如在useEffect中开启了一个定时器,我们想在组件卸载时把这个定时器再清理掉,这个过程就是清理副作用

注意
说明:清除副作用的函数最常见的执行时机是在组件卸载时自动执行
import { useEffect, useState } from "react"
function Son () {
// 1. 渲染时开启一个定时器
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setInterval(() => {
console.log('定时器执行中...')
}, 1000)
return () => {
// 清除副作用(组件卸载时)
clearInterval(timer)
}
}, [])
return <div>this is son</div>
}
function App () {
// 通过条件渲染模拟组件卸载
const [show, setShow] = useState(true)
return (
<div>
{show && <Son />}
<button onClick={() => setShow(false)}>卸载Son组件</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-9 自定义Hook实现
概念:自定义Hook是以
use打头的函数,通过自定义Hook函数可以用来实现逻辑的封装和复用
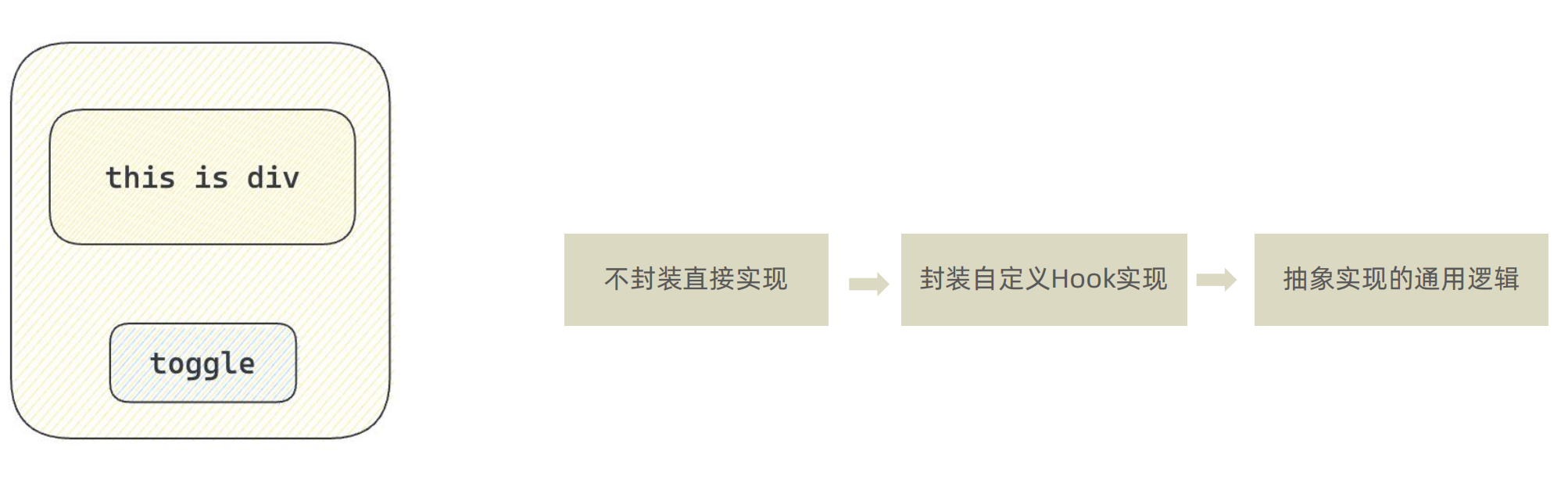
// 封装自定义Hook
// 问题: 布尔切换的逻辑 当前组件耦合在一起的 不方便复用
// 解决思路: 自定义hook
import { useState } from "react"
function useToggle () {
// 可复用的逻辑代码
const [value, setValue] = useState(true)
const toggle = () => setValue(!value)
// 哪些状态和回调函数需要在其他组件中使用 return
return {
value,
toggle
}
}
// 封装自定义hook通用思路
// 1. 声明一个以use打头的函数
// 2. 在函数体内封装可复用的逻辑(只要是可复用的逻辑)
// 3. 把组件中用到的状态或者回调return出去(以对象或者数组)
// 4. 在哪个组件中要用到这个逻辑,就执行这个函数,解构出来状态和回调进行使用
function App () {
const { value, toggle } = useToggle()
return (
<div>
{value && <div>this is div</div>}
<button onClick={toggle}>toggle</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-9-1 React Hooks使用规则
- 只能在组件中或者其他自定义Hook函数中调用
- 只能在组件的顶层调用,不能嵌套在if、for、其它的函数中

const [value, setValue] = useState('');
function App () {
return (
<div>
this is App
</div>
);
}function App () {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
const [value, setValue] = useState('');
}
return (
<div>
this is App
</div>
);
}1-10 案例-优化B站评论案例
- 使用请求接口的方式获取评论列表并渲染
- 使用自定义Hook函数封装数据请求的逻辑
- 把评论中的每一项抽象成一个独立的组件实现渲染
index.js
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client'
import App from './App'
const root = createRoot(document.querySelector('#root'))
root.render(<App />)app.js
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react'
import './App.scss'
import avatar from './images/bozai.png'
import _ from 'lodash'
import classNames from 'classnames'
import { v4 as uuidV4 } from 'uuid'
import dayjs from 'dayjs'
import axios from 'axios'
// 当前登录用户信息
const user = {
// 用户id
uid: '30009257',
// 用户头像
avatar,
// 用户昵称
uname: '黑马前端',
}
// 导航 Tab 数组
const tabs = [
{ type: 'hot', text: '最热' },
{ type: 'time', text: '最新' },
]
// 封装请求数据的Hook
function useGetList () {
// 获取接口数据渲染
const [commentList, setCommentList] = useState([])
useEffect(() => {
// 请求数据
async function getList () {
// axios请求数据
const res = await axios.get(' http://localhost:3004/list')
setCommentList(res.data)
}
getList()
}, [])
return {
commentList,
setCommentList
}
}
// 封装Item组件
function Item ({ item, onDel }) {
return (
<div className="reply-item">
{/* 头像 */}
<div className="root-reply-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img
className="bili-avatar-img"
alt=""
src={item.user.avatar}
/>
</div>
</div>
<div className="content-wrap">
{/* 用户名 */}
<div className="user-info">
<div className="user-name">{item.user.uname}</div>
</div>
{/* 评论内容 */}
<div className="root-reply">
<span className="reply-content">{item.content}</span>
<div className="reply-info">
{/* 评论时间 */}
<span className="reply-time">{item.ctime}</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="reply-time">点赞数:{item.like}</span>
{/* 条件:user.id === item.user.id */}
{user.uid === item.user.uid &&
<span className="delete-btn" onClick={() => onDel(item.rpid)}>
删除
</span>}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
// 渲染评论列表
// 1. 使用useState维护list
// const [commentList, setCommentList] = useState(_.orderBy(list, 'like', 'desc'))
const { commentList, setCommentList } = useGetList()
// 删除功能
const handleDel = (id) => {
console.log(id)
// 对commentList做过滤处理
setCommentList(commentList.filter(item => item.rpid !== id))
}
// tab切换功能
// 1. 点击谁就把谁的type记录下来
// 2. 通过记录的type和每一项遍历时的type做匹配 控制激活类名的显示
const [type, setType] = useState('hot')
const handleTabChange = (type) => {
console.log(type)
setType(type)
// 基于列表的排序
if (type === 'hot') {
// 根据点赞数量排序
// lodash
setCommentList(_.orderBy(commentList, 'like', 'desc'))
} else {
// 根据创建时间排序
setCommentList(_.orderBy(commentList, 'ctime', 'desc'))
}
}
// 发表评论
const [content, setContent] = useState('')
const inputRef = useRef(null)
const handlPublish = () => {
setCommentList([
...commentList,
{
rpid: uuidV4(), // 随机id
user: {
uid: '30009257',
avatar,
uname: '黑马前端',
},
content: content,
ctime: dayjs(new Date()).format('MM-DD hh:mm'), // 格式化 月-日 时:分
like: 66,
}
])
// 1. 清空输入框的内容
setContent('')
// 2. 重新聚焦 dom(useRef) - focus
inputRef.current.focus()
}
return (
<div className="app">
{/* 导航 Tab */}
<div className="reply-navigation">
<ul className="nav-bar">
<li className="nav-title">
<span className="nav-title-text">评论</span>
{/* 评论数量 */}
<span className="total-reply">{10}</span>
</li>
<li className="nav-sort">
{/* 高亮类名: active */}
{tabs.map(item =>
<span
key={item.type}
onClick={() => handleTabChange(item.type)}
className={classNames('nav-item', { active: type === item.type })}>
{item.text}
</span>)}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div className="reply-wrap">
{/* 发表评论 */}
<div className="box-normal">
{/* 当前用户头像 */}
<div className="reply-box-avatar">
<div className="bili-avatar">
<img className="bili-avatar-img" src={avatar} alt="用户头像" />
</div>
</div>
<div className="reply-box-wrap">
{/* 评论框 */}
<textarea
className="reply-box-textarea"
placeholder="发一条友善的评论"
ref={inputRef}
value={content}
onChange={(e) => setContent(e.target.value)}
/>
{/* 发布按钮 */}
<div className="reply-box-send">
<div className="send-text" onClick={handlPublish}>发布</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* 评论列表 */}
<div className="reply-list">
{/* 评论项 */}
{commentList.map(item => <Item key={item.id} item={item} onDel={handleDel} />)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default Appapp.css
.app {
width: 80%;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.reply-navigation {
margin-bottom: 22px;
.nav-bar {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
.nav-title {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
width: 114px;
font-size: 20px;
.nav-title-text {
color: #18191c;
font-weight: 500;
}
.total-reply {
margin: 0 36px 0 6px;
color: #9499a0;
font-weight: normal;
font-size: 13px;
}
}
.nav-sort {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 13px;
.nav-item {
cursor: pointer;
&:hover {
color: #00aeec;
}
&:last-child::after {
display: none;
}
&::after {
content: ' ';
display: inline-block;
height: 10px;
width: 1px;
margin: -1px 12px;
background-color: #9499a0;
}
}
.nav-item.active {
color: #18191c;
}
}
}
}
.reply-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.box-normal {
display: flex;
transition: 0.2s;
.reply-box-avatar {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
width: 80px;
height: 50px;
}
.reply-box-wrap {
display: flex;
position: relative;
flex: 1;
.reply-box-textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
padding: 5px 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
color: #181931;
font-family: inherit;
line-height: 38px;
background-color: #f1f2f3;
border: 1px solid #f1f2f3;
border-radius: 6px;
outline: none;
resize: none;
transition: 0.2s;
&::placeholder {
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 12px;
}
&:focus {
height: 60px;
background-color: #fff;
border-color: #c9ccd0;
}
}
}
.reply-box-send {
position: relative;
display: flex;
flex-basis: 86px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
margin-left: 10px;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: 0.2s;
& .send-text {
position: absolute;
z-index: 1;
color: #fff;
font-size: 16px;
}
&::after {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #00aeec;
border-radius: 4px;
opacity: 0.5;
content: '';
}
&:hover::after {
opacity: 1;
}
}
}
.bili-avatar {
position: relative;
display: block;
width: 48px;
height: 48px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.bili-avatar-img {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
display: block;
width: 48px;
height: 48px;
object-fit: cover;
border: none;
border-radius: 50%;
image-rendering: -webkit-optimize-contrast;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
// 评论列表
.reply-list {
margin-top: 14px;
}
.reply-item {
padding: 22px 0 0 80px;
.root-reply-avatar {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
width: 80px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.content-wrap {
position: relative;
flex: 1;
&::after {
content: ' ';
display: block;
height: 1px;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 14px;
background-color: #e3e5e7;
}
.user-info {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 4px;
.user-name {
height: 30px;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #61666d;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 30px;
cursor: pointer;
}
}
.root-reply {
position: relative;
padding: 2px 0;
color: #181931;
font-size: 15px;
line-height: 24px;
.reply-info {
position: relative;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 2px;
color: #9499a0;
font-size: 13px;
.reply-time {
width: 86px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.reply-like {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: 19px;
.like-icon {
width: 14px;
height: 14px;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #9499a0;
background-position: -153px -25px;
&:hover {
background-position: -218px -25px;
}
}
.like-icon.liked {
background-position: -154px -89px;
}
}
.reply-dislike {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: 19px;
.dislike-icon {
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
background-position: -153px -153px;
&:hover {
background-position: -217px -153px;
}
}
.dislike-icon.disliked {
background-position: -154px -217px;
}
}
.delete-btn {
cursor: pointer;
&:hover {
color: #00aeec;
}
}
}
}
}
}
.reply-none {
height: 64px;
margin-bottom: 80px;
color: #99a2aa;
font-size: 13px;
line-height: 64px;
text-align: center;
}1-11 Redux介绍
Redux 是React最常用的集中状态管理工具,类似于Vue中的Pinia(Vuex),可以独立于框架运行 作用:通过集中管理的方式管理应用的状态
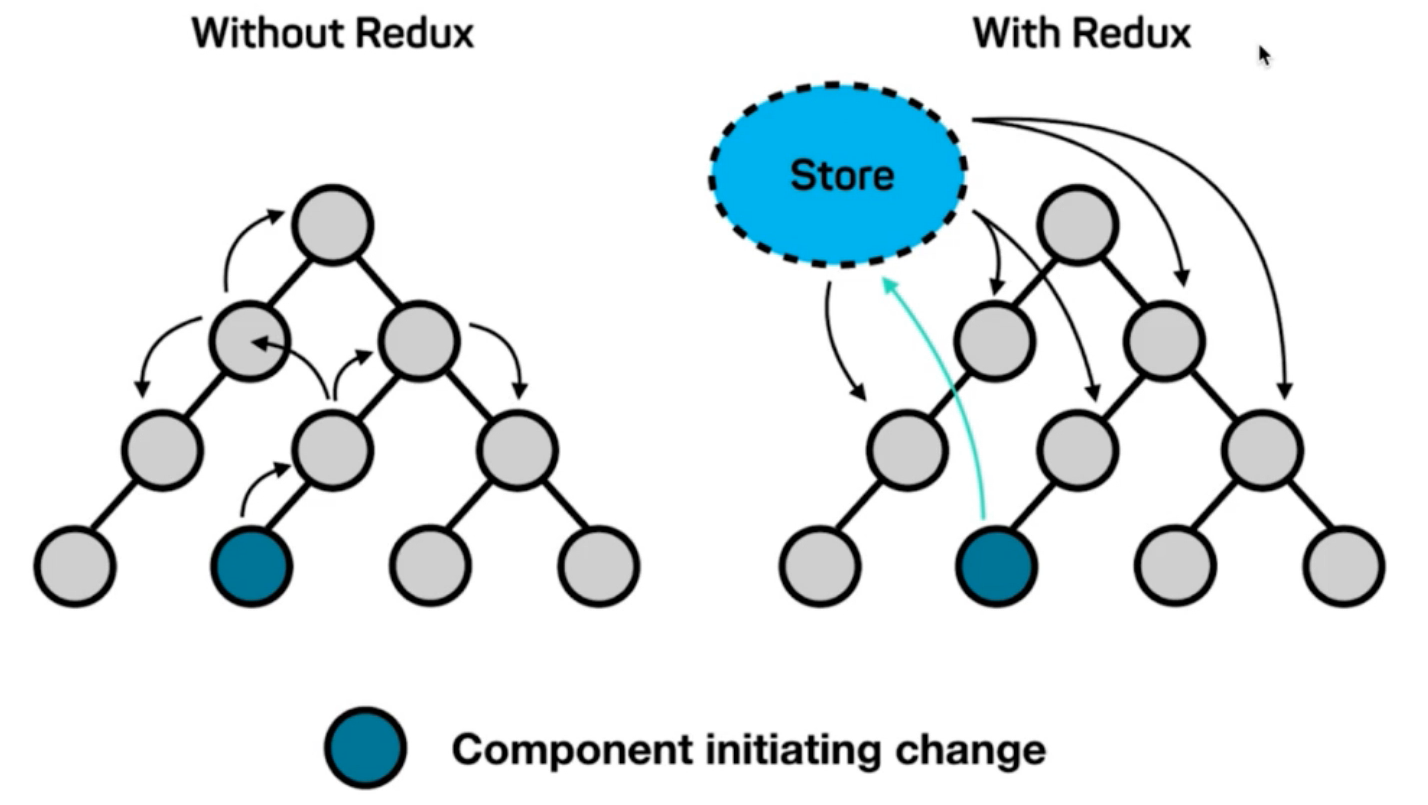 为什么要使用Redux?
为什么要使用Redux?
- 独立于组件,无视组件之间的层级关系,简化通信问题
- 单项数据流清晰,易于定位bug
- 调试工具配套良好,方便调试
1-11-1 Redux快速体验
1-1 实现计数器
需求:不和任何框架绑定,不使用任何构建工具,使用纯Redux实现计数器
 使用步骤:
使用步骤:
- 定义一个 reducer 函数 (根据当前想要做的修改返回一个新的状态)
- 使用createStore方法传入 reducer函数 生成一个store实例对象
- 使用store实例的 subscribe方法 订阅数据的变化(数据一旦变化,可以得到通知)
- 使用store实例的 dispatch方法提交action对象 触发数据变化(告诉reducer你想怎么改数据)
- 使用store实例的 getState方法 获取最新的状态数据更新到视图中
代码实现:
<button id="decrement">-</button>
<span id="count">0</span>
<button id="increment">+</button>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/redux@latest/dist/redux.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义reducer函数
// 内部主要的工作是根据不同的action 返回不同的state
function counterReducer (state = { count: 0 }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 }
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 }
default:
return state
}
}
// 使用reducer函数生成store实例
const store = Redux.createStore(counterReducer)
// 订阅数据变化
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState())
document.getElementById('count').innerText = store.getState().count
})
// 增
const inBtn = document.getElementById('increment')
inBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
store.dispatch({
type: 'INCREMENT'
})
})
// 减
const dBtn = document.getElementById('decrement')
dBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
store.dispatch({
type: 'DECREMENT'
})
})
</script>1-2. Redux数据流架构
Redux的难点是理解它对于数据修改的规则, 下图动态展示了在整个数据的修改中,数据的流向
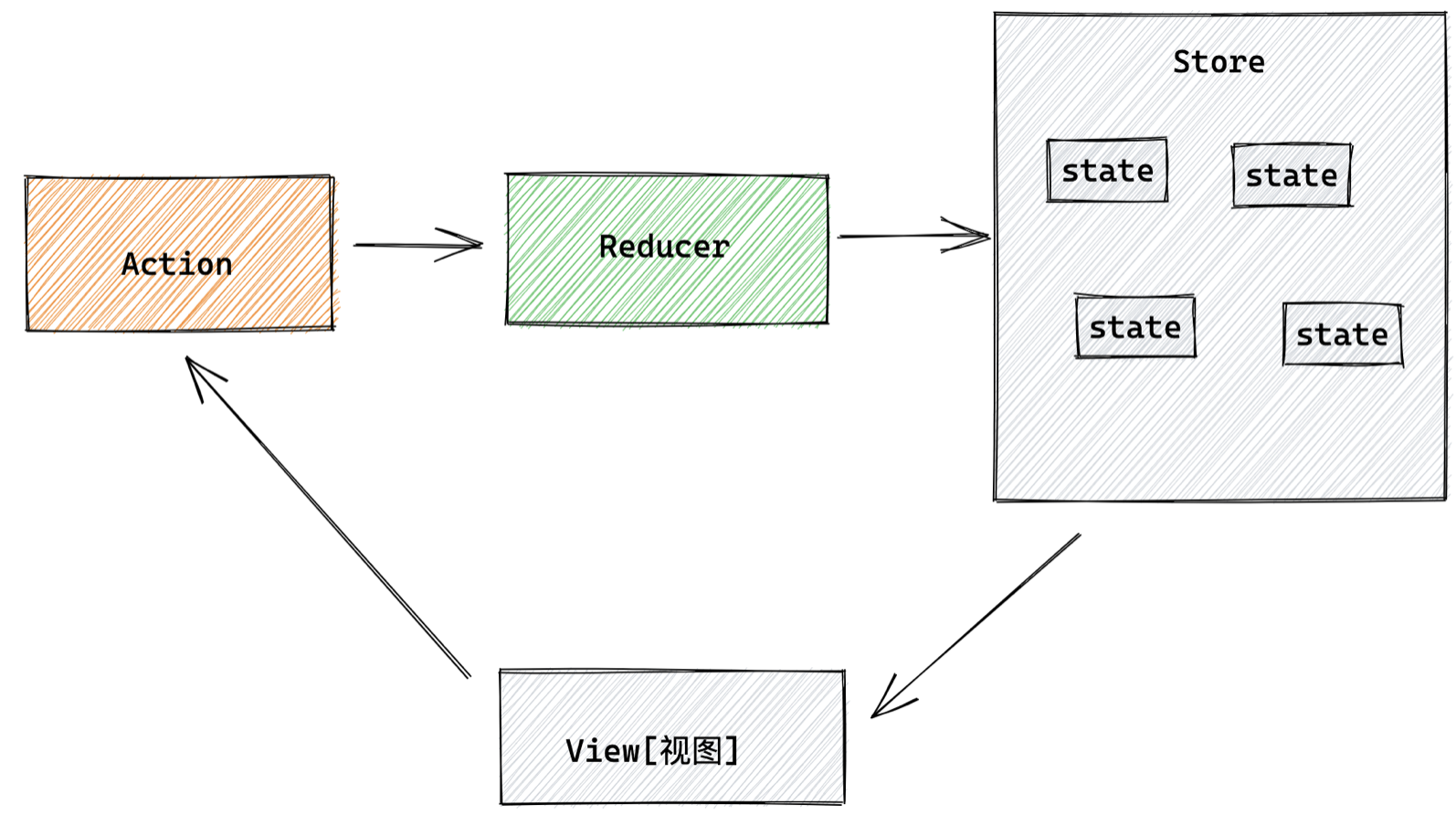 为了职责清晰,Redux代码被分为三个核心的概念,我们学redux,其实就是学这三个核心概念之间的配合,三个概念分别是:
为了职责清晰,Redux代码被分为三个核心的概念,我们学redux,其实就是学这三个核心概念之间的配合,三个概念分别是:
- state: 一个对象 存放着我们管理的数据
- action: 一个对象 用来描述你想怎么改数据
- reducer: 一个函数 根据action的描述更新state
1-11-2 Redux与React - 环境准备
Redux虽然是一个框架无关可以独立运行的插件,但是社区通常还是把它与React绑定在一起使用,以一个计数器案例体验一下Redux + React 的基础使用
2-1 . 配套工具
在React中使用redux,官方要求安装俩个其他插件 - Redux Toolkit 和 react-redux
Redux Toolkit(RTK)- 官方推荐编写Redux逻辑的方式,是一套工具的集合集,简化书写方式
react-redux - 用来 链接 Redux 和 React组件 的中间件

2-2. 配置基础环境
- 使用 CRA 快速创建 React 项目
npx create-react-app react-redux- 安装配套工具
npm i @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux- 启动项目
npm run start2-3. store目录结构设计
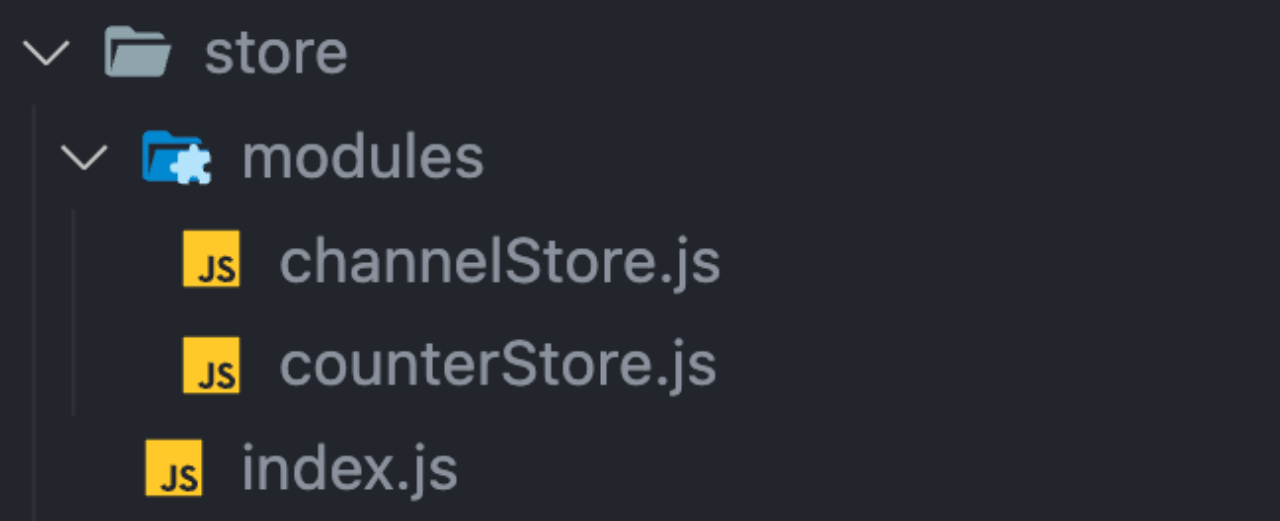
通常集中状态管理的部分都会单独创建一个单独的
store目录应用通常会有很多个子store模块,所以创建一个
modules目录,在内部编写业务分类的子storestore中的入口文件 index.js 的作用是组合modules中所有的子模块,并导出store
1-11-3 Redux与React - 实现counter
1-1. 整体路径熟悉
1-2. 使用React Toolkit 创建 counterStore
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const counterStore = createSlice({
// 模块名称独一无二
name: 'counter',
// 初始数据
initialState: {
count: 1
},
// 修改数据的同步方法
reducers: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state){
state.count--
}
}
})
// 结构出actionCreater
const { increment,decrement } = counter.actions
// 获取reducer函数
const counterReducer = counterStore.reducer
// 导出
export { increment, decrement }
export default counterReducerimport { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import counterReducer from './modules/counterStore'
export default configureStore({
reducer: {
// 注册子模块
counter: counterReducer
}
})1-3. 为React注入store
react-redux负责把Redux和React 链接 起来,内置 Provider组件 通过 store 参数把创建好的store实例注入到应用中,链接正式建立
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import App from './App'
// 导入store
import store from './store'
// 导入store提供组件Provider
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
// 提供store数据
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
)1-4. React组件使用store中的数据
在React组件中使用store中的数据,需要用到一个钩子函数 - useSelector,它的作用是把store中的数据映射到组件中,使用样例如下:

import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import counterReducer from "./modules/counterStore";
// 创建根store组合子模块
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
counter: counterReducer,
},
});
export default store;1-5. React组件修改store中的数据
React组件中修改store中的数据需要借助另外一个hook函数 - useDispatch,它的作用是生成提交action对象的dispatch函数,使用样例如下:

import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
// 导入创建action对象的方法
import { decrement, increment } from './store/modules/counterStore';
function App () {
const { count } = useSelector(state => state.counter);
// 得到dispatch函数
const dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 调用dispatch提交action对象 */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch(decrement())}>-</button>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(increment())}>+</button>
</div>
);
}1-11-4 Redux与React - 提交action传参
需求:组件中有俩个按钮
add to 10和add to 20可以直接把count值修改到对应的数字,目标count值是在组件中传递过去的,需要在提交action的时候传递参数
 实现方式:在reducers的同步修改方法中添加action对象参数,在调用actionCreater的时候传递参数,参数会被传递到action对象payload属性上
实现方式:在reducers的同步修改方法中添加action对象参数,在调用actionCreater的时候传递参数,参数会被传递到action对象payload属性上
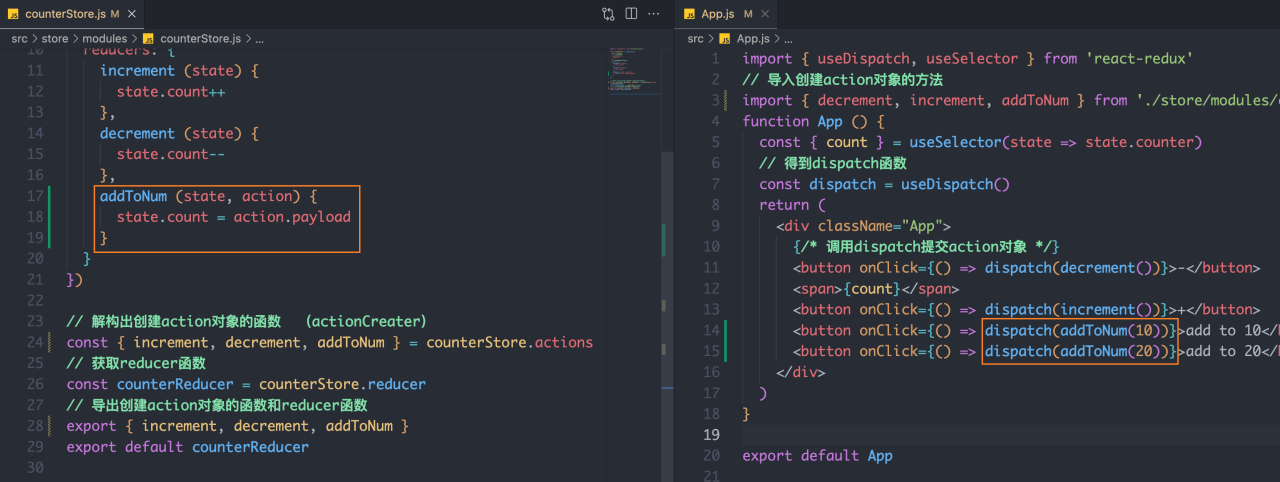
counterStore.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
const counterStore = createSlice({
name: 'counter',
initialState: {
count: 0,
},
reducers: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--;
},
addToNum(state, action) {
state.count = action.payload;
},
},
});
// 解构出创建action对象的函数(actionCreator)
const { increment, decrement, addToNum } = counterStore.actions;
// 获取reducer函数
const counterReducer = counterStore.reducer;
// 导出创建action对象的函数和reducer函数
export { increment, decrement, addToNum };
export default counterReducer;App.js
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
// 导入创建action对象的方法
import { decrement, increment, addToNum } from './store/modules/counterStore';
function App () {
const { count } = useSelector(state => state.counter);
// 得到dispatch函数
const dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<div className="App">
{/* 调用dispatch提交action对象 */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch(decrement())}>-</button>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(increment())}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(addToNum(10))}>add to 10</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch(addToNum(20))}>add to 20</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;1-11-5 Redux与React - 异步action处理
需求理解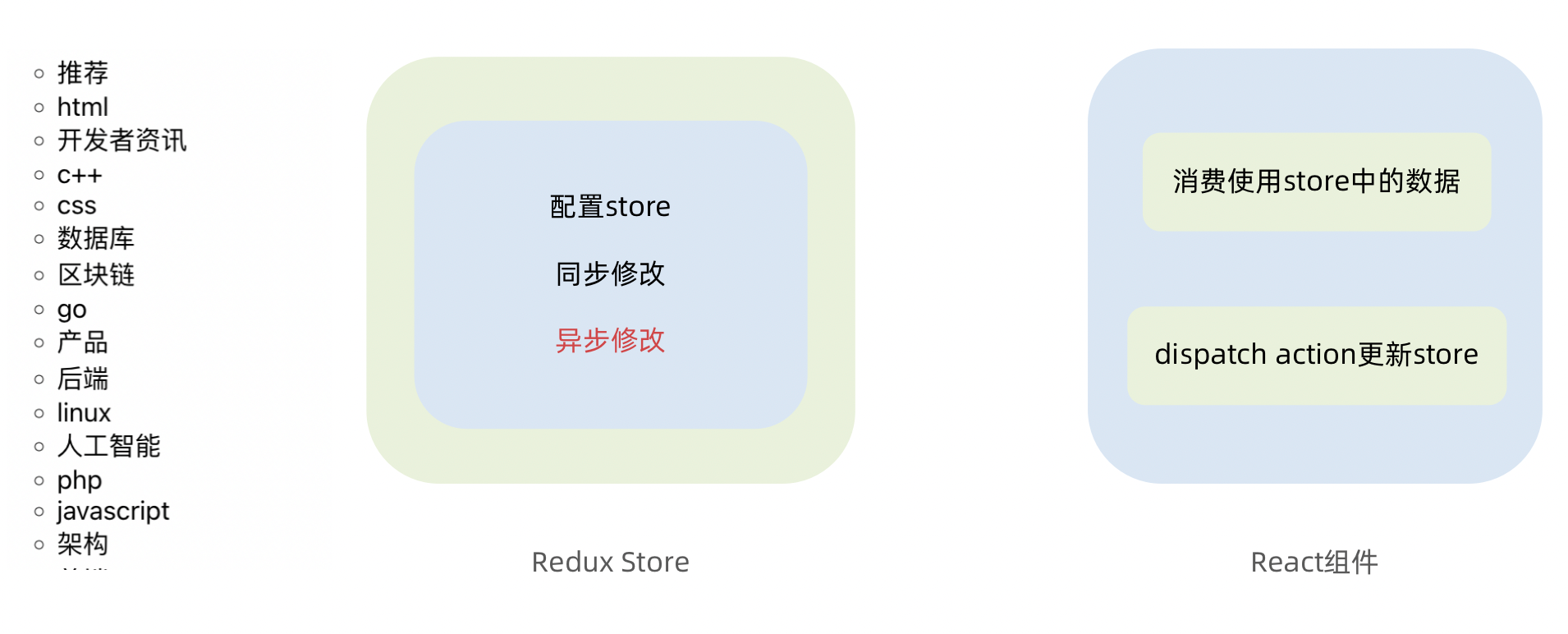
实现步骤
- 创建store的写法保持不变,配置好同步修改状态的方法
- 单独封装一个函数,在函数内部return一个新函数,在新函数中 2.1 封装异步请求获取数据 2.2 调用同步actionCreater传入异步数据生成一个action对象,并使用dispatch提交
- 组件中dispatch的写法保持不变
代码实现
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import axios from 'axios'
const channelStore = createSlice({
name: 'channel',
initialState: {
channelList: []
},
reducers: {
setChannelList (state, action) {
state.channelList = action.payload
}
}
})
// 创建异步
const { setChannelList } = channelStore.actions
const url = 'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels'
// 封装一个函数 在函数中return一个新函数 在新函数中封装异步
// 得到数据之后通过dispatch函数 触发修改
const fetchChannelList = () => {
return async (dispatch) => {
const res = await axios.get(url)
dispatch(setChannelList(res.data.data.channels))
}
}
export { fetchChannelList }
const channelReducer = channelStore.reducer
export default channelReducerimport { useEffect } from 'react'
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
import { fetchChannelList } from './store/channelStore'
function App () {
// 使用数据
const { channelList } = useSelector(state => state.channel)
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchChannelList())
}, [dispatch])
return (
<div className="App">
<ul>
{channelList.map(task => <li key={task.id}>{task.name}</li>)}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-11-6 Redux调试 - devtools
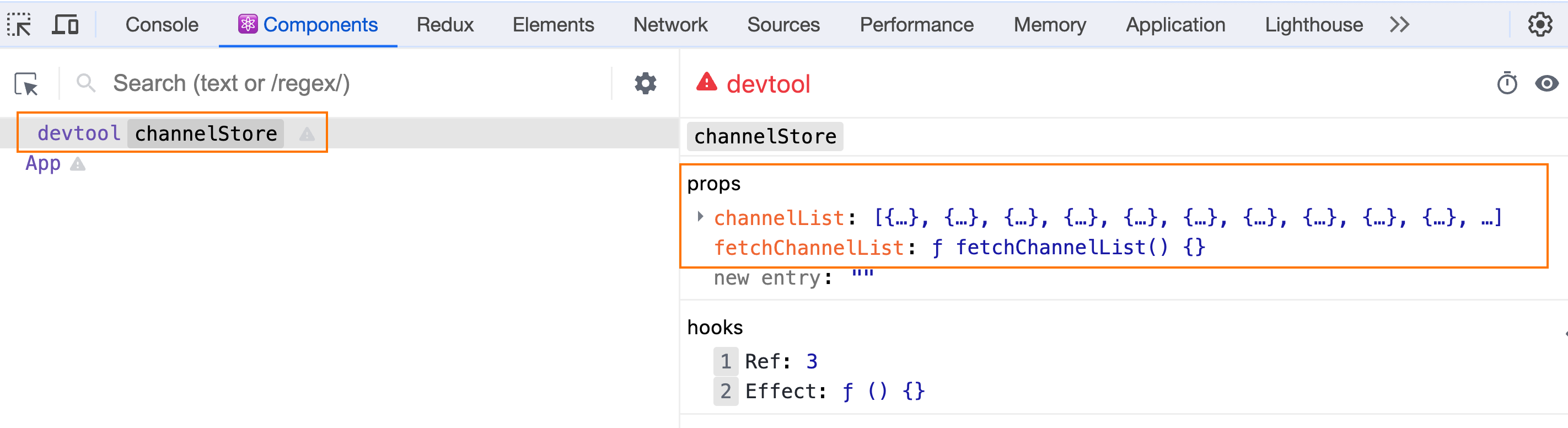
6-1 安装Redux DevTools扩展
安装Redux DevTools浏览器扩展
:
- 对于Chrome用户:Redux DevTools
- 对于Firefox用户:Redux DevTools
6-2 配置Redux Store以支持DevTools
安装依赖: 如果你使用的是Redux Toolkit,那么已经内置了对Redux DevTools的支持。如果没有使用,可以手动安装
redux-devtools-extension包。npm install @reduxjs/toolkit配置Store: 在配置Redux Store时,只需要简单配置就可以启用Redux DevTools。
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'; import counterReducer from './modules/counterStore'; const store = configureStore({ reducer: { counter: counterReducer, }, devTools: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', // 仅在开发环境中启用DevTools }); export default store;如果你没有使用Redux Toolkit,可以使用
redux-devtools-extension包进行配置。import { createStore } from 'redux'; import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension'; import rootReducer from './reducers'; const store = createStore( rootReducer, composeWithDevTools() ); export default store;
6-3 使用Redux DevTools
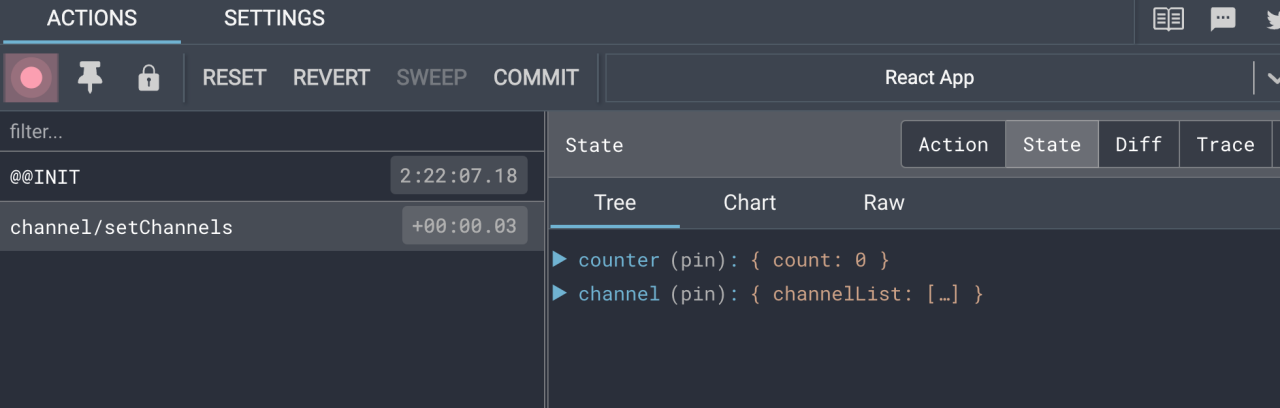
- 启动应用: 确保你的应用在开发模式下运行,然后打开浏览器中的Redux DevTools扩展。你将能够看到Redux的状态变化和actions的流动。
Redux官方提供了针对于Redux的调试工具,支持实时state信息展示,action提交信息查看等
1-12 美团小案例
1-12-1 . 案例演示

基本开发思路:使用 RTK(Redux Toolkit)来管理应用状态, 组件负责 数据渲染 和 dispatch action
1-12-2. 准备并熟悉环境
- 克隆项目到本地(内置了基础静态组件和模版)
git clone http://git.itcast.cn/heimaqianduan/redux-meituan.git- 安装所有依赖
npm i- 启动mock服务(内置了json-server)
npm run serve- 启动前端服务
npm run start1-12-3. 分类和商品列表渲染
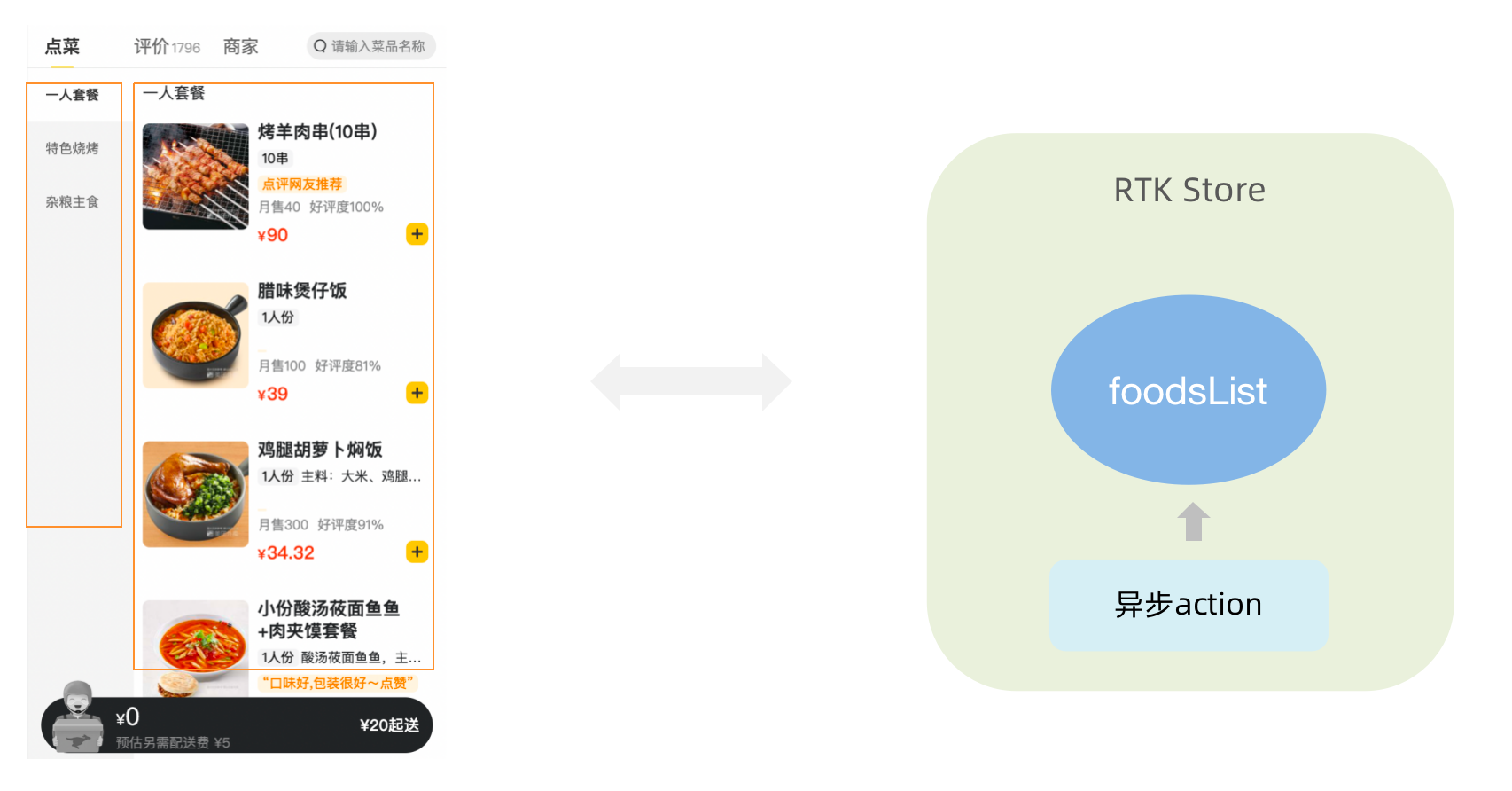
1-1- 编写store逻辑
// 编写store
import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit"
import axios from "axios"
const foodsStore = createSlice({
name: 'foods',
initialState: {
// 商品列表
foodsList: []
},
reducers: {
// 更改商品列表
setFoodsList (state, action) {
state.foodsList = action.payload
}
}
})
// 异步获取部分
const { setFoodsList } = foodsStore.actions
const fetchFoodsList = () => {
return async (dispatch) => {
// 编写异步逻辑
const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:3004/takeaway')
// 调用dispatch函数提交action
dispatch(setFoodsList(res.data))
}
}
export { fetchFoodsList }
const reducer = foodsStore.reducer
export default reducer1-2- 组件使用store数据
// 省略部分代码
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
import { fetchFoodsList } from './store/modules/takeaway'
import { useEffect } from 'react'
const App = () => {
// 触发action执行
// 1. useDispatch -> dispatch 2. actionCreater导入进来 3.useEffect
const dispatch = useDispatch()
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchFoodsList())
}, [dispatch])
return (
<div className="home">
{/* 导航 */}
<NavBar />
{/* 内容 */}
<div className="content-wrap">
<div className="content">
<Menu />
<div className="list-content">
<div className="goods-list">
{/* 外卖商品列表 */}
{foodsList.map(item => {
return (
<FoodsCategory
key={item.tag}
// 列表标题
name={item.name}
// 列表商品
foods={item.foods}
/>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* 购物车 */}
<Cart />
</div>
)
}
export default App1-12-4. 点击分类激活交互实现
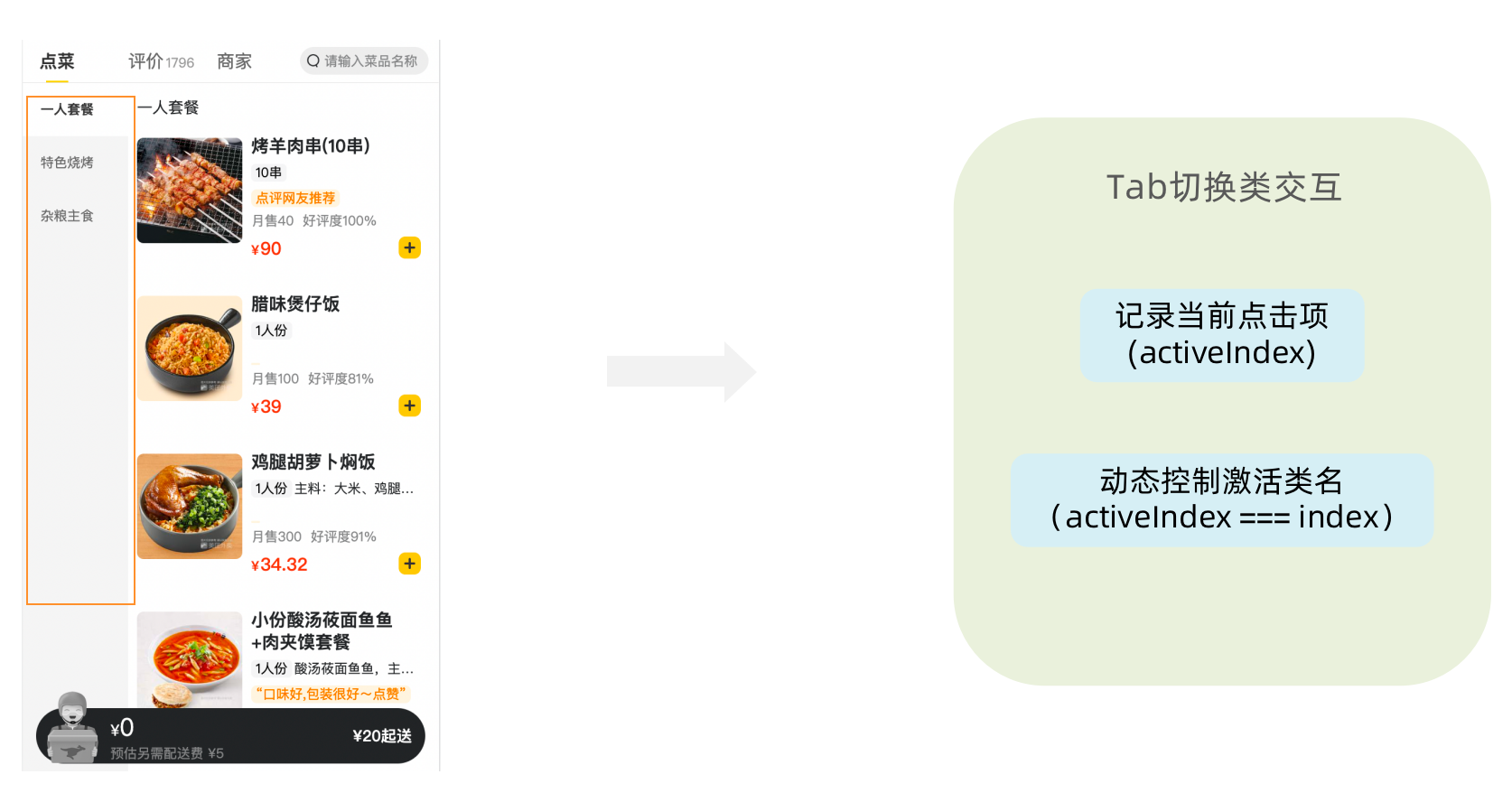
1-1-编写store逻辑
// 编写store
import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit"
import axios from "axios"
const foodsStore = createSlice({
name: 'foods',
initialState: {
// 菜单激活下标值
activeIndex: 0
},
reducers: {
// 更改activeIndex
changeActiveIndex (state, action) {
state.activeIndex = action.payload
}
}
})
// 导出
const { changeActiveIndex } = foodsStore.actions
export { changeActiveIndex }
const reducer = foodsStore.reducer
export default reducer1-2 编写组件逻辑
const Menu = () => {
const { foodsList, activeIndex } = useSelector(state => state.foods)
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const menus = foodsList.map(item => ({ tag: item.tag, name: item.name }))
return (
<nav className="list-menu">
{/* 添加active类名会变成激活状态 */}
{menus.map((item, index) => {
return (
<div
// 提交action切换激活index
onClick={() => dispatch(changeActiveIndex(index))}
key={item.tag}
// 动态控制active显示
className={classNames(
'list-menu-item',
activeIndex === index && 'active'
)}
>
{item.name}
</div>
)
})}
</nav>
)
}1-12-5. 商品列表切换显示
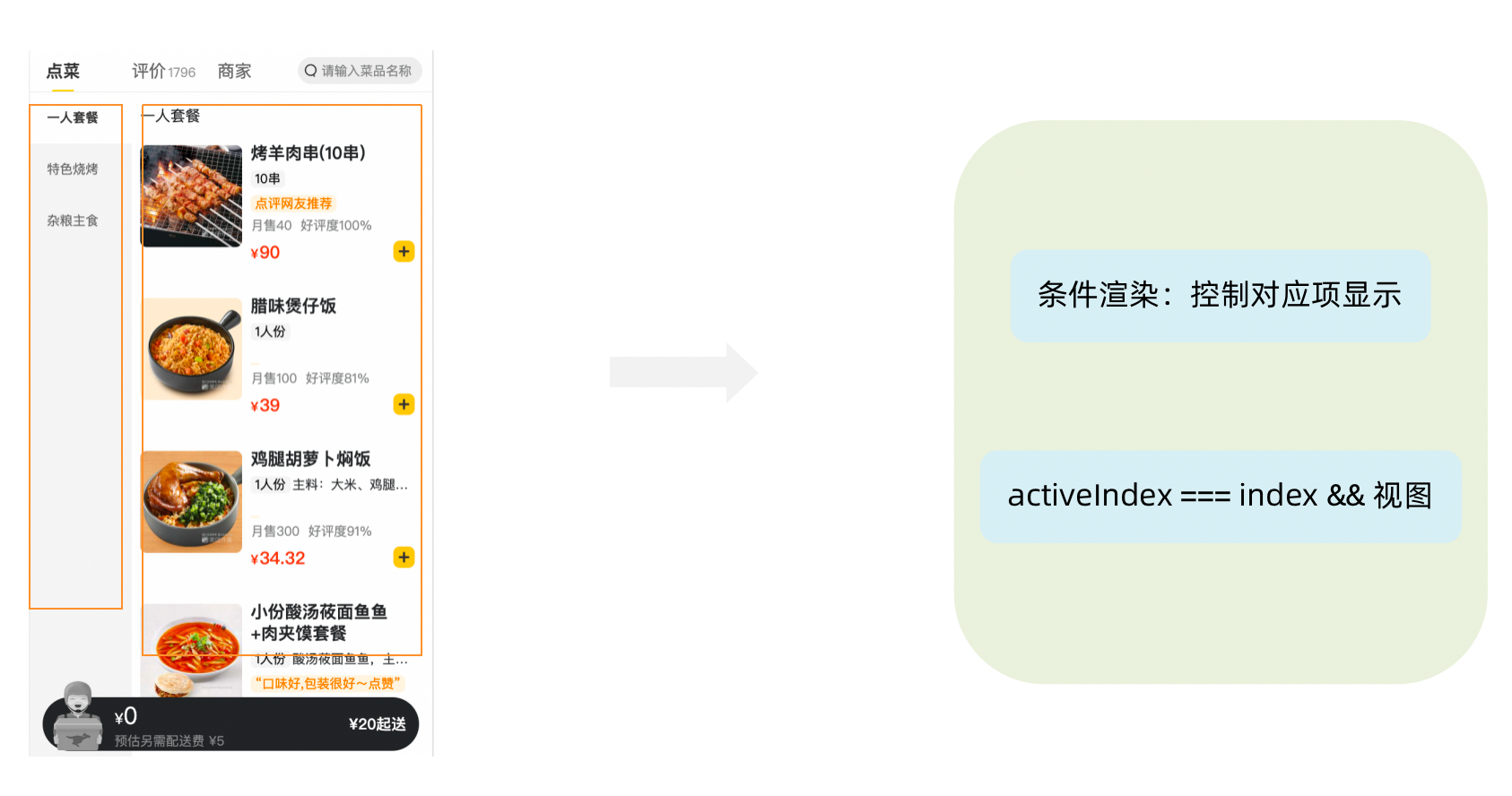
<div className="list-content">
<div className="goods-list">
{/* 外卖商品列表 */}
{foodsList.map((item, index) => {
return (
activeIndex === index && <FoodsCategory
key={item.tag}
// 列表标题
name={item.name}
// 列表商品
foods={item.foods}
/>
)
})}
</div>
</div>1-12-6. 添加购物车实现

1-1 编写store逻辑
// 编写store
import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit"
import axios from "axios"
const foodsStore = createSlice({
name: 'foods',
reducers: {
// 添加购物车
addCart (state, action) {
// 是否添加过?以action.payload.id去cartList中匹配 匹配到了 添加过
const item = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === action.payload.id)
if (item) {
item.count++
} else {
state.cartList.push(action.payload)
}
}
}
})
// 导出actionCreater
const { addCart } = foodsStore.actions
export { addCart }
const reducer = foodsStore.reducer
export default reducer1-2 编写组件逻辑
<div className="goods-count">
{/* 添加商品 */}
<span
className="plus"
onClick={() => dispatch(addCart({
id,
picture,
name,
unit,
description,
food_tag_list,
month_saled,
like_ratio_desc,
price,
tag,
count
}))}></span>
</div>1-12-7. 统计区域实现
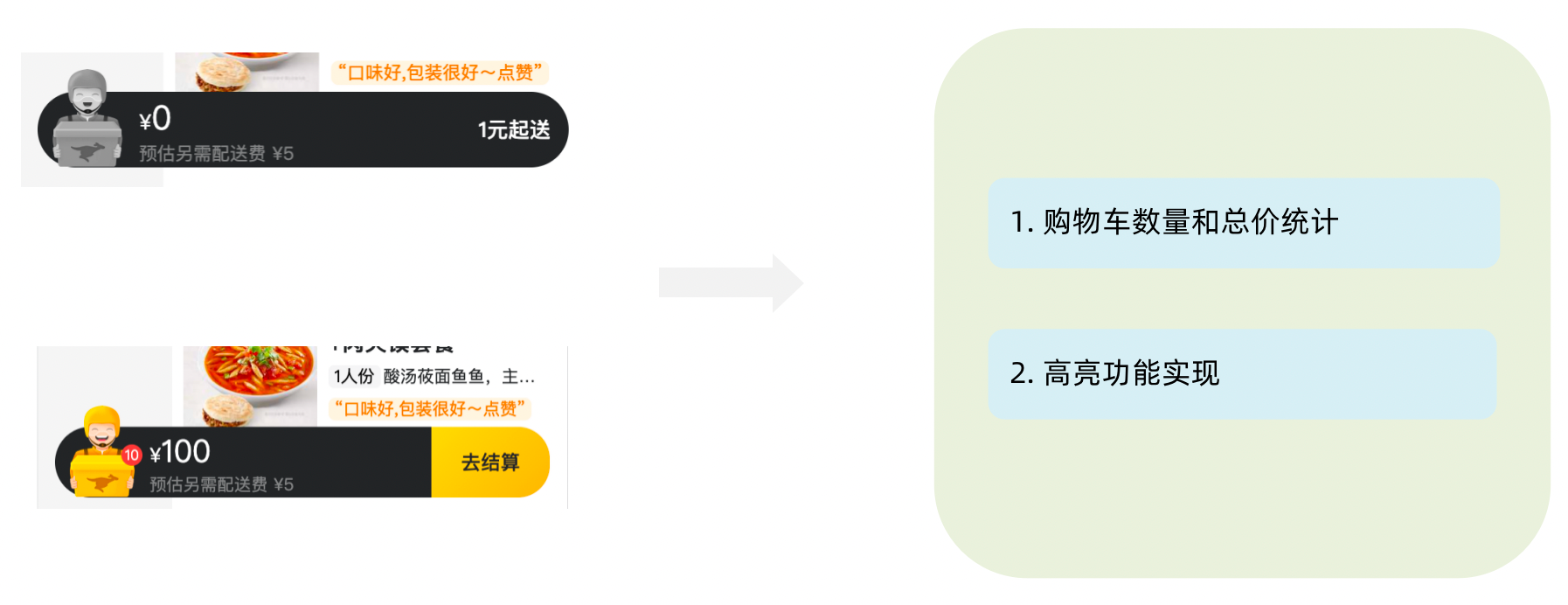
实现思路
- 基于store中的cartList的length渲染数量
- 基于store中的cartList累加price * count
- 购物车cartList的length不为零则高亮
// 计算总价
const totalPrice = cartList.reduce((a, c) => a + c.price * c.count, 0)
{/* fill 添加fill类名购物车高亮*/}
{/* 购物车数量 */}
<div onClick={onShow} className={classNames('icon', cartList.length > 0 && 'fill')}>
{cartList.length > 0 && <div className="cartCornerMark">{cartList.length}</div>}
</div>1-12-8. 购物车列表功能实现
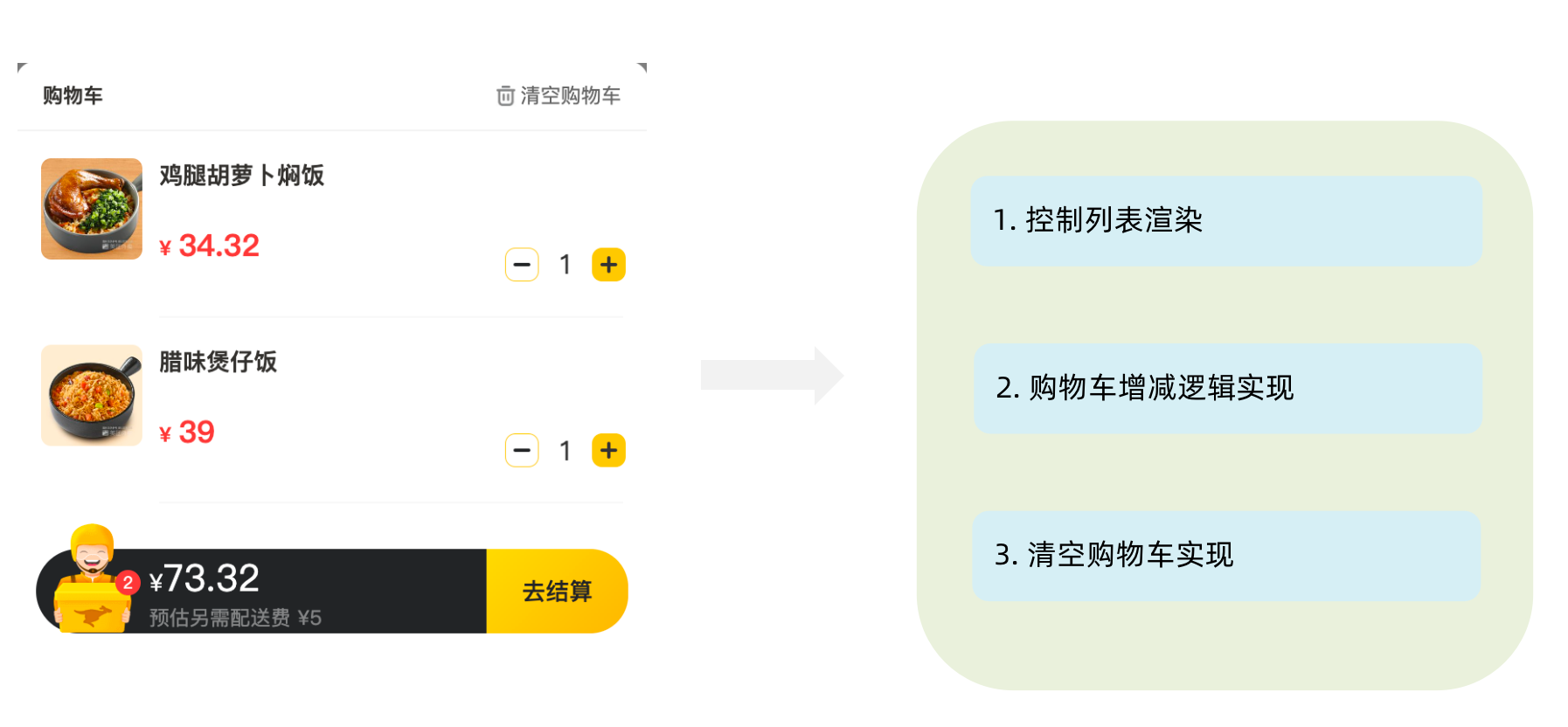
1-1 控制列表渲染
const Cart = () => {
return (
<div className="cartContainer">
{/* 添加visible类名 div会显示出来 */}
<div className={classNames('cartPanel', 'visible')}>
{/* 购物车列表 */}
<div className="scrollArea">
{cartList.map(item => {
return (
<div className="cartItem" key={item.id}>
<img className="shopPic" src={item.picture} alt="" />
<div className="main">
<div className="skuInfo">
<div className="name">{item.name}</div>
</div>
<div className="payableAmount">
<span className="yuan">¥</span>
<span className="price">{item.price}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div className="skuBtnWrapper btnGroup">
{/* 数量组件 */}
<Count
count={item.count}
/>
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default Cart1-2 购物车增减逻辑实现
// count增
increCount (state, action) {
// 关键点:找到当前要修改谁的count id
const item = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === action.payload.id)
item.count++
},
// count减
decreCount (state, action) {
// 关键点:找到当前要修改谁的count id
const item = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === action.payload.id)
if (item.count === 0) {
return
}
item.count--
}<div className="skuBtnWrapper btnGroup">
{/* 数量组件 */}
<Count
count={item.count}
onPlus={() => dispatch(increCount({ id: item.id }))}
onMinus={() => dispatch(decreCount({ id: item.id }))}
/>
</div>1-3 清空购物车实现
// 清除购物车
clearCart (state) {
state.cartList = []
}<div className="header">
<span className="text">购物车</span>
<span
className="clearCart"
onClick={() => dispatch(clearCart())}>
清空购物车
</span>
</div>1-12-9. 控制购物车显示和隐藏
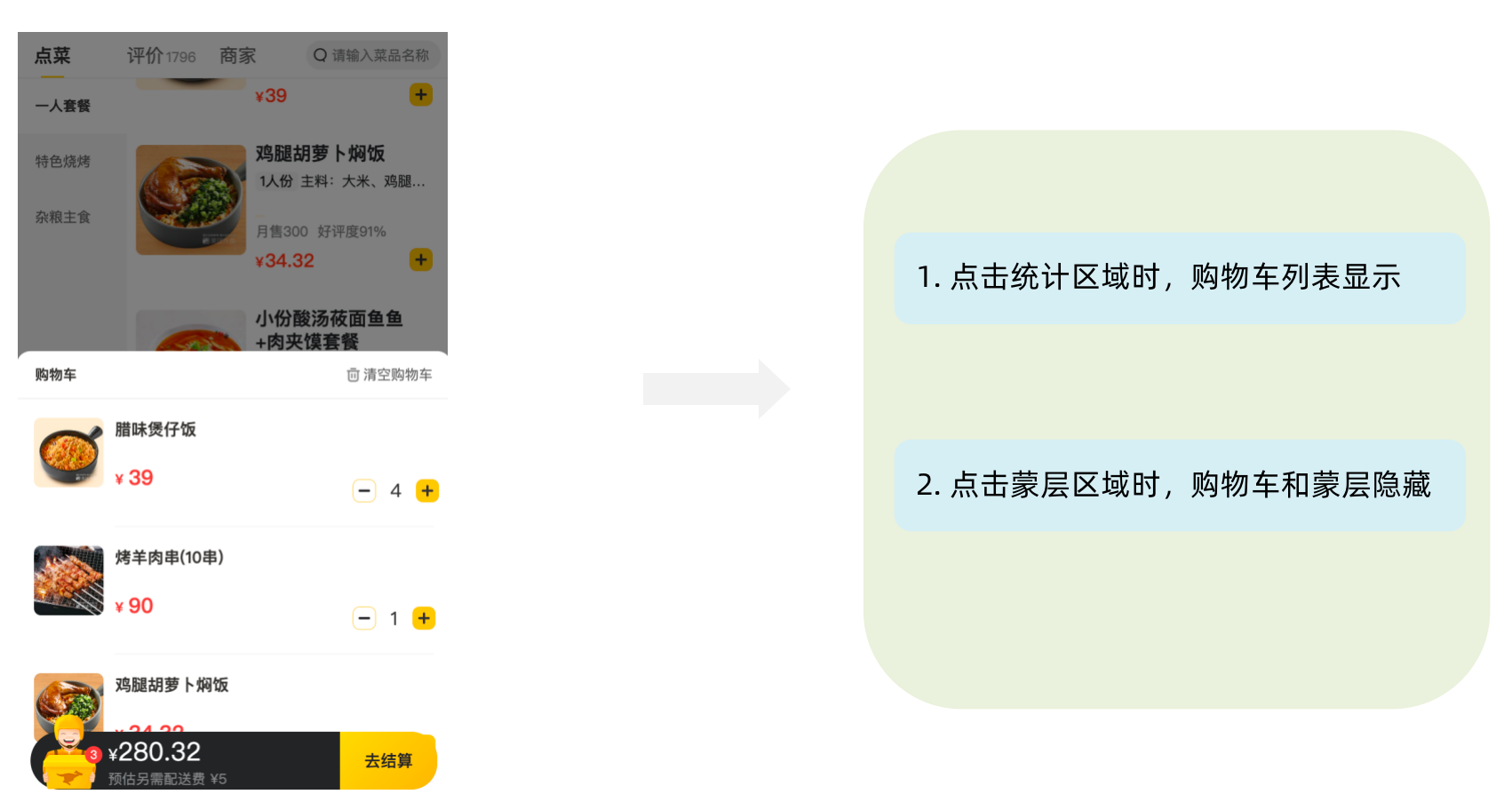
// 控制购物车打开关闭的状态
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(false)
const onShow = () => {
if (cartList.length > 0) {
setVisible(true)
}
}
{/* 遮罩层 添加visible类名可以显示出来 */}
<div
className={
classNames('cartOverlay', visible && 'visible')
}
onClick={() => setVisible(false)}
/>1-13 路由快速上手
1-13-1. 什么是前端路由
一个路径 path 对应一个组件 component 当我们在浏览器中访问一个 path 的时候,path 对应的组件会在页面中进行渲染 
const routes = [
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
},
{
path: '/article',
component: Article,
},
];1-13-2. 创建路由开发环境
# 使用CRA创建项目
npm create-react-app react-router-pro
# 安装最新的ReactRouter包
npm i react-router-dom
# 启动项目
npm run start1-13-3. 快速开始

import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path:'/login',
element: <div>登录</div>
},
{
path:'/article',
element: <div>文章</div>
}
])
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<RouterProvider router={router}/>
)1-13-4 抽象路由模块

1-13-5 路由导航
1-1. 什么是路由导航
路由系统中的多个路由之间需要进行路由跳转,并且在跳转的同时有可能需要传递参数进行通信 
1-2. 声明式导航
声明式导航是指通过在模版中通过
<Link/>组件描述出要跳转到哪里去,比如后台管理系统的左侧菜单通常使用这种方式进行
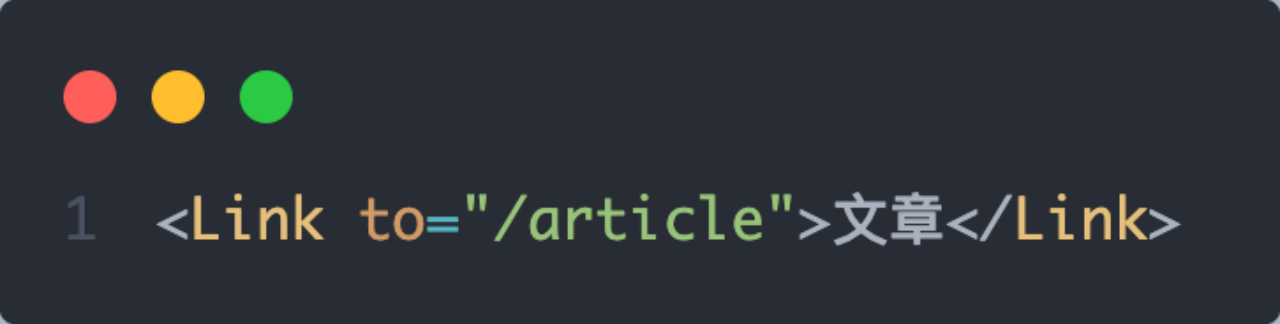
语法说明:通过给组件的to属性指定要跳转到路由path,组件会被渲染为浏览器支持的a链接,如果需要传参直接通过字符串拼接的方式拼接参数即可
1-3. 编程式导航
编程式导航是指通过 useNavigate 钩子得到导航方法,然后通过调用方法以命令式的形式进行路由跳转,比如想在登录请求完毕之后跳转就可以选择这种方式,更加灵活

语法说明:通过调用navigate方法传入地址path实现跳转
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
const Login = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
我是登录页
<button onClick={() => navigate('/article')}>跳转至文章</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Login;1-13-6 导航传参
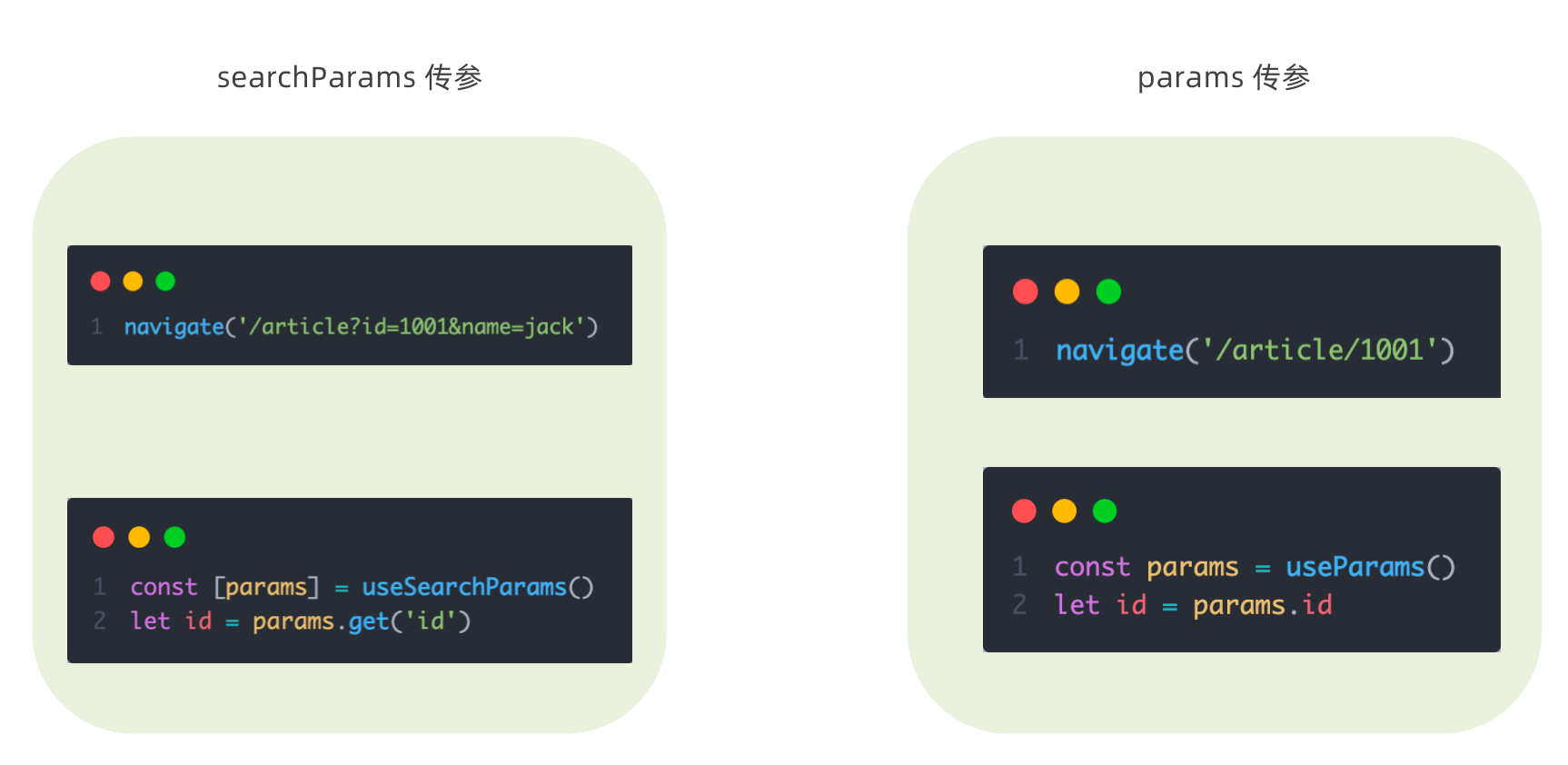
1-13-7 嵌套路由配置
7-1. 什么是嵌套路由
在一级路由中又内嵌了其他路由,这种关系就叫做嵌套路由,嵌套至一级路由内的路由又称作二级路由,例如: 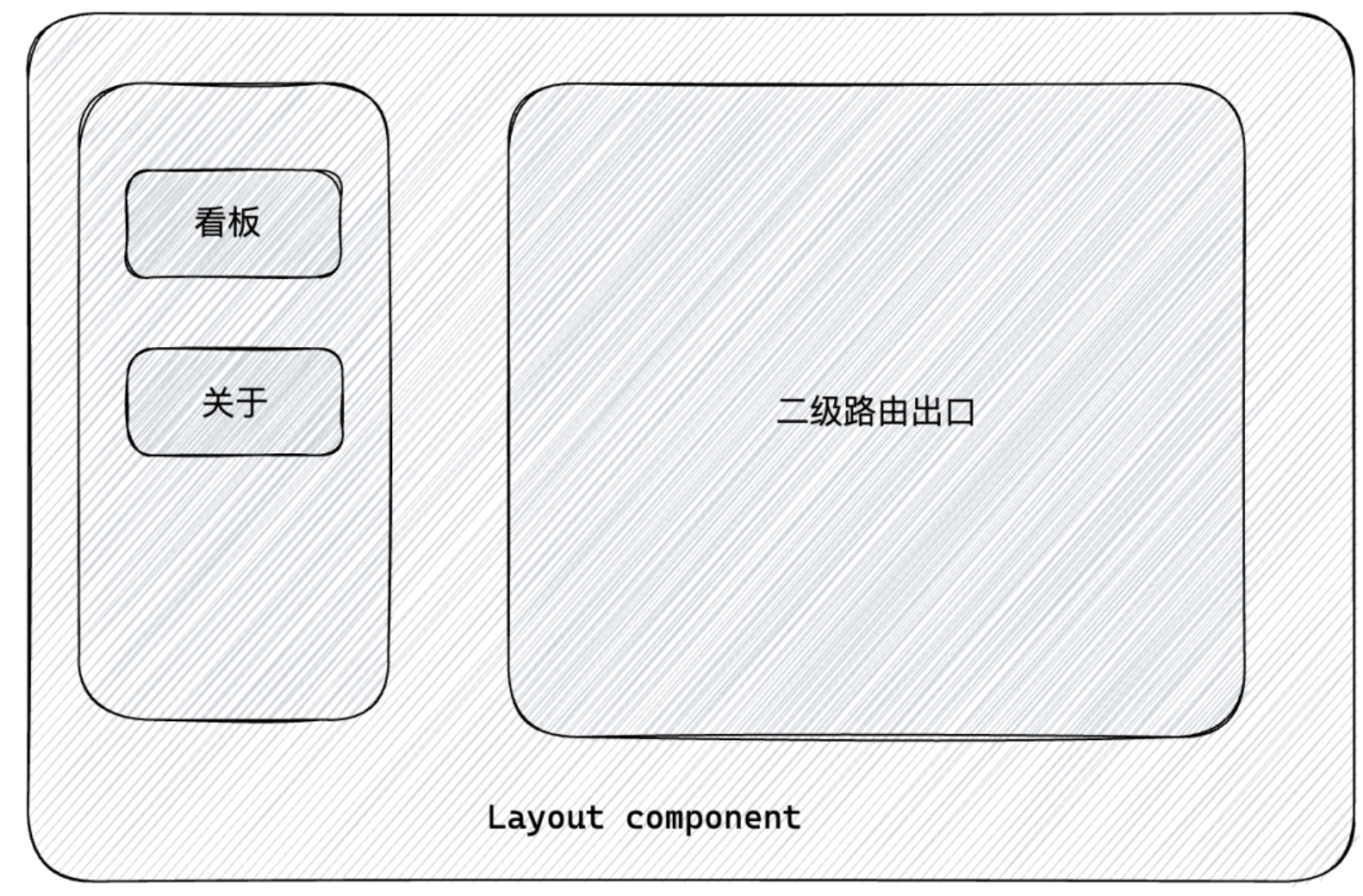
7-2. 嵌套路由配置
实现步骤
1. 使用 `children`属性配置路由嵌套关系 2. 使用 `<Outlet/>` 组件配置二级路由渲染位置

const routes = [
{
path: '/',
element: <Layout />,
children: [
{
path: 'board',
element: <Board />,
},
{
path: 'about',
element: <About />,
},
],
},
];const Layout = () => {
return (
<div>
<div>我是Layout</div>
<Link to="/board">面板</Link>
<Link to="/about">关于</Link>
{/* 二级路由出口 */}
<Outlet />
</div>
);
}7-3. 默认二级路由
当访问的是一级路由时,默认的二级路由组件可以得到渲染,只需要在二级路由的位置去掉path,设置index属性为true
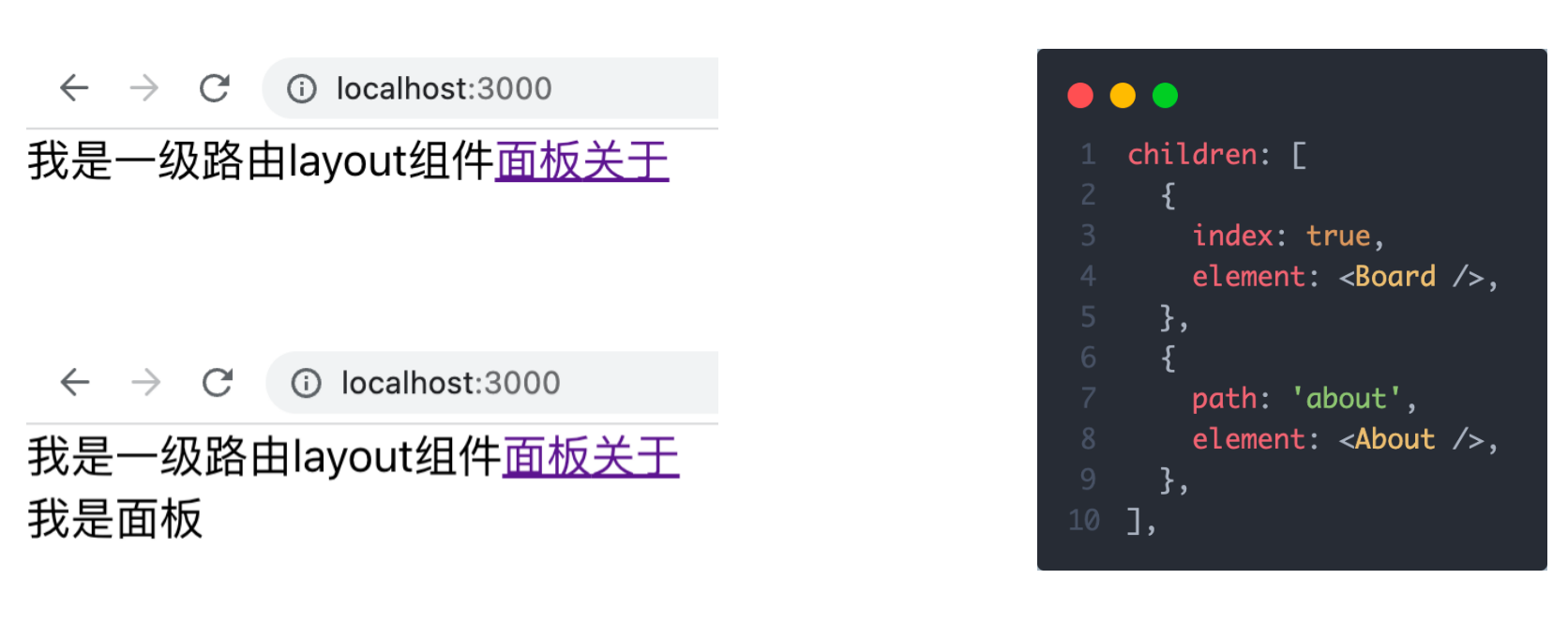
children: [
{
index: true,
element: <Board />,
},
{
path: 'about',
element: <About />,
},
],7-4. 404路由配置
场景:当浏览器输入url的路径在整个路由配置中都找不到对应的 path,为了用户体验,可以使用 404 兜底组件进行渲染
实现步骤:
- 准备一个NotFound组件
- 在路由表数组的末尾,以*号作为路由path配置路由

const NotFound = () => {
// 自定义模版
return <div>this is NotFound</div>
}
export default NotFound;{
path: '*',
element: <NotFound />,
}7-5. 俩种路由模式
各个主流框架的路由常用的路由模式有俩种,history模式和hash模式, ReactRouter分别由 createBrowerRouter 和 createHashRouter 函数负责创建
| 路由模式 | url表现 | 底层原理 | 是否需要后端支持 |
|---|---|---|---|
| history | url/login | history对象 + pushState事件 | 需要 |
| hash | url/#/login | 监听hashChange事件 | 不需要 |
1-14 记账本案例
1-14-1 环境搭建
使用CRA创建项目,并安装必要依赖,包括下列基础包
- Redux状态管理 - @reduxjs/toolkit 、 react-redux
- 路由 - react-router-dom
- 时间处理 - dayjs
- class类名处理 - classnames
- 移动端组件库 - antd-mobile
- 请求插件 - axios
1-14-2 配置别名路径
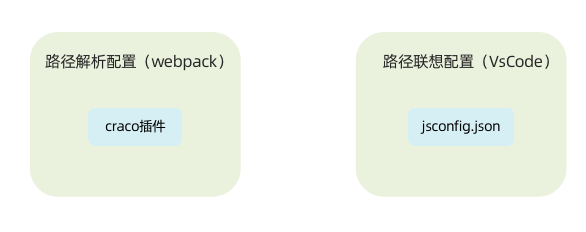
1-1 . 背景知识
- 路径解析配置(webpack),把 @/ 解析为 src/
- 路径联想配置(VsCode),VsCode 在输入 @/ 时,自动联想出来对应的 src/下的子级目录
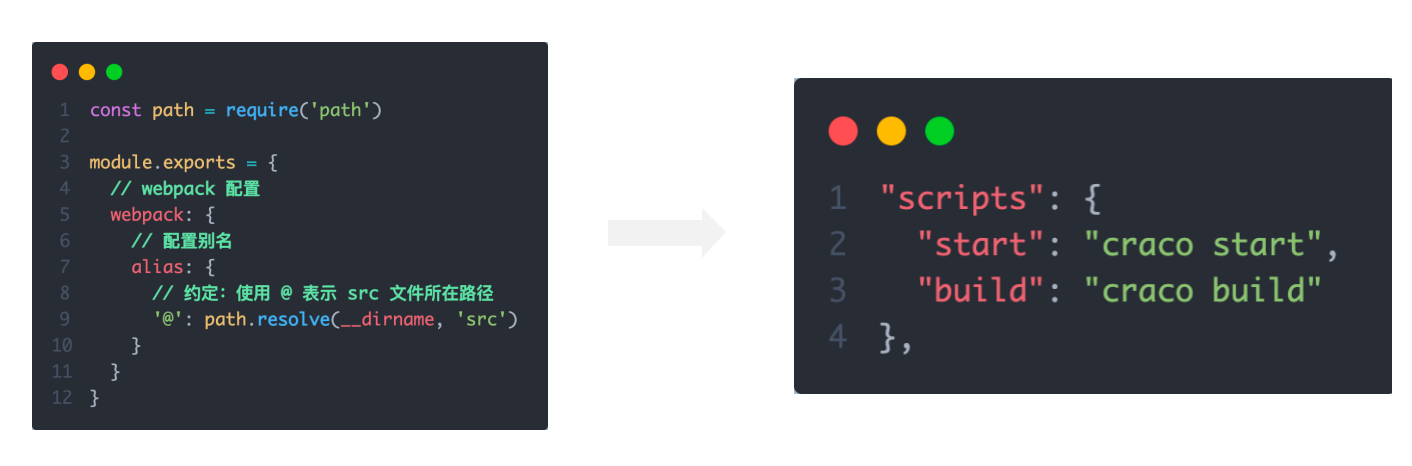
1-2. 路径解析配置
配置步骤:
- 安装craco npm i -D @craco/craco
- 项目根目录下创建配置文件 craco.config.js
- 配置文件中添加路径解析配置
- 包文件中配置启动和打包命令
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
// webpack 配置
webpack: {
// 配置别名
alias: {
// 约定: 使用 @ 表示 src 文件所在路径
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
},
},
};"scripts": {
"start": "craco start",
"build": "craco build"
},1-3. 联想路径配置
配置步骤:
- 根目录下新增配置文件 - jsconfig.json
- 添加路径提示配置
{
"compilerOptions":{
"baseUrl":"./",
"paths":{
"@/*":[
"src/*"
]
}
}
}1-14-3 数据Mock实现
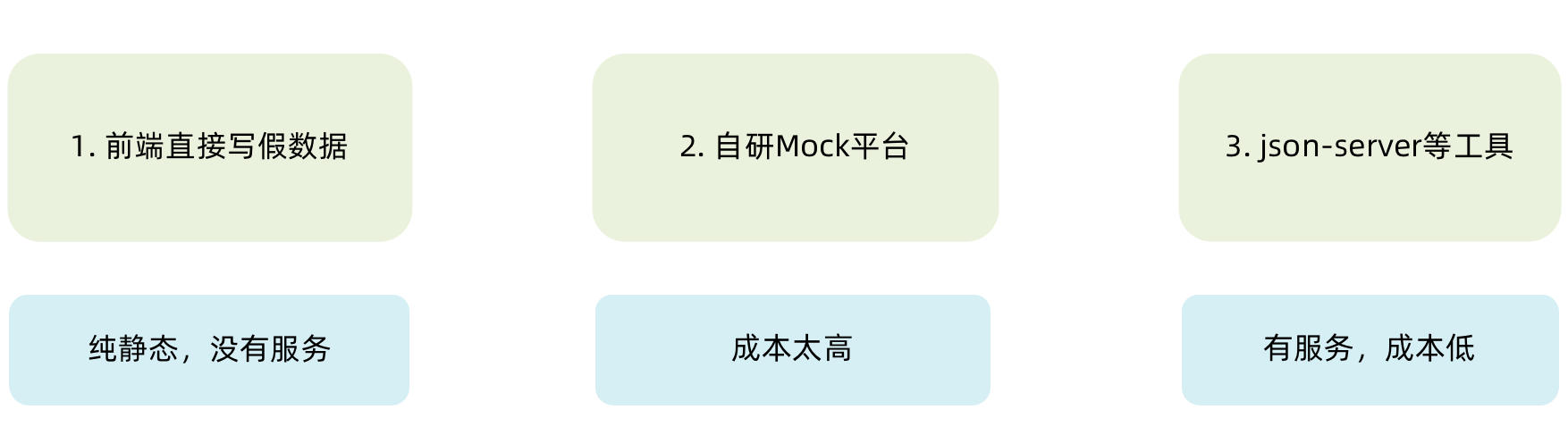
在前后端分类的开发模式下,前端可以在没有实际后端接口的支持下先进行接口数据的模拟,进行正常的业务功能开发
1-1. 常见的Mock方式
1-2. json-server实现Mock
实现步骤:
- 项目中安装json-server npm i -D json-server
- 准备一个json文件 (素材里获取)
- 添加启动命令
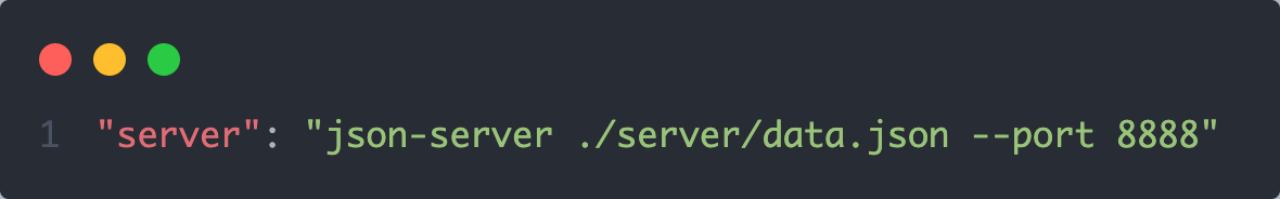
- 访问接口进行测试
"server": "json-server ./server/data.json --port 8888"1-14-5 整体路由设计
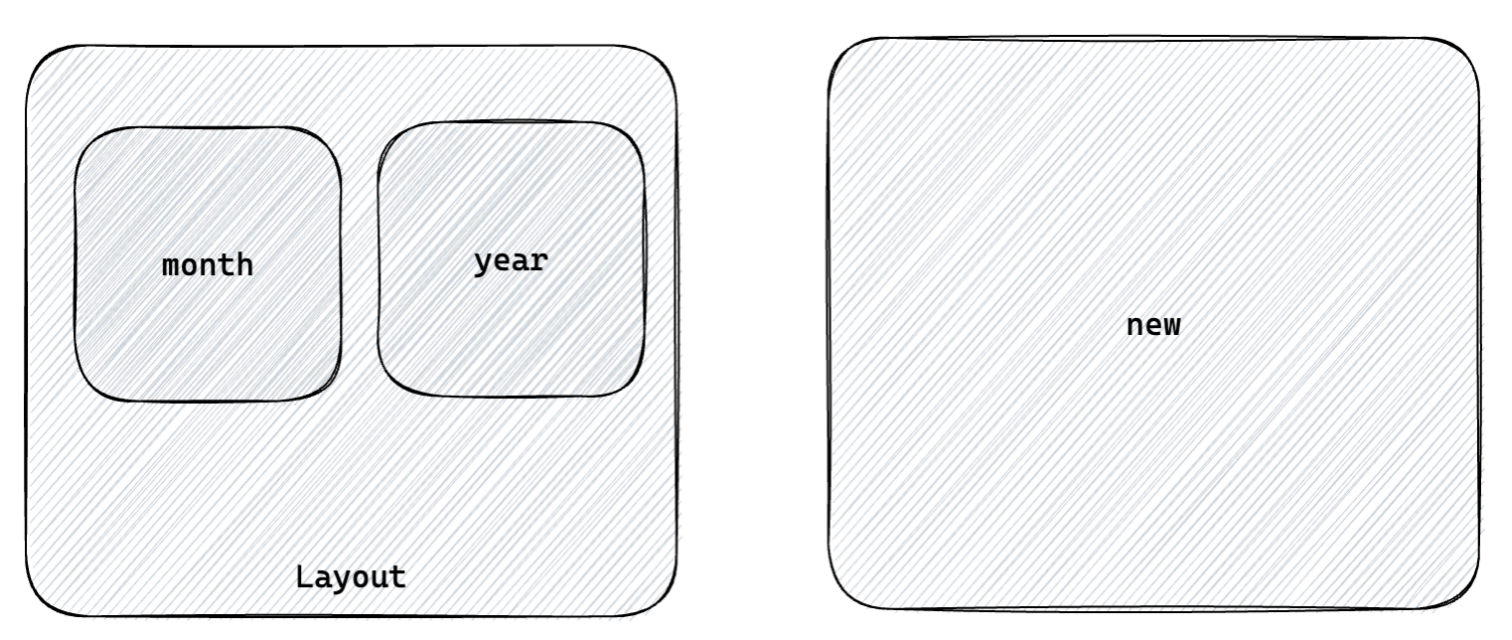
- 俩个一级路由 (Layout / new)2. 俩个二级路由 (Layout - mouth/year)
1-14-6 antD主题定制
6-1. 定制方案

6-2. 实现方式
- 全局定制

- 局部定制

6-3. 记账本主题色
:root:root {
--adm-color-primary: rgb(105, 174, 120);
}1-14-7 Redux管理账目列表
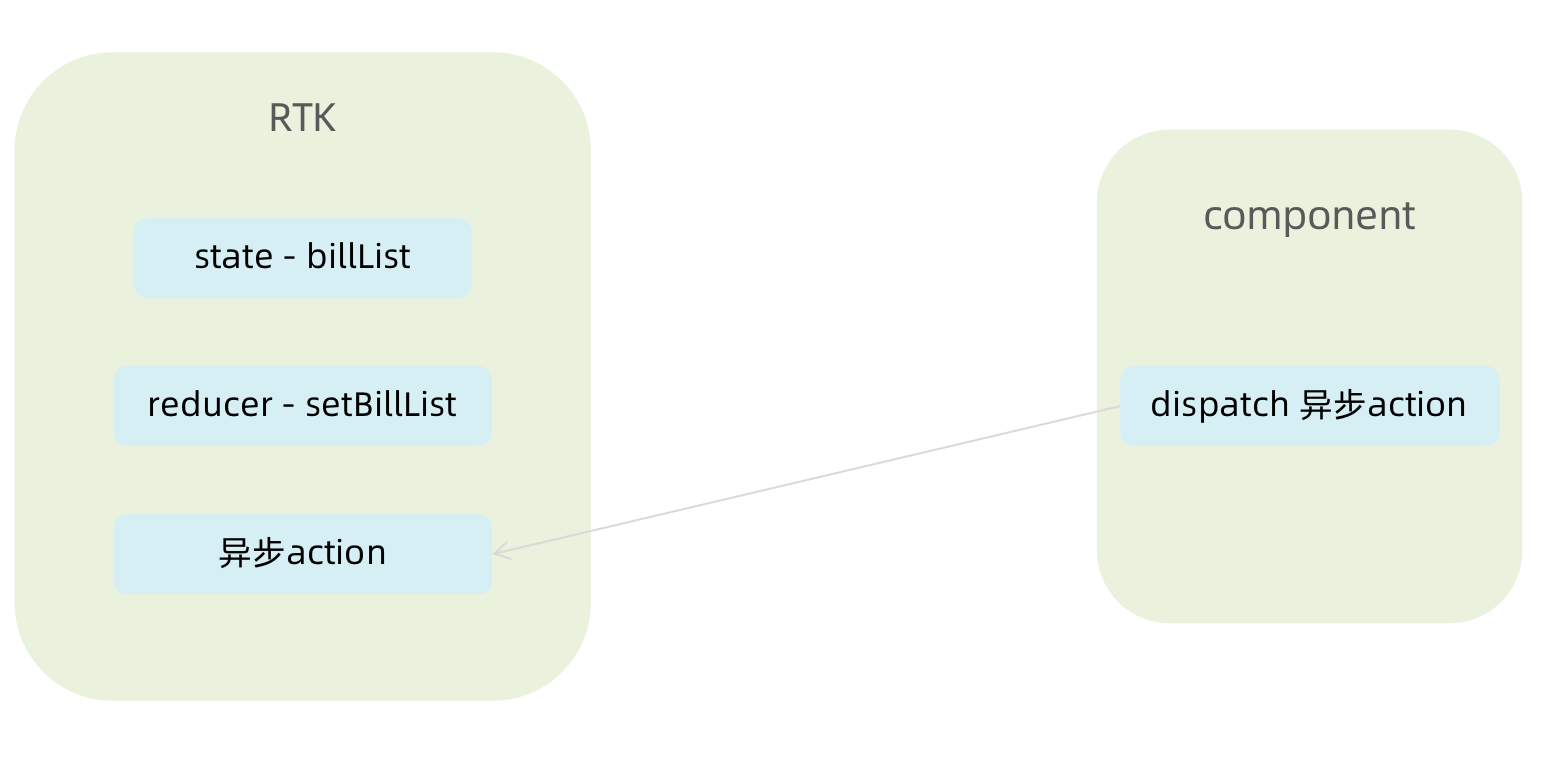
// 账单列表相关store
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import axios from 'axios'
const billStore = createSlice({
name: 'bill',
// 数据状态state
initialState: {
billList: []
},
reducers: {
// 同步修改方法
setBillList (state, action) {
state.billList = action.payload
}
}
})
// 解构actionCreater函数
const { setBillList } = billStore.actions
// 编写异步
const getBillList = () => {
return async (dispatch) => {
// 编写异步请求
const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:8888/ka')
// 触发同步reducer
dispatch(setBillList(res.data))
}
}
export { getBillList }
// 导出reducer
const reducer = billStore.reducer
export default reducer// 组合子模块 导出store实例
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import billReducer from './modules/billStore'
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
bill: billReducer
}
})
export default storeimport router from './router'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'))
root.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<RouterProvider router={router} />
</Provider>
)1-14-8 TabBar功能实现

8-1. 静态布局实现
配套静态模版和样式文件
import { TabBar } from "antd-mobile"
import { useEffect } from "react"
import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom"
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
import { getBillList } from "@/store/modules/billStore"
import './index.scss'
import {
BillOutline,
CalculatorOutline,
AddCircleOutline
} from 'antd-mobile-icons'
const tabs = [
{
key: '/month',
title: '月度账单',
icon: <BillOutline />,
},
{
key: '/new',
title: '记账',
icon: <AddCircleOutline />,
},
{
key: '/year',
title: '年度账单',
icon: <CalculatorOutline />,
},
]
const Layout = () => {
const dispatch = useDispatch()
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(getBillList())
}, [dispatch])
return (
<div className="layout">
<div className="container">
<Outlet />
</div>
<div className="footer">
<TabBar>
{tabs.map(item => (
<TabBar.Item key={item.key} icon={item.icon} title={item.title} />
))}
</TabBar>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default Layout.layout {
.container {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
bottom: 50px;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
}
}8- 2. 切换路由实现
监听change事件,在事件回调中调用路由跳转方法
// 切换菜单跳转路由
const navigate = useNavigate()
const swithRoute = (path) => {
console.log(path)
navigate(path)
}
return (
<div className="layout">
<div className="footer">
<TabBar onChange={swithRoute}>
{/* 省略... */}
</TabBar>
</div>
</div>
)1-14-9 月度账单-统计区域
9- 1. 准备静态结构
import { NavBar, DatePicker } from 'antd-mobile'
import './index.scss'
const Month = () => {
return (
<div className="monthlyBill">
<NavBar className="nav" backArrow={false}>
月度收支
</NavBar>
<div className="content">
<div className="header">
{/* 时间切换区域 */}
<div className="date">
<span className="text">
2023 | 3月账单
</span>
<span className='arrow expand'></span>
</div>
{/* 统计区域 */}
<div className='twoLineOverview'>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{100}</span>
<span className="type">支出</span>
</div>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{200}</span>
<span className="type">收入</span>
</div>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{200}</span>
<span className="type">结余</span>
</div>
</div>
{/* 时间选择器 */}
<DatePicker
className="kaDate"
title="记账日期"
precision="month"
visible={false}
max={new Date()}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div >
)
}
export default Month.monthlyBill {
--ka-text-color: #191d26;
height: 100%;
background: linear-gradient(180deg, #ffffff, #f5f5f5 100%);
background-size: 100% 240px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-color: rgba(245, 245, 245, 0.9);
color: var(--ka-text-color);
.nav {
--adm-font-size-10: 16px;
color: #121826;
background-color: transparent;
.adm-nav-bar-back-arrow {
font-size: 20px;
}
}
.content {
height: 573px;
padding: 0 10px;
overflow-y: scroll;
-ms-overflow-style: none; /* Internet Explorer 10+ */
scrollbar-width: none; /* Firefox */
&::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: none; /* Safari and Chrome */
}
> .header {
height: 135px;
padding: 20px 20px 0px 18.5px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
background-image: url(https://zqran.gitee.io/images/ka/month-bg.png);
background-size: 100% 100%;
.date {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 25px;
font-size: 16px;
.arrow {
display: inline-block;
width: 7px;
height: 7px;
margin-top: -3px;
margin-left: 9px;
border-top: 2px solid #121826;
border-left: 2px solid #121826;
transform: rotate(225deg);
transform-origin: center;
transition: all 0.3s;
}
.arrow.expand {
transform: translate(0, 2px) rotate(45deg);
}
}
}
}
.twoLineOverview {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 250px;
.item {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
.money {
height: 24px;
line-height: 24px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
font-size: 18px;
}
.type {
height: 14px;
line-height: 14px;
font-size: 12px;
}
}
}
}9- 2. 点击切换时间选择框
实现思路:
- 准备一个状态数据
- 点击切换状态
- 根据状态控制弹框打开关闭以及箭头样式
import { NavBar, DatePicker } from 'antd-mobile'
import './index.scss'
import { useState } from "react"
import classNames from "classnames"
const Month = () => {
// 控制时间选择器打开关闭
const [dateVisible, setDateVisible] = useState(false)
// 时间选择框确实事件
const dateConfirm = (date) => {
// 关闭弹框
setDateVisible(false)
}
return (
<div className="monthlyBill">
<NavBar className="nav" backArrow={false}>
月度收支
</NavBar>
<div className="content">
<div className="header">
{/* 时间切换区域 */}
<div className="date" onClick={() => setDateVisible(true)}>
{/* 省略.. */}
<span className={classNames('arrow', dateVisible && 'expand')}></span>
</div>
{/* 统计区域 */}
{/* 时间选择器 */}
<DatePicker
className="kaDate"
title="记账日期"
precision="month"
visible={dateVisible}
max={new Date()}
onConfirm={dateConfirm}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div >
)
}
export default Month9-3. 切换时间显示

实现思路:
- 以当前时间作为默认值
- 在时间切换时完成时间修改
import dayjs from "dayjs"
const [currentMonth, setCurrentMonth] = useState(() => {
return dayjs().format('YYYY-MM')
})
const dateConfirm = (date) => {
setDateVisible(false)
const month = dayjs(date).format('YYYY-MM')
setCurrentMonth(month)
}9-4. 统计功能实现
实现思路:
- 按月分组
- 根据获取到的时间作为key取当月的账单数组
- 根据当月的账单数组计算支出、收入、总计
// 按月分组
const billList = useSelector(state => state.bill.billList)
const monthGroup = useMemo(() => {
return _.groupBy(billList, item => dayjs(item.date).format('YYYY-MM'))
}, [billList])
// 根据获取到的时间作为key取当月的账单数组
const dateConfirm = (date) => {
const monthKey = dayjs(date).format('YYYY-MM')
setMonthList(monthGroup[monthKey])
}
// 计算统计
const overview = useMemo(() => {
const income = currentMonthList.filter(item => item.type === 'income')
.reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
const pay = currentMonthList.filter(item => item.type === 'pay')
.reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
return {
income,
pay,
total: income + pay
}
}, [currentMonthList])9-5. 完整代码
import { useSelector } from "react-redux"
import { NavBar, DatePicker } from 'antd-mobile'
import './index.scss'
import _ from 'lodash'
import dayjs from "dayjs"
import { useMemo, useState } from "react"
import { useEffect } from "react"
import classNames from "classnames"
const Month = () => {
// 按月分组
const billList = useSelector(state => state.bill.billList)
const monthGroup = useMemo(() => {
return _.groupBy(billList, item => dayjs(item.date).format('YYYY-MM'))
}, [billList])
// 控制时间选择器打开关闭
const [dateVisible, setDateVisible] = useState(false)
const [currentMonthList, setMonthList] = useState([])
const [currentMonth, setCurrentMonth] = useState(() => {
return dayjs().format('YYYY-MM')
})
const dateConfirm = (date) => {
setDateVisible(false)
const monthKey = dayjs(date).format('YYYY-MM')
setCurrentMonth(monthKey)
setMonthList(monthGroup[monthKey])
}
// 首次加载
useEffect(() => {
const list = monthGroup[dayjs().format('YYYY-MM')]
if(list){
setMonthList(list)
}
}, [monthGroup])
// 计算统计
const overview = useMemo(() => {
if (!currentMonthList) return { income: 0, pay: 0, total: 0 }
const income = currentMonthList.filter(item => item.type === 'income')
.reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
const pay = currentMonthList.filter(item => item.type === 'pay')
.reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
return {
income,
pay,
total: income + pay
}
}, [currentMonthList])
return (
<div className="monthlyBill">
<NavBar className="nav" backArrow={false}>
月度收支
</NavBar>
<div className="content">
<div className="header">
{/* 时间切换区域 */}
<div className="date" onClick={() => setDateVisible(true)}>
<span className="text">
{currentMonth} 账单
</span>
<span className={classNames('arrow', dateVisible && 'expand')}></span>
</div>
{/* 统计区域 */}
<div className='twoLineOverview'>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{overview.pay.toFixed(2)}</span>
<span className="type">支出</span>
</div>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{overview.income.toFixed(2)}</span>
<span className="type">收入</span>
</div>
<div className="item">
<span className="money">{(overview.total).toFixed(2)}</span>
<span className="type">结余</span>
</div>
</div>
{/* 时间选择器 */}
<DatePicker
className="kaDate"
title="记账日期"
precision="month"
visible={dateVisible}
max={new Date()}
onConfirm={dateConfirm}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div >
)
}
export default Month1-14-10 月度账单-单日统计列表实现
10-1. 准备组件和配套样式
import classNames from 'classnames'
import './index.scss'
const DailyBill = () => {
return (
<div className={classNames('dailyBill')}>
<div className="header">
<div className="dateIcon">
<span className="date">{'03月23日'}</span>
<span className={classNames('arrow')}></span>
</div>
<div className="oneLineOverview">
<div className="pay">
<span className="type">支出</span>
<span className="money">{100}</span>
</div>
<div className="income">
<span className="type">收入</span>
<span className="money">{200}</span>
</div>
<div className="balance">
<span className="money">{100}</span>
<span className="type">结余</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default DailyBill配套样式
.dailyBill {
margin-bottom: 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: #ffffff;
.header {
--ka-text-color: #888c98;
padding: 15px 15px 10px 15px;
.dateIcon {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
height: 21px;
margin-bottom: 9px;
.arrow {
display: inline-block;
width: 5px;
height: 5px;
margin-top: -3px;
margin-left: 9px;
border-top: 2px solid #888c98;
border-left: 2px solid #888c98;
transform: rotate(225deg);
transform-origin: center;
transition: all 0.3s;
}
.arrow.expand {
transform: translate(0, 2px) rotate(45deg);
}
.date {
font-size: 14px;
}
}
}
.oneLineOverview {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
.pay {
flex: 1;
.type {
font-size: 10px;
margin-right: 2.5px;
color: #e56a77;
}
.money {
color: var(--ka-text-color);
font-size: 13px;
}
}
.income {
flex: 1;
.type {
font-size: 10px;
margin-right: 2.5px;
color: #4f827c;
}
.money {
color: var(--ka-text-color);
font-size: 13px;
}
}
.balance {
flex: 1;
margin-bottom: 5px;
text-align: right;
.money {
line-height: 17px;
margin-right: 6px;
font-size: 17px;
}
.type {
font-size: 10px;
color: var(--ka-text-color);
}
}
}
.billList {
padding: 15px 10px 15px 15px;
border-top: 1px solid #ececec;
.bill {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
height: 43px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
&:last-child {
margin-bottom: 0;
}
.icon {
margin-right: 10px;
font-size: 25px;
}
.detail {
flex: 1;
padding: 4px 0;
.billType {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
height: 17px;
line-height: 17px;
font-size: 14px;
padding-left: 4px;
}
}
.money {
font-size: 17px;
&.pay {
color: #ff917b;
}
&.income {
color: #4f827c;
}
}
}
}
}
.dailyBill.expand {
.header {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ececec;
}
.billList {
display: block;
}
}10-2. 按日分组账单数据

// 把当前月按日分组账单数据
const dayGroup = useMemo(() => {
const group = _.groupBy(currentMonthList, (item) => dayjs(item.date).format('YYYY-MM-DD'))
return {
dayKeys: Object.keys(group),
group
}
}, [currentMonthList])
console.log(dayGroup)10-3. 遍历日账单组件并传入参数
{/* 日账单 */}
{dayGroup.dayKeys.map(dayKey => (
<DailyBill key={dayKey} date={dayKey} billList={dayGroup.group[dayKey]} />
))}10-4. 接收数据计算统计渲染页面
const DailyBill = ({ date, billList }) => {
const dayResult = useMemo(() => {
// 支出 / 收入 / 结余
const pay = billList.filter(item => item.type === 'pay').reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
const income = billList.filter(item => item.type === 'income').reduce((a, c) => a + c.money, 0)
return {
pay,
income,
total: pay + income
}
}, [billList])
return (
<div className={classNames('dailyBill')}>
<div className="header">
<div className="dateIcon">
<span className="date">{date}</span>
</div>
<div className="oneLineOverview">
<div className="pay">
<span className="type">支出</span>
<span className="money">{dayResult.pay.toFixed(2)}</span>
</div>
<div className="income">
<span className="type">收入</span>
<span className="money">{dayResult.income.toFixed(2)}</span>
</div>
<div className="balance">
<span className="money">{dayResult.total.toFixed(2)}</span>
<span className="type">结余</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default DailyBill1-14-11 月度账单-单日账单列表展示
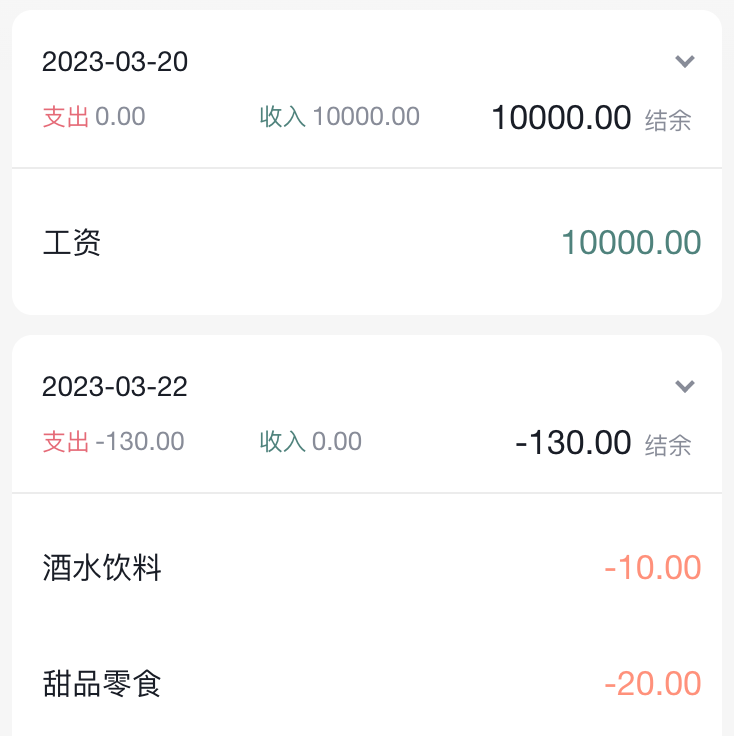
11-1. 渲染基础列表
{/* 单日列表 */}
<div className="billList">
{billList.map(item => {
return (
<div className="bill" key={item.id}>
<div className="detail">
<div className="billType">{item.useFor}</div>
</div>
<div className={classNames('money', item.type)}>
{item.money.toFixed(2)}
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>11-2. 适配Type
2-1-准备静态数据
export const billListData = {
pay: [
{
type: 'foods',
name: '餐饮',
list: [
{ type: 'food', name: '餐费' },
{ type: 'drinks', name: '酒水饮料' },
{ type: 'dessert', name: '甜品零食' },
],
},
{
type: 'taxi',
name: '出行交通',
list: [
{ type: 'taxi', name: '打车租车' },
{ type: 'longdistance', name: '旅行票费' },
],
},
{
type: 'recreation',
name: '休闲娱乐',
list: [
{ type: 'bodybuilding', name: '运动健身' },
{ type: 'game', name: '休闲玩乐' },
{ type: 'audio', name: '媒体影音' },
{ type: 'travel', name: '旅游度假' },
],
},
{
type: 'daily',
name: '日常支出',
list: [
{ type: 'clothes', name: '衣服裤子' },
{ type: 'bag', name: '鞋帽包包' },
{ type: 'book', name: '知识学习' },
{ type: 'promote', name: '能力提升' },
{ type: 'home', name: '家装布置' },
],
},
{
type: 'other',
name: '其他支出',
list: [{ type: 'community', name: '社区缴费' }],
},
],
income: [
{
type: 'professional',
name: '其他支出',
list: [
{ type: 'salary', name: '工资' },
{ type: 'overtimepay', name: '加班' },
{ type: 'bonus', name: '奖金' },
],
},
{
type: 'other',
name: '其他收入',
list: [
{ type: 'financial', name: '理财收入' },
{ type: 'cashgift', name: '礼金收入' },
],
},
],
}
export const billTypeToName = Object.keys(billListData).reduce((prev, key) => {
billListData[key].forEach(bill => {
bill.list.forEach(item => {
prev[item.type] = item.name
})
})
return prev
}, {})2-2-适配type
<div className="billType">{billTypeToName[item.useFor]}</div>1-14-12 月度账单-切换打开关闭

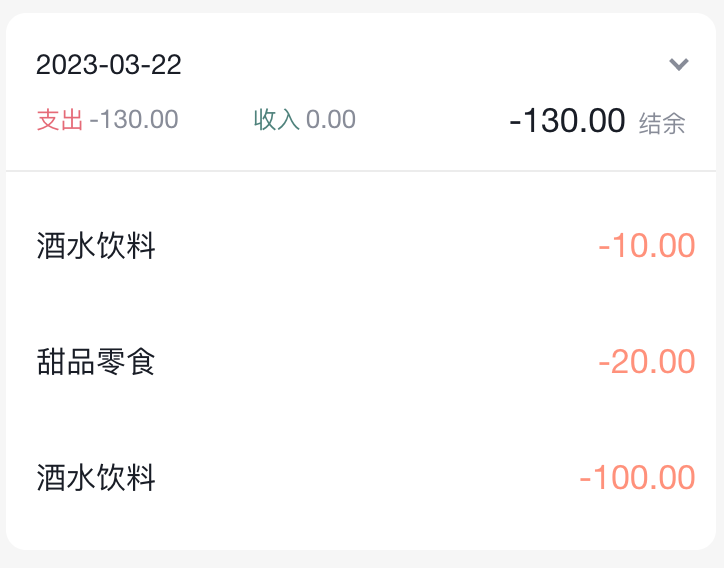
// 声明状态
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(false)
// 控制箭头
<span
className={classNames('arrow', !visible && 'expand')}
onClick={() => setVisible(!visible)}></span>
// 控制列表显示
<div className="billList" style={{ display: !visible && 'none' }}></div>1-14-13 月度账单-Icon组件封装

13-1. 准备静态结构
const Icon = () => {
return (
<img
src={`https://yjy-teach-oss.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/reactbase/ka/food.svg`}
alt="icon"
style={{
width: 20,
height: 20,
}}
/>
)
}
export default Icon13-2. 设计参数
const BASE_URL = 'https://yjy-teach-oss.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/reactbase/ka/'
const Icon = ({ type }) => {
return (
<img
src={`${BASE_URL + type}.svg`}
alt="icon"
style={{
width: 20,
height: 20,
}}
/>
)
}
export default Icon12-3. 使用组件
<div className="billList" style={{ display: visible ? 'block' : 'none' }}>
{billList.map(item => {
return (
<div className="bill" key={item.id}>
<Icon type={item.useFor} />
</div>
)
})}
</div>1-14-14 记账功能
14-1 记账 - 结构渲染
import { Button, DatePicker, Input, NavBar } from 'antd-mobile'
import Icon from '@/components/Icon'
import './index.scss'
import classNames from 'classnames'
import { billListData } from '@/contants'
import { useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom'
const New = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate()
return (
<div className="keepAccounts">
<NavBar className="nav" onBack={() => navigate(-1)}>
记一笔
</NavBar>
<div className="header">
<div className="kaType">
<Button
shape="rounded"
className={classNames('selected')}
>
支出
</Button>
<Button
className={classNames('')}
shape="rounded"
>
收入
</Button>
</div>
<div className="kaFormWrapper">
<div className="kaForm">
<div className="date">
<Icon type="calendar" className="icon" />
<span className="text">{'今天'}</span>
<DatePicker
className="kaDate"
title="记账日期"
max={new Date()}
/>
</div>
<div className="kaInput">
<Input
className="input"
placeholder="0.00"
type="number"
/>
<span className="iconYuan">¥</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="kaTypeList">
{billListData['pay'].map(item => {
return (
<div className="kaType" key={item.type}>
<div className="title">{item.name}</div>
<div className="list">
{item.list.map(item => {
return (
<div
className={classNames(
'item',
''
)}
key={item.type}
>
<div className="icon">
<Icon type={item.type} />
</div>
<div className="text">{item.name}</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
<div className="btns">
<Button className="btn save">
保 存
</Button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default New配套样式
.keepAccounts {
--ka-bg-color: #daf2e1;
--ka-color: #69ae78;
--ka-border-color: #191d26;
height: 100%;
background-color: var(--ka-bg-color);
.nav {
--adm-font-size-10: 16px;
color: #121826;
background-color: transparent;
&::after {
height: 0;
}
.adm-nav-bar-back-arrow {
font-size: 20px;
}
}
.header {
height: 132px;
.kaType {
padding: 9px 0;
text-align: center;
.adm-button {
--adm-font-size-9: 13px;
&:first-child {
margin-right: 10px;
}
}
.selected {
color: #fff;
--background-color: var(--ka-border-color);
}
}
.kaFormWrapper {
padding: 10px 22.5px 20px;
.kaForm {
display: flex;
padding: 11px 15px 11px 12px;
border: 0.5px solid var(--ka-border-color);
border-radius: 9px;
background-color: #fff;
.date {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
height: 28px;
padding: 5.5px 5px;
border-radius: 4px;
// color: #4f825e;
color: var(--ka-color);
background-color: var(--ka-bg-color);
.icon {
margin-right: 6px;
font-size: 17px;
}
.text {
font-size: 16px;
}
}
.kaInput {
flex: 1;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
.input {
flex: 1;
margin-right: 10px;
--text-align: right;
--font-size: 24px;
--color: var(--ka-color);
--placeholder-color: #d1d1d1;
}
.iconYuan {
font-size: 24px;
}
}
}
}
}
.container {
}
.kaTypeList {
height: 490px;
padding: 20px 11px;
padding-bottom: 70px;
overflow-y: scroll;
background: #ffffff;
border-radius: 20px 20px 0 0;
-ms-overflow-style: none; /* Internet Explorer 10+ */
scrollbar-width: none; /* Firefox */
&::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: none; /* Safari and Chrome */
}
.kaType {
margin-bottom: 25px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #333;
.title {
padding-left: 5px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
font-size: 13px;
color: #808080;
}
.list {
display: flex;
.item {
width: 65px;
height: 65px;
padding: 9px 0;
margin-right: 7px;
text-align: center;
border: 0.5px solid #fff;
&:last-child {
margin-right: 0;
}
.icon {
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
font-size: 25px;
}
}
.item.selected {
border: 0.5px solid var(--ka-border-color);
border-radius: 5px;
background: var(--ka-bg-color);
}
}
}
}
.btns {
position: fixed;
bottom: 15px;
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
.btn {
width: 200px;
--border-width: 0;
--background-color: #fafafa;
--text-color: #616161;
&:first-child {
margin-right: 15px;
}
}
.btn.save {
--background-color: var(--ka-bg-color);
--text-color: var(--ka-color);
}
}
}14-2 记账 - 支出和收入切换
const new = ()=>{
// 1. 区分账单状态
const [billType, setBillType] = useState('income')
return (
<div className="keepAccounts">
<div className="kaType">
{/* 2. 点击切换状态 */}
<Button
shape="rounded"
className={classNames(billType==='pay'?'selected':'')}
onClick={() => setBillType('pay')}
>
支出
</Button>
<Button
className={classNames(billType==='income'?'selected':'')}
onClick={() => setBillType('income')}
shape="rounded"
>
收入
</Button>
</div>
{/* 2. 适配数据 */}
<div className="kaTypeList">
{billListData[billType].map(item => {
})}
</div>
</div>
)
}14-3 记账 - 新增一笔
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
const New = () => {
// 收集金额
const [money, setMoney] = useState(0)
const moneyChange = (value) => {
setMoney(value)
}
// 收集账单类型
const [useFor, setUseFor] = useState('')
const dispatch = useDispatch()
// 保存账单
const saveBill = () => {
// 收集表单数据
const data = {
type: billType,
money: billType === 'pay' ? -money : +money,
date: new Date(),
useFor: useFor
}
console.log(data)
dispatch(addBillList(data))
}
return (
<div className="keepAccounts">
<NavBar className="nav" onBack={() => navigate(-1)}>
记一笔
</NavBar>
<div className="header">
<div className="kaType">
<Button
shape="rounded"
className={classNames(billType === 'pay' ? 'selected' : '')}
onClick={() => setBillType('pay')}
>
支出
</Button>
<Button
className={classNames(billType === 'income' ? 'selected' : '')}
shape="rounded"
onClick={() => setBillType('income')}
>
收入
</Button>
</div>
<div className="kaFormWrapper">
<div className="kaForm">
<div className="date">
<Icon type="calendar" className="icon" />
<span className="text">{'今天'}</span>
<DatePicker
className="kaDate"
title="记账日期"
max={new Date()}
/>
</div>
<div className="kaInput">
<Input
className="input"
placeholder="0.00"
type="number"
value={money}
onChange={moneyChange}
/>
<span className="iconYuan">¥</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="kaTypeList">
{/* 数据区域 */}
{billListData[billType].map(item => {
return (
<div className="kaType" key={item.type}>
<div className="title">{item.name}</div>
<div className="list">
{item.list.map(item => {
return (
<div
className={classNames(
'item',
''
)}
key={item.type}
onClick={() => setUseFor(item.type)}
>
<div className="icon">
<Icon type={item.type} />
</div>
<div className="text">{item.name}</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
)
})}
</div>
<div className="btns">
<Button className="btn save" onClick={saveBill}>
保 存
</Button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default New1-15 文章管理系统案例
1-15-1 项目搭建
1-1 基于CRA创建项目
CRA是一个底层基于webpack快速创建React项目的脚手架工具
# 使用npx创建项目
npx create-react-app react-jike
# 进入到项
cd react-jike
# 启动项目
npm start
1-2 调整项目目录结构
-src
-apis 项目接口函数
-assets 项目资源文件,比如,图片等
-components 通用组件
-pages 页面组件
-store 集中状态管理
-utils 工具,比如,token、axios 的封装等
-App.js 根组件
-index.css 全局样式
-index.js 项目入口src/index.js
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import './index.scss'
import './App.js'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App/>
</React.StrictMode>
)src/App.js
const App = () => {
return <div>this is app</div>
}
export default App1-3 使用scss预处理器
SASS是一种预编译的 CSS,支持一些比较高级的语法,可以提高编写样式的效率,CRA接入scss非常简单只需要我们装一个sass工具
实现步骤
- 安装解析 sass 的包:
npm i sass -D - 创建全局样式文件:
index.scss
body {
margin: 0;
div {
color: blue;
}
}1-4 组件库antd使用
我们的项目是一个传统的PC管理后台,有现成的组件库可以使用,帮助我们提升开发效率,其中使用最广的就是antD
Ant Design of React - Ant Design实现步骤
- 安装 antd 组件库:
npm i antd - 导入 Button 组件
- 在 Login 页面渲染 Button 组件进行测试
测试Buttonpages/Login/index.jsx
import { Button } from 'antd'
const Login = () => {
return <div>this is login<Button type='primary'>test</Button></div>
}
export default Login
1-5 配置基础路由
单页应用需要对应的路由支持,我们使用
react-router-dom最新版本
实现步骤
- 安装路由包
npm i react-router-dom - 准备
Layout和Login俩个基础组件 - 配置路由
代码实现pages/Layout/index.js
const Layout = () => {
return <div>this is layout</div>
}
export default Layoutpages/Login/index.js
const Login = () => {
return <div>this is login</div>
}
export default Loginrouter/index.js
import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import Login from '../pages/Login'
import Layout from '../pages/Layout'
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: <Layout />,
},
{
path: '/login',
element: <Login />,
},
])
export default routerindex.js
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import './index.scss'
import router from './router'
import { RouterProvider } from 'react-router-dom'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<RouterProvider router={router} />
)1-6 配置别名路径
项目背景:在业务开发过程中文件夹的嵌套层级可能会比较深,通过传统的路径选择会比较麻烦也容易出错,设置路径别名可以简化这个过程
6-1 路径编译配置
- 安装
craco工具包 - 增加
craco.config.js配置文件 - 修改
scripts 命令 - 测试是否生效
npm i @craco/craco -Dconst path = require('path')
module.exports = {
// webpack 配置
webpack: {
// 配置别名
alias: {
// 约定:使用 @ 表示 src 文件所在路径
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
}
}
}"scripts": {
"start": "craco start",
"build": "craco build",
"test": "craco test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
}import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import Login from '@/pages/Login'
import Layout from '@/pages/Layout'
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: <Layout />,
},
{
path: '/login',
element: <Login />,
},
])
export default router6-2 VsCode提示配置
实现步骤
- 在项目根目录创建
jsconfig.json配置文件 - 在配置文件中添加以下配置
代码实现
{
"compilerOptions": {
"baseUrl": "./",
"paths": {
"@/*": ["src/*"]
}
}
}注意
说明:VSCode会自动读取jsconfig.json 中的配置,让vscode知道@就是src目录
1-15-2 登录模块
2-1 基本结构搭建
实现步骤
- 在
Login/index.js中创建登录页面基本结构 - 在 Login 目录中创建 index.scss 文件,指定组件样式
- 将
logo.png和login.png拷贝到 assets 目录中
代码实现pages/Login/index.js
import './index.scss'
import { Card, Form, Input, Button } from 'antd'
import logo from '@/assets/logo.png'
const Login = () => {
return (
<div className="login">
<Card className="login-container">
<img className="login-logo" src={logo} alt="" />
{/* 登录表单 */}
<Form>
<Form.Item>
<Input size="large" placeholder="请输入手机号" />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item>
<Input size="large" placeholder="请输入验证码" />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item>
<Button type="primary" htmlType="submit" size="large" block>
登录
</Button>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
</Card>
</div>
)
}
export default Loginpages/Login/index.scss
.login {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
background: center/cover url('~@/assets/login.png');
.login-logo {
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
display: block;
margin: 0 auto 20px;
}
.login-container {
width: 440px;
height: 360px;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
box-shadow: 0 0 50px rgb(0 0 0 / 10%);
}
.login-checkbox-label {
color: #1890ff;
}
}2-2 表单校验实现
 实现步骤
实现步骤
- 为 Form 组件添加
validateTrigger属性,指定校验触发时机的集合 - 为 Form.Item 组件添加 name 属性
- 为 Form.Item 组件添加
rules属性,用来添加表单校验规则对象
代码实现page/Login/index.js
const Login = () => {
return (
<Form validateTrigger={['onBlur']}>
<Form.Item
name="mobile"
rules={[
{ required: true, message: '请输入手机号' },
{
pattern: /^1[3-9]\d{9}$/,
message: '手机号码格式不对'
}
]}
>
<Input size="large" placeholder="请输入手机号" />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item
name="code"
rules={[
{ required: true, message: '请输入验证码' },
]}
>
<Input size="large" placeholder="请输入验证码" maxLength={6} />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item>
<Button type="primary" htmlType="submit" size="large" block>
登录
</Button>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
)
}2-3 获取登录表单数据
实现步骤
- 为 Form 组件添加
onFinish属性,该事件会在点击登录按钮时触发 - 创建 onFinish 函数,通过函数参数 values 拿到表单值
- Form 组件添加
initialValues属性,来初始化表单值
代码实现pages/Login/index.js
// 点击登录按钮时触发 参数values即是表单输入数据
const onFinish = formValue => {
console.log(formValue)
}
<Form
onFinish={ onFinish }
>...</Form>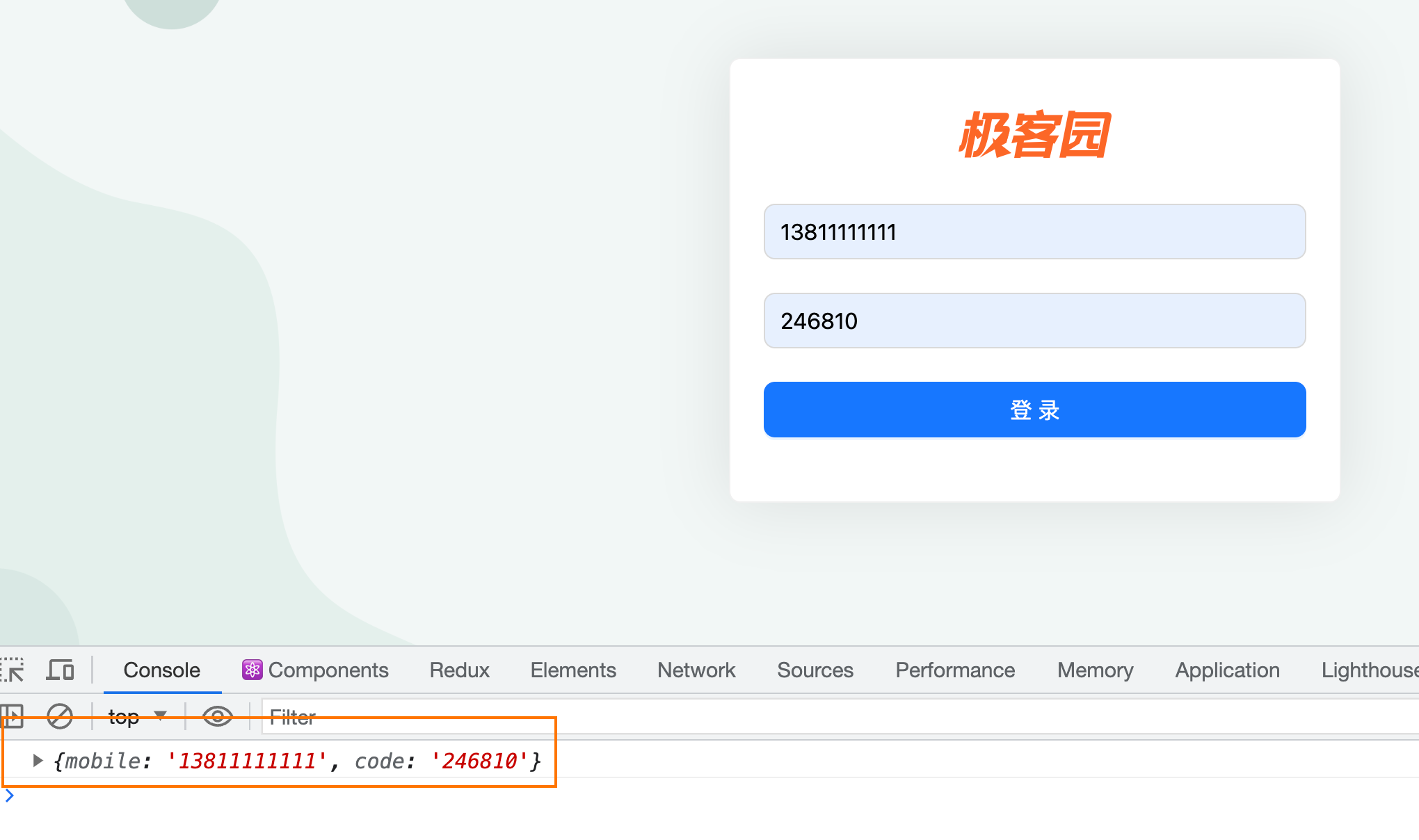
2-4 封装request工具模块
业务背景: 前端需要和后端拉取接口数据,axios是使用最广的工具插件,针对于项目中的使用,我们需要做一些简单的封装
实现步骤
- 安装 axios 到项目
- 创建 utils/request.js 文件
- 创建 axios 实例,配置
baseURL,请求拦截器,响应拦截器 - 在 utils/index.js 中,统一导出request
npm i axiosimport axios from 'axios'
const http = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0',
timeout: 5000
})
// 添加请求拦截器
http.interceptors.request.use((config)=> {
return config
}, (error)=> {
return Promise.reject(error)
})
// 添加响应拦截器
http.interceptors.response.use((response)=> {
// 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response.data
}, (error)=> {
// 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error)
})
export { http }import { request } from './request'
export { request }2-5 使用Redux管理token
5-1 安装Redux相关工具包
npm i react-redux @reduxjs/toolkit5-2 配置Redux
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import { http } from '@/utils'
const userStore = createSlice({
name: 'user',
// 数据状态
initialState: {
token:''
},
// 同步修改方法
reducers: {
setUserInfo (state, action) {
state.userInfo = action.payload
}
}
})
// 解构出actionCreater
const { setUserInfo } = userStore.actions
// 获取reducer函数
const userReducer = userStore.reducer
// 异步方法封装
const fetchLogin = (loginForm) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
const res = await http.post('/authorizations', loginForm)
dispatch(setUserInfo(res.data.token))
}
}
export { fetchLogin }
export default userReducerimport { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import userReducer from './modules/user'
export default configureStore({
reducer: {
// 注册子模块
user: userReducer
}
})2-6 实现登录逻辑
业务逻辑:
- 跳转到首页
- 提示用户登录成功
import { message } from 'antd'
import useStore from '@/store'
import { fetchLogin } from '@/store/modules/user'
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux'
const Login = () => {
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const navigate = useNavigate()
const onFinish = async formValue => {
await dispatch(fetchLogin(formValue))
navigate('/')
message.success('登录成功')
}
return (
<div className="login">
<!-- 省略... -->
</div>
)
}
export default Login2-7 token持久化
业务背景: Token数据具有一定的时效时间,通常在几个小时,有效时间内无需重新获取,而基于Redux的存储方式又是基于内存的,刷新就会丢失,为了保持持久化,我们需要单独做处理
7-1 封装存取方法
// 封装存取方法
const TOKENKEY = 'token_key'
function setToken (token) {
return localStorage.setItem(TOKENKEY, token)
}
function getToken () {
return localStorage.getItem(TOKENKEY)
}
function clearToken () {
return localStorage.removeItem(TOKENKEY)
}
export {
setToken,
getToken,
clearToken
}7-2 实现持久化逻辑
import { getToken, setToken } from '@/utils'
const userStore = createSlice({
name: 'user',
// 数据
initialState: {
token: getToken() || ''
},
// 同步修改方法
reducers: {
setUserInfo (state, action) {
state.token = action.payload
// 存入本地
setToken(state.token)
}
}
})刷新浏览器,通过Redux调试工具查看token数据 
2-8 请求拦截器注入token
业务背景: Token作为用户的数据标识,在接口层面起到了接口权限控制的作用,也就是说后端有很多接口都需要通过查看当前请求头信息中是否含有token数据,来决定是否正常返回数据
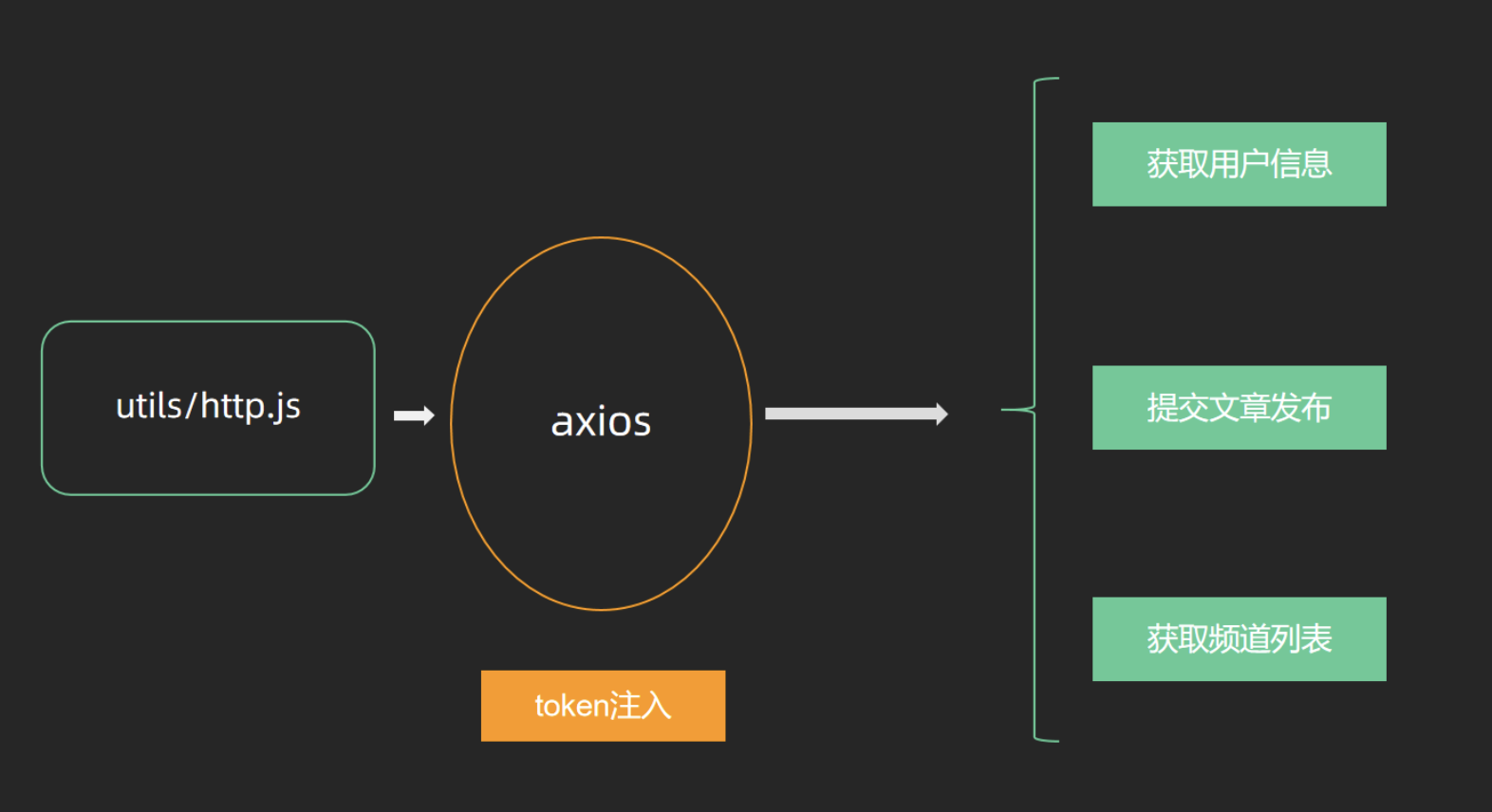
拼接方式:config.headers.Authorization =
Bearer ${token}}
utils/request.js
// 添加请求拦截器
request.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// if not login add token
const token = getToken()
if (token) {
config.headers.Authorization = `Bearer ${token}`
}
return config
})2-9 路由鉴权实现
业务背景:封装
AuthRoute路由鉴权高阶组件,实现未登录拦截,并跳转到登录页面 实现思路:判断本地是否有token,如果有,就返回子组件,否则就重定向到登录Login
实现步骤
- 在 components 目录中,创建
AuthRoute/index.jsx文件 - 登录时,直接渲染相应页面组件
- 未登录时,重定向到登录页面
- 将需要鉴权的页面路由配置,替换为 AuthRoute 组件渲染
代码实现components/AuthRoute/index.jsx
import { getToken } from '@/utils'
import { Navigate } from 'react-router-dom'
const AuthRoute = ({ children }) => {
const isToken = getToken()
if (isToken) {
return <>{children}</>
} else {
return <Navigate to="/login" replace />
}
}
export default AuthRoutesrc/router/index.jsx
import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import Login from '@/pages/Login'
import Layout from '@/pages/Layout'
import AuthRoute from '@/components/Auth'
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: <AuthRoute><Layout /></AuthRoute>,
},
{
path: '/login',
element: <Login />,
},
])
export default router1-15-3 Layout模块
3-1 结构创建

实现步骤
- 打开
antd/Layout布局组件文档,找到示例:顶部-侧边布局-通栏 - 拷贝示例代码到我们的 Layout 页面中
- 分析并调整页面布局
代码实现pages/Layout/index.js
import { Layout, Menu, Popconfirm } from 'antd'
import {
HomeOutlined,
DiffOutlined,
EditOutlined,
LogoutOutlined,
} from '@ant-design/icons'
import './index.scss'
const { Header, Sider } = Layout
const items = [
{
label: '首页',
key: '1',
icon: <HomeOutlined />,
},
{
label: '文章管理',
key: '2',
icon: <DiffOutlined />,
},
{
label: '创建文章',
key: '3',
icon: <EditOutlined />,
},
]
const GeekLayout = () => {
return (
<Layout>
<Header className="header">
<div className="logo" />
<div className="user-info">
<span className="user-name">柴柴老师</span>
<span className="user-logout">
<Popconfirm title="是否确认退出?" okText="退出" cancelText="取消">
<LogoutOutlined /> 退出
</Popconfirm>
</span>
</div>
</Header>
<Layout>
<Sider width={200} className="site-layout-background">
<Menu
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
defaultSelectedKeys={['1']}
items={items}
style={{ height: '100%', borderRight: 0 }}></Menu>
</Sider>
<Layout className="layout-content" style={{ padding: 20 }}>
内容
</Layout>
</Layout>
</Layout>
)
}
export default GeekLayoutpages/Layout/index.scss
.ant-layout {
height: 100%;
}
.header {
padding: 0;
}
.logo {
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
background: url('~@/assets/logo.png') no-repeat center / 160px auto;
}
.layout-content {
overflow-y: auto;
}
.user-info {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
padding-right: 20px;
color: #fff;
.user-name {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.user-logout {
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
}
}
.ant-layout-header {
padding: 0 !important;
}3-2 样式reset
npm install normalize.csshtml,
body {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
#root {
height: 100%;
}3-3 二级路由配置
使用步骤
- 在 pages 目录中,分别创建:Home(数据概览)/Article(内容管理)/Publish(发布文章)页面文件夹
- 分别在三个文件夹中创建 index.jsx 并创建基础组件后导出
- 在
router/index.js中配置嵌套子路由,在Layout中配置二级路由出口 - 使用 Link 修改左侧菜单内容,与子路由规则匹配实现路由切换
代码实现pages/Home/index.js
const Home = () => {
return <div>Home</div>
}
export default Homepages/Article/index.js
const Article = () => {
return <div>Article</div>
}
export default Articlepages/Publish/index.js
const Publish = () => {
return <div>Publish</div>
}
export default Publishrouter/index.js
import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import Login from '@/pages/Login'
import Layout from '@/pages/Layout'
import Publish from '@/pages/Publish'
import Article from '@/pages/Article'
import Home from '@/pages/Home'
import { AuthRoute } from '@/components/Auth'
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: (
<AuthRoute>
<Layout />
</AuthRoute>
),
children: [
{
index: true,
element: <Home />,
},
{
path: 'article',
element: <Article />,
},
{
path: 'publish',
element: <Publish />,
},
],
},
{
path: '/login',
element: <Login />,
},
])
export default router配置二级路由出口
<Layout className="layout-content" style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<Outlet />
</Layout>3-4 路由菜单点击交互实现
4-1 点击菜单跳转路由
import { Outlet, useNavigate } from 'react-router-dom'
const items = [
{
label: '首页',
key: '/',
icon: <HomeOutlined />,
},
{
label: '文章管理',
key: '/article',
icon: <DiffOutlined />,
},
{
label: '创建文章',
key: '/publish',
icon: <EditOutlined />,
},
]
const GeekLayout = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate()
const menuClick = (route) => {
navigate(route.key)
}
return (
<Menu
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
selectedKeys={selectedKey}
items={items}
style={{ height: '100%', borderRight: 0 }}
onClick={menuClick}
/>
)
}
export default GeekLayout4-2 菜单反向高亮
const GeekLayout = () => {
// 省略部分代码
const location = useLocation()
const selectedKey = location.pathname
return (
<Layout>
<Header className="header">
<div className="logo" />
<div className="user-info">
<span className="user-name">{name}</span>
<span className="user-logout">
<Popconfirm title="是否确认退出?" okText="退出" cancelText="取消">
<LogoutOutlined /> 退出
</Popconfirm>
</span>
</div>
</Header>
<Layout>
<Sider width={200} className="site-layout-background">
<Menu
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
selectedKeys={selectedKey}
items={items}
style={{ height: '100%', borderRight: 0 }}
onClick={menuClickHandler}></Menu>
</Sider>
<Layout className="layout-content" style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
</Layout>
</Layout>
)
}3-5 展示个人信息
 实现步骤
实现步骤
- 在Redux的store中编写获取用户信息的相关逻辑
- 在Layout组件中触发action的执行
- 在Layout组件使用使用store中的数据进行用户名的渲染
代码实现store/userStore.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import { http } from '@/utils/request'
import { getToken, setToken } from '@/utils'
const userStore = createSlice({
name: 'user',
// 数据
initialState: {
token: getToken() || '',
userInfo: {}
},
// 同步修改方法
reducers: {
setUserToken (state, action) {
state.token = action.payload
// 存入本地
setToken(state.token)
},
setUserInfo (state, action) {
state.userInfo = action.payload
}
}
})
// 解构出actionCreater
const { setUserToken, setUserInfo } = userStore.actions
// 获取reducer函数
const userReducer = userStore.reducer
const fetchLogin = (loginForm) => {
return async (dispatch) => {
const res = await http.post('/authorizations', loginForm)
dispatch(setUserToken(res.data.token))
}
}
const fetchUserInfo = () => {
return async (dispatch) => {
const res = await http.get('/user/profile')
dispatch(setUserInfo(res.data))
}
}
export { fetchLogin, fetchUserInfo }
export default userReducerpages/Layout/index.js
// 省略部分代码
import { fetchUserInfo } from '@/store/modules/user'
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux'
const GeekLayout = () => {
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const name = useSelector(state => state.user.userInfo.name)
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchUserInfo())
}, [dispatch])
return (
<Layout>
<Header className="header">
<div className="logo" />
<div className="user-info">
<span className="user-name">{name}</span>
<span className="user-logout">
<Popconfirm title="是否确认退出?" okText="退出" cancelText="取消">
<LogoutOutlined /> 退出
</Popconfirm>
</span>
</div>
</Header>
<Layout>
<Sider width={200} className="site-layout-background">
<Menu
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
defaultSelectedKeys={['1']}
items={items}
style={{ height: '100%', borderRight: 0 }}></Menu>
</Sider>
<Layout className="layout-content" style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
</Layout>
</Layout>
)
}
export default GeekLayout3-6 退出登录实现
实现步骤
- 为气泡确认框添加确认回调事件
- 在
store/userStore.js中新增退出登录的action函数,在其中删除token - 在回调事件中,调用userStore中的退出action
- 清除用户信息,返回登录页面
代码实现store/modules/user.js
import { createSlice } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
import { http } from '@/utils/request'
import { clearToken, getToken, setToken } from '@/utils'
const userStore = createSlice({
name: 'user',
// 数据
initialState: {
token: getToken() || '',
userInfo: {}
},
// 同步修改方法
reducers: {
setUserToken (state, action) {
state.token = action.payload
// 存入本地
setToken(state.token)
},
setUserInfo (state, action) {
state.userInfo = action.payload
},
clearUserInfo (state) {
state.token = ''
state.userInfo = {}
clearToken()
}
}
})
// 解构出actionCreater
const { setUserToken, setUserInfo, clearUserInfo } = userStore.actions
// 获取reducer函数
const userReducer = userStore.reducer
export { fetchLogin, fetchUserInfo, clearUserInfo }
export default userReducerpages/Layout/index.js
const GeekLayout = () => {
// 退出登录
const loginOut = () => {
dispatch(clearUserInfo())
navigator('/login')
}
return (
<Layout>
<Header className="header">
<div className="logo" />
<div className="user-info">
<span className="user-name">{name}</span>
<span className="user-logout">
<Popconfirm
title="是否确认退出?"
okText="退出"
cancelText="取消"
onConfirm={loginOut}>
<LogoutOutlined /> 退出
</Popconfirm>
</span>
</div>
</Header>
<Layout>
<Sider width={200} className="site-layout-background">
<Menu
mode="inline"
theme="dark"
selectedKeys={selectedKey}
items={items}
style={{ height: '100%', borderRight: 0 }}
onClick={menuClickHandler}></Menu>
</Sider>
<Layout className="layout-content" style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<Outlet />
</Layout>
</Layout>
</Layout>
)
}
3-7 处理Token失效
业务背景:如果用户一段时间不做任何操作,到时之后应该清除所有过期用户信息跳回到登录
http.interceptors.response.use((response) => {
// 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response.data
}, (error) => {
// 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应错误做点什么
console.dir(error)
if (error.response.status === 401) {
clearToken()
router.navigate('/login')
window.location.reload()
}
return Promise.reject(error)
})3-8 首页Home图表展示
8-1 图表基础Demo实现
图表类业务渲染,我们可以通过下面的顺序来实现
- 跑通基础DEMO
- 按照实际业务需求进行修改
安装echarts
npm i echarts实现基础Demo
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react'
import * as echarts from 'echarts'
const Home = () => {
const chartRef = useRef(null)
useEffect(() => {
// 1. 生成实例
const myChart = echarts.init(chartRef.current)
// 2. 准备图表参数
const option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: ['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun']
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [
{
data: [120, 200, 150, 80, 70, 110, 130],
type: 'bar'
}
]
}
// 3. 渲染参数
myChart.setOption(option)
}, [])
return (
<div>
<div ref={chartRef} style={{ width: '400px', height: '300px' }} />
</div >
)
}
export default Home
8-2 组件封装
基础抽象
import { useRef, useEffect } from 'react'
import * as echarts from 'echarts'
const BarChart = () => {
const chartRef = useRef(null)
useEffect(() => {
// 1. 生成实例
const myChart = echarts.init(chartRef.current)
// 2. 准备图表参数
const option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: ['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun']
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [
{
data: [120, 200, 150, 80, 70, 110, 130],
type: 'bar'
}
]
}
// 3. 渲染参数
myChart.setOption(option)
}, [])
return <div ref={chartRef} style={{ width: '400px', height: '300px' }}></div>
}
export { BarChart }抽象可变参数
import { useRef, useEffect } from 'react'
import * as echarts from 'echarts'
const BarChart = ({ xData, sData, style = { width: '400px', height: '300px' } }) => {
const chartRef = useRef(null)
useEffect(() => {
// 1. 生成实例
const myChart = echarts.init(chartRef.current)
// 2. 准备图表参数
const option = {
xAxis: {
type: 'category',
data: xData
},
yAxis: {
type: 'value'
},
series: [
{
data: sData,
type: 'bar'
}
]
}
// 3. 渲染参数
myChart.setOption(option)
}, [sData, xData])
return <div ref={chartRef} style={style}></div>
}
export { BarChart }import { BarChart } from './BarChart'
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
<BarChart
xData={['Vue', 'React', 'Angular']}
sData={[2000, 5000, 1000]} />
<BarChart
xData={['Vue', 'React', 'Angular']}
sData={[200, 500, 100]}
style={{ width: '500px', height: '400px' }} />
</div >
)
}
export default Home1-15-4 发布文章模块
4-1 实现基础文章发布
1-1 创建基础结构
import {
Card,
Breadcrumb,
Form,
Button,
Radio,
Input,
Upload,
Space,
Select
} from 'antd'
import { PlusOutlined } from '@ant-design/icons'
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom'
import './index.scss'
const { Option } = Select
const Publish = () => {
return (
<div className="publish">
<Card
title={
<Breadcrumb items={[
{ title: <Link to={'/'}>首页</Link> },
{ title: '发布文章' },
]}
/>
}
>
<Form
labelCol={{ span: 4 }}
wrapperCol={{ span: 16 }}
initialValues={{ type: 1 }}
>
<Form.Item
label="标题"
name="title"
rules={[{ required: true, message: '请输入文章标题' }]}
>
<Input placeholder="请输入文章标题" style={{ width: 400 }} />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item
label="频道"
name="channel_id"
rules={[{ required: true, message: '请选择文章频道' }]}
>
<Select placeholder="请选择文章频道" style={{ width: 400 }}>
<Option value={0}>推荐</Option>
</Select>
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item
label="内容"
name="content"
rules={[{ required: true, message: '请输入文章内容' }]}
></Form.Item>
<Form.Item wrapperCol={{ offset: 4 }}>
<Space>
<Button size="large" type="primary" htmlType="submit">
发布文章
</Button>
</Space>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
</Card>
</div>
)
}
export default Publishpages/Publish/index.scss
.publish {
position: relative;
}
.ant-upload-list {
.ant-upload-list-picture-card-container,
.ant-upload-select {
width: 146px;
height: 146px;
}
}1-2 准备富文本编辑器
实现步骤
- 安装富文本编辑器
- 导入富文本编辑器组件以及样式文件
- 渲染富文本编辑器组件
- 调整富文本编辑器的样式
代码落地 1-安装 react-quill
npm i [email protected]2-导入资源渲染组件
import ReactQuill from 'react-quill'
import 'react-quill/dist/quill.snow.css'
const Publish = () => {
return (
// ...
<Form
labelCol={{ span: 4 }}
wrapperCol={{ span: 16 }}
>
<Form.Item
label="内容"
name="content"
rules={[{ required: true, message: '请输入文章内容' }]}
>
<ReactQuill
className="publish-quill"
theme="snow"
placeholder="请输入文章内容"
/>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
)
}.publish-quill {
.ql-editor {
min-height: 300px;
}
}1-3 频道数据获取
 实现步骤
实现步骤
- 使用useState初始化数据和修改数据的方法
- 在useEffect中调用接口并保存数据
- 使用数据渲染对应模版
代码实现
import { http } from '@/utils'
// 频道列表
const [channels, setChannels] = useState([])
// 调用接口
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchChannels() {
const res = await http.get('/channels')
setChannels(res.data.channels)
}
fetchChannels()
}, [])
// 模板渲染
return (
<Form.Item
label="频道"
name="channel_id"
rules={[{ required: true, message: '请选择文章频道' }]}
>
<Select placeholder="请选择文章频道" style={{ width: 200 }}>
{channels.map(item => (
<Option key={item.id} value={item.id}>
{item.name}
</Option>
))}
</Select>
</Form.Item>
)1-4 发布文章
// 发布文章
const onFinish = async (formValue) => {
const { channel_id, content, title } = formValue
const params = {
channel_id,
content,
title,
type: 1,
cover: {
type: 1,
images: []
}
}
await http.post('/mp/articles?draft=false', params)
message.success('发布文章成功')
}
4-2 上传封面实现
2-1 准备上传结构

<Form.Item label="封面">
<Form.Item name="type">
<Radio.Group>
<Radio value={1}>单图</Radio>
<Radio value={3}>三图</Radio>
<Radio value={0}>无图</Radio>
</Radio.Group>
</Form.Item>
<Upload
listType="picture-card"
showUploadList
>
<div style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<PlusOutlined />
</div>
</Upload>
</Form.Item>2-2 实现基础上传
实现步骤
- 为 Upload 组件添加
action 属性,配置封面图片上传接口地址 - 为 Upload组件添加
name属性, 接口要求的字段名 - 为 Upload 添加
onChange 属性,在事件中拿到当前图片数据,并存储到React状态中
代码实现
import { useState } from 'react'
const Publish = () => {
// 上传图片
const [imageList, setImageList] = useState([])
const onUploadChange = (info) => {
setImageList(info.fileList)
}
return (
<Form.Item label="封面">
<Form.Item name="type">
<Radio.Group>
<Radio value={1}>单图</Radio>
<Radio value={3}>三图</Radio>
<Radio value={0}>无图</Radio>
</Radio.Group>
</Form.Item>
<Upload
name="image"
listType="picture-card"
showUploadList
action={'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/upload'}
onChange={onUploadChange}
>
<div style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<PlusOutlined />
</div>
</Upload>
</Form.Item>
)
}4-3 切换图片Type
实现步骤
- 点击单选框时拿到当前的类型value
- 根据value控制上传组件的显示(大于零时才显示)
const Publish = ()=>{
// 控制图片Type
const [imageType, setImageType] = useState(0)
const onTypeChange = (e) => {
console.log(e)
setImageType(e.target.value)
}
return (
<FormItem>
<Radio.Group onChange={onTypeChange}>
<Radio value={1}>单图</Radio>
<Radio value={3}>三图</Radio>
<Radio value={0}>无图</Radio>
</Radio.Group>
{imageType > 0 &&
<Upload
name="image"
listType="picture-card"
showUploadList
action={'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/upload'}
onChange={onUploadChange}
>
<div style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<PlusOutlined />
</div>
</Upload>}
</FormItem>
)
}
4-4 控制最大上传图片数量
实现步骤
- 通过 maxCount 属性限制图片的上传图片数量
{imageType > 0 &&
<Upload
name="image"
listType="picture-card"
className="avatar-uploader"
showUploadList
action={'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/upload'}
onChange={onUploadChange}
maxCount={imageType}
multiple={imageType > 1}
>
<div style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<PlusOutlined />
</div>
</Upload>}4-5 暂存图片列表实现
业务描述 如果当前为三图模式,已经完成了上传,选择单图只显示一张,再切换到三图继续显示三张,该如何实现?
实现思路 在上传完毕之后通过ref存储所有图片,需要几张就显示几张,其实也就是把ref当仓库,用多少拿多少
实现步骤
- 通过useRef创建一个暂存仓库,在上传完毕图片的时候把图片列表存入
- 如果是单图模式,就从仓库里取第一张图,以数组的形式存入fileList
- 如果是三图模式,就把仓库里所有的图片,以数组的形式存入fileList
代码实现
const Publish = () => {
// 上传图片
const cacheImageList = useRef([])
const [imageList, setImageList] = useState([])
const onUploadChange = (info) => {
setImageList(info.fileList)
cacheImageList.current = info.fileList
}
// 控制图片Type
const [imageType, setImageType] = useState(0)
const onRadioChange = (e) => {
const type = e.target.value
setImageType(type)
if (type === 1) {
// 单图,截取第一张展示
const imgList = cacheImageList.current[0] ? [cacheImageList.current[0]] : []
setImageList(imgList)
} else if (type === 3) {
// 三图,取所有图片展示
setImageList(cacheImageList.current)
}
}
return (
{imageType > 0 &&
<Upload
name="image"
listType="picture-card"
className="avatar-uploader"
showUploadList
action={'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/upload'}
onChange={onUploadChange}
maxCount={imageType}
multiple={imageType > 1}
fileList={imageList}
>
<div style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<PlusOutlined />
</div>
</Upload>}
)
}注意:需要给Upload组件添加fileList属性,达成受控的目的
4-6 发布带封面的文章
6-1 校验图片类型和数量是否吻合
// 发布文章
const onFinish = async (formValue) => {
if (imageType !== imageList.length) return message.warning('图片类型和数量不一致')
const { channel_id, content, title } = formValue
const params = {
channel_id,
content,
title,
type: imageType,
cover: {
type: imageType,
images: imageList.map(item => item.response.data.url)
}
}
await http.post('/mp/articles?draft=false', params)
message.success('发布文章成功')
}6-2 处理图片列表格式为接口格式
// 发布文章
const onFinish = async (formValue) => {
const { channel_id, content, title } = formValue
const params = {
channel_id,
content,
title,
type: imageType,
cover: {
type: imageType,
images: imageList.map(item => item.response.data.url)
}
}
await http.post('/mp/articles?draft=false', params)
message.success('发布文章成功')
}1-15-5 文章列表模块
5-1 静态结构创建
1-1 筛选区结构搭建
- 如何让RangePicker日期范围选择框选择中文
- Select组件配合Form.Item使用时,如何配置默认选中项
<Form initialValues={{ status: null }} >
代码实现
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom'
import { Card, Breadcrumb, Form, Button, Radio, DatePicker, Select } from 'antd'
import locale from 'antd/es/date-picker/locale/zh_CN'
const { Option } = Select
const { RangePicker } = DatePicker
const Article = () => {
return (
<div>
<Card
title={
<Breadcrumb items={[
{ title: <Link to={'/'}>首页</Link> },
{ title: '文章列表' },
]} />
}
style={{ marginBottom: 20 }}
>
<Form initialValues={{ status: '' }}>
<Form.Item label="状态" name="status">
<Radio.Group>
<Radio value={''}>全部</Radio>
<Radio value={0}>草稿</Radio>
<Radio value={2}>审核通过</Radio>
</Radio.Group>
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label="频道" name="channel_id">
<Select
placeholder="请选择文章频道"
defaultValue="lucy"
style={{ width: 120 }}
>
<Option value="jack">Jack</Option>
<Option value="lucy">Lucy</Option>
</Select>
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label="日期" name="date">
{/* 传入locale属性 控制中文显示*/}
<RangePicker locale={locale}></RangePicker>
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item>
<Button type="primary" htmlType="submit" style={{ marginLeft: 40 }}>
筛选
</Button>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
</Card>
</div>
)
}
export default Article1-2 表格区域结构
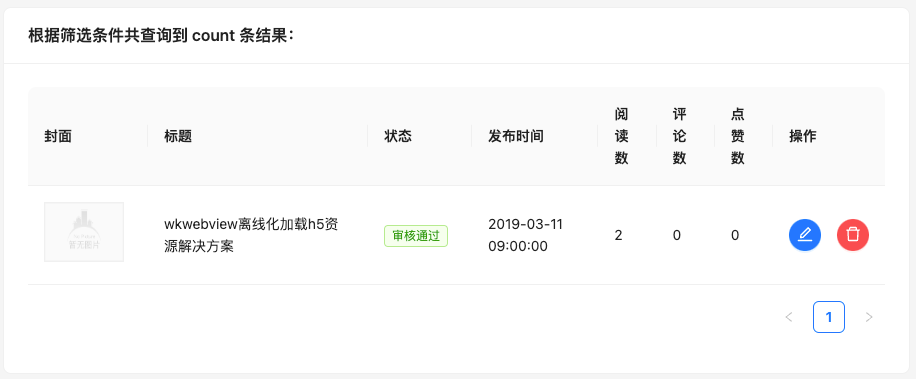 代码实现
代码实现
// 导入资源
import { Table, Tag, Space } from 'antd'
import { EditOutlined, DeleteOutlined } from '@ant-design/icons'
import img404 from '@/assets/error.png'
const Article = () => {
// 准备列数据
const columns = [
{
title: '封面',
dataIndex: 'cover',
width: 120,
render: cover => {
return <img src={cover.images[0] || img404} width={80} height={60} alt="" />
}
},
{
title: '标题',
dataIndex: 'title',
width: 220
},
{
title: '状态',
dataIndex: 'status',
render: data => <Tag color="green">审核通过</Tag>
},
{
title: '发布时间',
dataIndex: 'pubdate'
},
{
title: '阅读数',
dataIndex: 'read_count'
},
{
title: '评论数',
dataIndex: 'comment_count'
},
{
title: '点赞数',
dataIndex: 'like_count'
},
{
title: '操作',
render: data => {
return (
<Space size="middle">
<Button type="primary" shape="circle" icon={<EditOutlined />} />
<Button
type="primary"
danger
shape="circle"
icon={<DeleteOutlined />}
/>
</Space>
)
}
}
]
// 准备表格body数据
const data = [
{
id: '8218',
comment_count: 0,
cover: {
images: [],
},
like_count: 0,
pubdate: '2019-03-11 09:00:00',
read_count: 2,
status: 2,
title: 'wkwebview离线化加载h5资源解决方案'
}
]
return (
<div>
{/* */}
<Card title={`根据筛选条件共查询到 count 条结果:`}>
<Table rowKey="id" columns={columns} dataSource={data} />
</Card>
</div>
)
}5-2 渲染频道数据
实现步骤
- 使用axios获取数据
- 将使用频道数据列表改写下拉框组件
代码实现pages/Article/index.js
const Article = ()=>{
// 获取频道列表
const [channels, setChannels] = useState([])
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchChannels() {
const res = await http.get('/channels')
setChannels(res.data.channels)
}
fetchChannels()
}, [])
// 渲染模板
return (
<Form.Item label="频道" name="channel_id" >
<Select placeholder="请选择频道" style={{ width: 200 }} >
{channels.map(item => (
<Option key={item.id} value={item.id}>
{item.name}
</Option>
))}
</Select>
</Form.Item>
)
}5-3 渲染表格数据
实现步骤
- 声明列表相关数据管理
- 使用useState声明参数相关数据管理
- 调用接口获取数据
- 使用接口数据渲染模板
代码实现
const Article = ()=>{
// 省略部分代码...
// 文章列表数据管理
const [article, setArticleList] = useState({
list: [],
count: 0
})
const [params, setParams] = useState({
page: 1,
per_page: 4,
begin_pubdate: null,
end_pubdate: null,
status: null,
channel_id: null
})
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchArticleList () {
const res = await http.get('/mp/articles', { params })
const { results, total_count } = res.data
setArticleList({
list: results,
count: total_count
})
}
fetchArticleList()
}, [params])
// 模板渲染
return (
<Card title={`根据筛选条件共查询到 ${article.count} 条结果:`}>
<Table
dataSource={article.list}
columns={columns}
/>
</Card>
)
}5-4 筛选功能实现
实现步骤
- 为表单添加
onFinish属性监听表单提交事件,获取参数 - 根据接口字段格式要求格式化参数格式
- 修改
params参数并重新使用新参数重新请求数据
代码实现
// 获取文章列表
const [list, setList] = useState([])
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
async function getList (reqData = {}) {
const res = await getArticleListAPI(reqData)
setList(res.data.results)
setCount(res.data.total_count)
}
useEffect(() => {
getList()
}, [])
// 筛选文章列表
const onFinish = async (formValue) => {
console.log(formValue)
// 1. 准备参数
const { channel_id, date, status } = formValue
const reqData = {
status,
channel_id,
begin_pubdate: date[0].format('YYYY-MM-DD'),
end_pubdate: date[1].format('YYYY-MM-DD'),
}
// 2. 使用参数获取新的列表
getList(reqData)
}5-5 分页功能实现
实现步骤
- 为Table组件指定pagination属性来展示分页效果
- 在分页切换事件中获取到筛选表单中选中的数据
- 使用当前页数据修改params参数依赖引起接口重新调用获取最新数据
代码实现
const pageChange = (page) => {
// 拿到当前页参数 修改params 引起接口更新
setParams({
...params,
page
})
}
return (
<Table rowKey="id" columns={columns} dataSource={article.list} pagination={{
current: params.page,
pageSize: params.per_page,
onChange: pageChange,
total: article.count
}} />
)5-6 删除功能
 实现步骤
实现步骤
- 给删除文章按钮绑定点击事件
- 弹出确认窗口,询问用户是否确定删除文章
- 拿到参数调用删除接口,更新列表
代码实现
// 删除回调
const delArticle = async (data) => {
await http.delete(`/mp/articles/${data.id}`)
// 更新列表
setParams({
page: 1,
per_page: 10
})
}
const columns = [
// ...
{
title: '操作',
render: data => {
return (
<Space size="middle">
<Button type="primary" shape="circle" icon={<EditOutlined />} />
<Popconfirm
title="确认删除该条文章吗?"
onConfirm={() => delArticle(data)}
okText="确认"
cancelText="取消"
>
<Button
type="primary"
danger
shape="circle"
icon={<DeleteOutlined />}
/>
</Popconfirm>
</Space>
)
}
]5-7 编辑文章跳转
代码实现
const columns = [
// ...
{
title: '操作',
render: data => (
<Space size="middle">
<Button
type="primary"
shape="circle"
icon={<EditOutlined />}
onClick={() => navagite(`/publish?id=${data.id}`)} />
/>
</Space>
)
}
]1-15-6 编辑文章
6-1 基础数据回填
const Publish = ()=>{
// 回填数据
const [searchParams] = useSearchParams()
const articleId = searchParams.get('id')
const [form] = Form.useForm()
useEffect(() => {
async function getArticle () {
const res = await http.get(`/mp/articles/${articleId}`)
const { cover, ...formValue } = res.data
// 设置表单数据
form.setFieldsValue({ ...formValue, type: cover.type })
}
if (articleId) {
// 拉取数据回显
getArticle()
}
}, [articleId, form])
return (
<Form form={form}/>
)
}6-2 回填封面信息
useEffect(() => {
async function getArticle () {
const res = await http.get(`/mp/articles/${articleId}`)
const { cover, ...formValue } = res.data
// 1. 回填表单数据
form.setFieldsValue({ ...formValue, type: cover.type })
// 2. 回填封面图片
setImageType(cover.type) // 封面类型
setImageList(cover.images.map(url => ({ url }))) // 封面list
}
if (articleId) {
getArticle()
}
}, [articleId, form])6-3 适配不同状态下的文案
<Card
title={
<Breadcrumb items={[
{ title: <Link to={'/'}>首页</Link> },
{ title: `${articleId ? '编辑文章' : '发布文章'}` },
]}
/>
}
>
{articleId ? '更新文章' : '发布文章'}6-4 更新文章
// 发布文章
const onFinish = async (formValue) => {
const { channel_id, content, title } = formValue
const formatUrl = (list) => {
return list.map(item => {
if (item.response) {
return item.response.data.url
} else {
return item.url
}
})
}
const data = {
channel_id,
content,
title,
type: imageType,
cover: {
type: imageType,
images: formatUrl(imageList)
}
}
if (imageType !== imageList.length) return message.warning('图片类型和数量不一致')
if (articleId) {
// 编辑
await http.put(`/mp/articles/${articleId}?draft=false`, data)
} else {
// 新增
await http.post('/mp/articles?draft=false', data)
}
message.success(`${articleId ? '编辑' : '发布'}文章成功`)
}1-15-7 项目打包
7-1 项目打包
npm run build
7-2 项目本地预览
实现步骤
- 全局安装本地服务包
npm i -g serve该包提供了serve命令,用来启动本地服务器 - 在项目根目录中执行命令
serve -s ./build在build目录中开启服务器 - 在浏览器中访问:
http://localhost:3000/预览项目
7-3 优化-路由懒加载
使用步骤
- 使用 lazy 方法导入路由组件
- 使用内置的 Suspense 组件渲染路由组件
代码实现router/index.js
import { createBrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import { lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
import Login from '@/pages/Login'
import Layout from '@/pages/Layout'
import AuthRoute from '@/components/Auth'
const Publish = lazy(() => import('@/pages/Publish'))
const Article = lazy(() => import('@/pages/Article'))
const Home = lazy(() => import('@/pages/Article'))
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: (
<AuthRoute>
<Layout />
</AuthRoute>
),
children: [
{
index: true,
element: (
<Suspense fallback={'加载中'}>
<Home />
</Suspense>
)
},
{
path: 'article',
element: (
<Suspense fallback={'加载中'}>
<Article />
</Suspense>
)
},
{
path: 'publish',
element: (
<Suspense fallback={'加载中'}>
<Publish />
</Suspense>
)
},
],
},
{
path: '/login',
element: <Login />,
},
])
export default router查看效果 我们可以在打包之后,通过切换路由,监控network面板资源的请求情况,验证是否分隔成功
7-4 打包-打包体积分析
业务背景 通过分析打包体积,才能知道项目中的哪部分内容体积过大,方便知道哪些包如何来优化 使用步骤
- 安装分析打包体积的包:
npm i source-map-explorer - 在 package.json 中的 scripts 标签中,添加分析打包体积的命令
- 对项目打包:
npm run build(如果已经打过包,可省略这一步) - 运行分析命令:
npm run analyze - 通过浏览器打开的页面,分析图表中的包体积
核心代码:
"scripts": {
"analyze": "source-map-explorer 'build/static/js/*.js'",
}
7-5 优化-配置CDN
分析说明:通过 craco 来修改 webpack 配置,从而实现 CDN 优化 核心代码craco.config.js
// 添加自定义对于webpack的配置
const path = require('path')
const { whenProd, getPlugin, pluginByName } = require('@craco/craco')
module.exports = {
// webpack 配置
webpack: {
// 配置别名
alias: {
// 约定:使用 @ 表示 src 文件所在路径
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
},
// 配置webpack
// 配置CDN
configure: (webpackConfig) => {
let cdn = {
js:[]
}
whenProd(() => {
// key: 不参与打包的包(由dependencies依赖项中的key决定)
// value: cdn文件中 挂载于全局的变量名称 为了替换之前在开发环境下
webpackConfig.externals = {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM'
}
// 配置现成的cdn资源地址
// 实际开发的时候 用公司自己花钱买的cdn服务器
cdn = {
js: [
'https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/react/18.1.0/umd/react.production.min.js',
'https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/react-dom/18.1.0/umd/react-dom.production.min.js',
]
}
})
// 通过 htmlWebpackPlugin插件 在public/index.html注入cdn资源url
const { isFound, match } = getPlugin(
webpackConfig,
pluginByName('HtmlWebpackPlugin')
)
if (isFound) {
// 找到了HtmlWebpackPlugin的插件
match.userOptions.files = cdn
}
return webpackConfig
}
}
}public/index.html
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<!-- 加载第三发包的 CDN 链接 -->
<% htmlWebpackPlugin.options.files.js.forEach(cdnURL => { %>
<script src="<%= cdnURL %>"></script>
<% }) %>
</body>1-16 useReducer
1-16-1 基础使用
作用: 让 React 管理多个相对关联的状态数据
import { useReducer } from 'react'
// 1. 定义reducer函数,根据不同的action返回不同的新状态
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INC':
return state + 1
case 'DEC':
return state - 1
default:
return state
}
}
function App() {
// 2. 使用useReducer分派action
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, 0)
return (
<>
{/* 3. 调用dispatch函数传入action对象 触发reducer函数,分派action操作,使用新状态更新视图 */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'DEC' })}>-</button>
{state}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'INC' })}>+</button>
</>
)
}
export default App1-16-2 更新流程
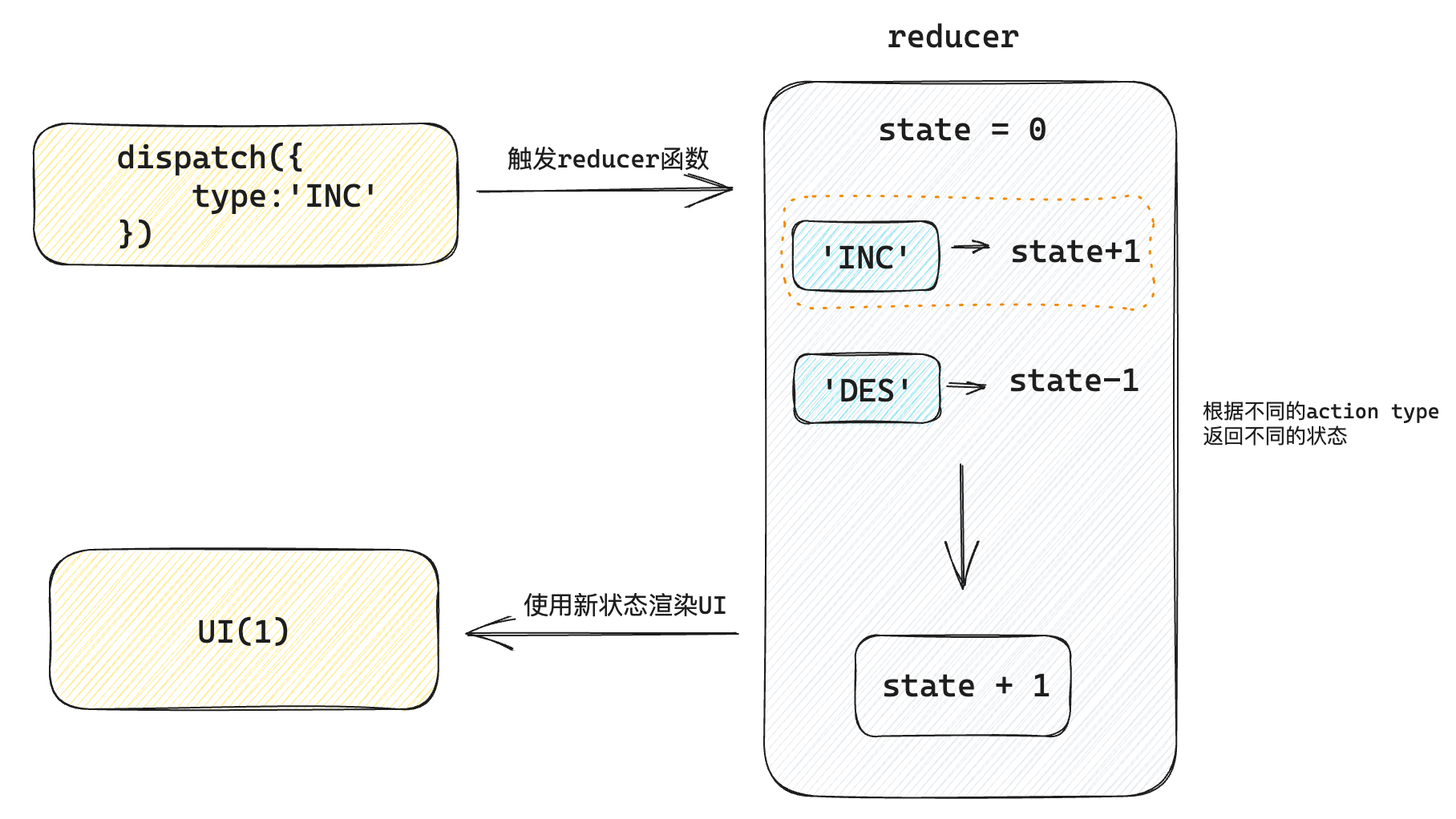
1-16-3 分派action传参
做法:分派action时如果想要传递参数,需要在action对象中添加一个payload参数,放置状态参数
// 定义reducer
import { useReducer } from 'react'
// 1. 根据不同的action返回不同的新状态
function reducer(state, action) {
console.log('reducer执行了')
switch (action.type) {
case 'INC':
return state + 1
case 'DEC':
return state - 1
case 'UPDATE':
return state + action.payload
default:
return state
}
}
function App() {
// 2. 使用useReducer分派action
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, 0)
return (
<>
{/* 3. 调用dispatch函数传入action对象 触发reducer函数,分派action操作,使用新状态更新视图 */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'DEC' })}>-</button>
{state}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'INC' })}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE', payload: 100 })}>
update to 100
</button>
</>
)
}
export default App1-17 渲染性能优化
1-17-1 useMemo
作用:它在每次重新渲染的时候能够缓存计算的结果
7-1 看个场景
下面我们的本来的用意是想基于count的变化计算斐波那契数列之和,但是当我们修改num状态的时候,斐波那契求和函数也会被执行,显然是一种浪费
// useMemo
// 作用:在组件渲染时缓存计算的结果
import { useState } from 'react'
function factorialOf(n) {
console.log('斐波那契函数执行了')
return n <= 0 ? 1 : n * factorialOf(n - 1)
}
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
// 计算斐波那契之和
const sumByCount = factorialOf(count)
const [num, setNum] = useState(0)
return (
<>
{sum}
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+count:{count}</button>
<button onClick={() => setNum(num + 1)}>+num:{num}</button>
</>
)
}
export default App7-2 useMemo缓存计算结果
思路: 只有count发生变化时才重新进行计算
import { useMemo, useState } from 'react'
function fib (n) {
console.log('计算函数执行了')
if (n < 3) return 1
return fib(n - 2) + fib(n - 1)
}
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
// 计算斐波那契之和
// const sum = fib(count)
// 通过useMemo缓存计算结果,只有count发生变化时才重新计算
const sum = useMemo(() => {
return fib(count)
}, [count])
const [num, setNum] = useState(0)
return (
<>
{sum}
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+count:{count}</button>
<button onClick={() => setNum(num + 1)}>+num:{num}</button>
</>
)
}
export default App1-17-2 React.memo
作用:允许组件在props没有改变的情况下跳过重新渲染
2-1 组件默认的渲染机制
默认机制:顶层组件发生重新渲染,这个组件树的子级组件都会被重新渲染
// memo
// 作用:允许组件在props没有改变的情况下跳过重新渲染
import { useState } from 'react'
function Son() {
console.log('子组件被重新渲染了')
return <div>this is son</div>
}
function App() {
const [, forceUpdate] = useState()
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
return (
<>
<Son />
<button onClick={() => forceUpdate(Math.random())}>update</button>
</>
)
}
export default App2-2 使用React.memo优化
机制:只有props发生变化时才重新渲染 下面的子组件通过 memo 进行包裹之后,返回一个新的组件MemoSon, 只有传给MemoSon的props参数发生变化时才会重新渲染
import React, { useState } from 'react'
const MemoSon = React.memo(function Son() {
console.log('子组件被重新渲染了')
return <div>this is span</div>
})
function App() {
const [, forceUpdate] = useState()
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
return (
<>
<MemoSon />
<button onClick={() => forceUpdate(Math.random())}>update</button>
</>
)
}
export default App2-3 props变化重新渲染
import React, { useState } from 'react'
const MemoSon = React.memo(function Son() {
console.log('子组件被重新渲染了')
return <div>this is span</div>
})
function App() {
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<>
<MemoSon count={count} />
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+{count}</button>
</>
)
}
export default App2-4 props的比较机制
对于props的比较,进行的是‘浅比较’,底层使用
Object.is进行比较,针对于对象数据类型,只会对比俩次的引用是否相等,如果不相等就会重新渲染,React并不关心对象中的具体属性
import React, { useState } from 'react'
const MemoSon = React.memo(function Son() {
console.log('子组件被重新渲染了')
return <div>this is span</div>
})
function App() {
// const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const [list, setList] = useState([1, 2, 3])
return (
<>
<MemoSon list={list} />
<button onClick={() => setList([1, 2, 3])}>
{JSON.stringify(list)}
</button>
</>
)
}
export default App说明:虽然俩次的list状态都是 [1,2,3] , 但是因为组件App俩次渲染生成了不同的对象引用list,所以传给MemoSon组件的props视为不同,子组件就会发生重新渲染
2-5 自定义比较函数
如果上一小节的例子,我们不想通过引用来比较,而是完全比较数组的成员是否完全一致,则可以通过自定义比较函数来实现
import React, { useState } from 'react'
// 自定义比较函数
function arePropsEqual(oldProps, newProps) {
console.log(oldProps, newProps)
return (
oldProps.list.length === newProps.list.length &&
oldProps.list.every((oldItem, index) => {
const newItem = newProps.list[index]
console.log(newItem, oldItem)
return oldItem === newItem
})
)
}
const MemoSon = React.memo(function Son() {
console.log('子组件被重新渲染了')
return <div>this is span</div>
}, arePropsEqual)
function App() {
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
const [list, setList] = useState([1, 2, 3])
return (
<>
<MemoSon list={list} />
<button onClick={() => setList([1, 2, 3])}>
内容一样{JSON.stringify(list)}
</button>
<button onClick={() => setList([4, 5, 6])}>
内容不一样{JSON.stringify(list)}
</button>
</>
)
}
export default App1-17-3 useCallback
3-1 看个场景
上一小节我们说到,当给子组件传递一个引用类型prop的时候,即使我们使用了memo 函数依旧无法阻止子组件的渲染,其实传递prop的时候,往往传递一个回调函数更为常见,比如实现子传父,此时如果想要避免子组件渲染,可以使用 useCallback缓存回调函数
// useCallBack
import { memo, useState } from 'react'
const MemoSon = memo(function Son() {
console.log('Son组件渲染了')
return <div>this is son</div>
})
function App() {
const [, forceUpate] = useState()
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
const onGetSonMessage = (message) => {
console.log(message)
}
return (
<div>
<MemoSon onGetSonMessage={onGetSonMessage} />
<button onClick={() => forceUpate(Math.random())}>update</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App3-2 useCallback缓存函数
useCallback缓存之后的函数可以在组件渲染时保持引用稳定,也就是返回同一个引用
// useCallBack
import { memo, useCallback, useState } from 'react'
const MemoSon = memo(function Son() {
console.log('Son组件渲染了')
return <div>this is son</div>
})
function App() {
const [, forceUpate] = useState()
console.log('父组件重新渲染了')
const onGetSonMessage = useCallback((message) => {
console.log(message)
}, [])
return (
<div>
<MemoSon onGetSonMessage={onGetSonMessage} />
<button onClick={() => forceUpate(Math.random())}>update</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-18 forwardRef
作用:允许组件使用ref将一个DOM节点暴露给父组件
import { forwardRef, useRef } from 'react'
const MyInput = forwardRef(function Input(props, ref) {
return <input {...props} type="text" ref={ref} />
}, [])
function App() {
const ref = useRef(null)
const focusHandle = () => {
console.log(ref.current.focus())
}
return (
<div>
<MyInput ref={ref} />
<button onClick={focusHandle}>focus</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App1-19 useImperativeHandle
作用:如果我们并不想暴露子组件中的DOM而是想暴露子组件内部的方法
import { forwardRef, useImperativeHandle, useRef } from 'react'
const MyInput = forwardRef(function Input(props, ref) {
// 实现内部的聚焦逻辑
const inputRef = useRef(null)
const focus = () => inputRef.current.focus()
// 暴露子组件内部的聚焦方法
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => {
return {
focus,
}
})
return <input {...props} ref={inputRef} type="text" />
})
function App() {
const ref = useRef(null)
const focusHandle = () => ref.current.focus()
return (
<div>
<MyInput ref={ref} />
<button onClick={focusHandle}>focus</button>
</div>
)
}
export default App顾名思义,Class API就是使用ES6支持的原生Class API来编写React组件
1-20 class API
1-20-1 基础体验
通过一个简单的 Counter 自增组件看一下组件的基础编写结构
// class API
import { Component } from 'react'
class Counter extends Component {
// 状态变量
state = {
count: 0,
}
// 事件回调
clickHandler = () => {
// 修改状态变量 触发UI组件渲染
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
}
// UI模版
render() {
return <button onClick={this.clickHandler}>+{this.state.count}</button>
}
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Counter />
</div>
)
}
export default App1-20-2 组件通信
2-1 父传子
// class API
import { Component } from 'react'
class Son extends Component {
render() {
const { count } = this.props
return <div>this is Son, {count}</div>
}
}
class App extends Component {
// 状态变量
state = {
count: 0,
}
setCount = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
}
// UI模版
render() {
return (
<>
<Son count={this.state.count} />
<button onClick={this.setCount}>+</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App2-2 子传父
// class API
import { Component } from 'react'
class Son extends Component {
render() {
const { msg, onGetSonMsg } = this.props
return (
<>
<div>this is Son, {msg}</div>
<button onClick={() => onGetSonMsg('this is son msg')}>
changeMsg
</button>
</>
)
}
}
class App extends Component {
// 状态变量
state = {
msg: 'this is initail app msg',
}
onGetSonMsg = (msg) => {
this.setState({ msg })
}
// UI模版
render() {
return (
<>
<Son msg={this.state.msg} onGetSonMsg={this.onGetSonMsg} />
</>
)
}
}
export default App1-21 zustand
1-21-1 快速上手
1-1 store/index.js - 创建store
import { create } from 'zustand'
const useStore = create((set) => {
return {
count: 0,
inc: () => {
set(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 }))
}
}
})
export default useStore1-2 app.js - 绑定组件
import useStore from './store/useCounterStore.js'
function App() {
const { count, inc } = useStore()
return <button onClick={inc}>{count}</button>
}
export default App1-21-2 异步支持
对于异步操作的支持不需要特殊的操作,直接在函数中编写异步逻辑,最后把接口的数据放到set函数中返回即可
2-1 store/index.js - 创建store
import { create } from 'zustand'
const URL = 'http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels'
const useStore = create((set) => {
return {
count: 0,
ins: () => {
return set(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 }))
},
channelList: [],
fetchChannelList: async () => {
const res = await fetch(URL)
const jsonData = await res.json()
set({channelList: jsonData.data.channels})
}
}
})
export default useStore2-2 app.js - 绑定组件
import { useEffect } from 'react'
import useChannelStore from './store/channelStore'
function App() {
const { channelList, fetchChannelList } = useChannelStore()
useEffect(() => {
fetchChannelList()
}, [fetchChannelList])
return (
<ul>
{channelList.map((item) => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
)
}
export default App1-21-3 切片模式
场景:当我们单个store比较大的时候,可以采用一种切片模式进行模块拆分再组合
3-1 拆分并组合切片
import { create } from 'zustand'
// 创建counter相关切片
const createCounterStore = (set) => {
return {
count: 0,
setCount: () => {
set(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 }))
}
}
}
// 创建channel相关切片
const createChannelStore = (set) => {
return {
channelList: [],
fetchGetList: async () => {
const res = await fetch(URL)
const jsonData = await res.json()
set({ channelList: jsonData.data.channels })
}
}
}
// 组合切片
const useStore = create((...a) => ({
...createCounterStore(...a),
...createChannelStore(...a)
}))3-2 组件使用
function App() {
const {count, inc, channelList, fetchChannelList } = useStore()
return (
<>
<button onClick={inc}>{count}</button>
<ul>
{channelList.map((item) => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
)
}
export default App1-21-3 对接DevTools
简单的调试我们可以安装一个 名称为 simple-zustand-devtools 的调试工具
3-1 安装调试包
npm i simple-zustand-devtools -D3-2 配置调试工具
import create from 'zustand'
// 导入核心方法
import { mountStoreDevtool } from 'simple-zustand-devtools'
// 省略部分代码...
// 开发环境开启调试
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
mountStoreDevtool('channelStore', useChannelStore)
}
export default useChannelStore3-3 打开 React调试工具